Alaska: A Land of Extremes, Positioned at the Top of the World
Related Articles: Alaska: A Land of Extremes, Positioned at the Top of the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Alaska: A Land of Extremes, Positioned at the Top of the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Alaska: A Land of Extremes, Positioned at the Top of the World

Alaska, the largest state in the United States by area, occupies a unique position on the world map. Its vast, rugged landscape and diverse ecosystems are a testament to its location at the northernmost edge of North America, bordering the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Understanding Alaska’s geographical position is crucial to appreciating its distinct features and its importance in the global context.
Alaska’s Position on the Map:
Alaska’s geographical coordinates place it between 54° and 71° North latitude and 130° and 172° West longitude. This positioning situates it in the northernmost part of North America, with its southern border extending into the contiguous United States along the Panhandle region, which is connected to British Columbia, Canada.
Alaska’s Unique Geographic Features:
- Arctic Circle: Alaska is the only state in the United States that extends above the Arctic Circle, a significant boundary that marks the region where the sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours during the summer solstice and below the horizon for 24 hours during the winter solstice.
- The Aleutian Islands: This volcanic island chain stretches westward from the Alaskan Peninsula, forming a natural barrier between the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The Aleutians are strategically positioned in the North Pacific, contributing to the region’s complex marine ecosystems and serving as a crucial link between North America and Asia.
- The Bering Strait: This narrow body of water separates Alaska from Russia, serving as a vital historical and cultural connection between the two countries. The Bering Strait is also a significant route for marine life migration and a critical area for studying the effects of climate change on the Arctic region.
- The Brooks Range: This mountain range runs across northern Alaska, forming a natural boundary between the Arctic tundra and the boreal forests. The Brooks Range is characterized by its rugged terrain and diverse wildlife, offering opportunities for outdoor recreation and scientific research.
The Importance of Alaska’s Location:
Alaska’s location at the top of the world has profound implications for its environment, economy, and culture.
- Environmental Significance: Alaska’s vast wilderness areas are home to a wide array of ecosystems, including glaciers, mountains, tundra, boreal forests, and coastal areas. These diverse habitats support a rich biodiversity, including iconic species like brown bears, caribou, wolves, and whales. Alaska’s location makes it a crucial area for studying climate change impacts on the Arctic region.
- Economic Importance: Alaska’s natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, timber, and seafood, are vital to the state’s economy. Its strategic location also makes it a crucial hub for transportation and logistics, connecting North America to Asia and the Arctic.
- Cultural Significance: Alaska is home to a diverse population of indigenous cultures, each with a unique history and relationship to the land. The state’s location has shaped its cultural identity, fostering a strong sense of community and resilience in the face of challenging environmental conditions.
FAQs about Alaska’s Location:
- What is the closest country to Alaska? Russia is the closest country to Alaska, separated by the Bering Strait.
- Is Alaska part of North America? Yes, Alaska is the northernmost state in North America.
- What is the capital of Alaska? The capital of Alaska is Juneau, located in the southeastern part of the state.
- What is the largest city in Alaska? The largest city in Alaska is Anchorage, located in the south-central part of the state.
- What is the climate like in Alaska? Alaska’s climate varies greatly depending on the region, ranging from the cold, icy conditions of the Arctic to the milder, more temperate climate of the Pacific coast.
Tips for Understanding Alaska’s Location:
- Use a map: Refer to a physical or digital map to visualize Alaska’s position in relation to other countries and states.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and educational materials provide detailed information about Alaska’s geography, history, and culture.
- Visit Alaska: Experiencing Alaska firsthand offers the best way to understand its unique location and appreciate its diverse ecosystems and cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
Alaska’s location at the top of the world makes it a unique and fascinating region. Its geographical position has shaped its environment, economy, and culture, contributing to its importance as a global hub for natural resources, scientific research, and cultural heritage. Understanding Alaska’s location on the map is essential for appreciating its distinct features and its role in the global context.



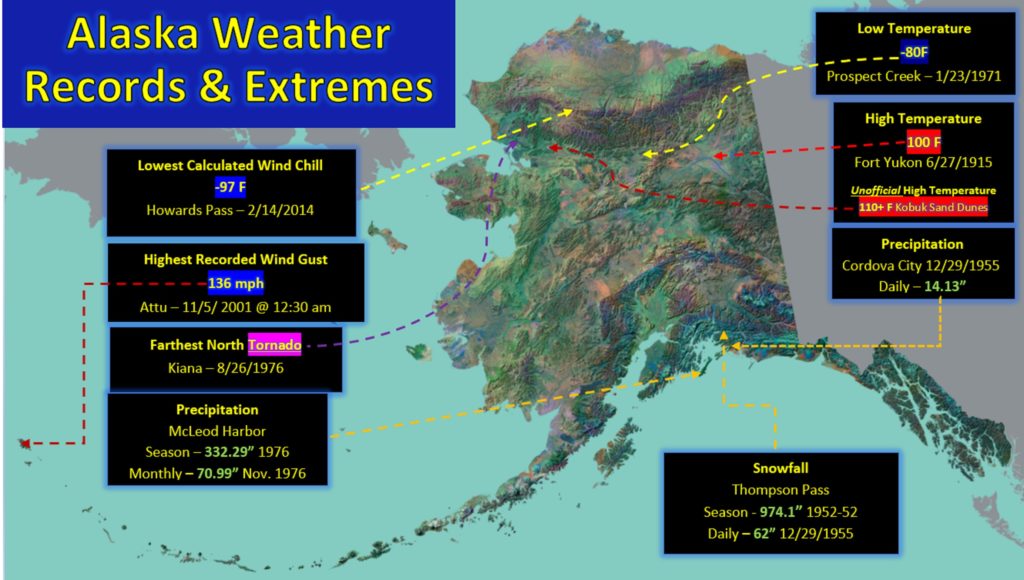



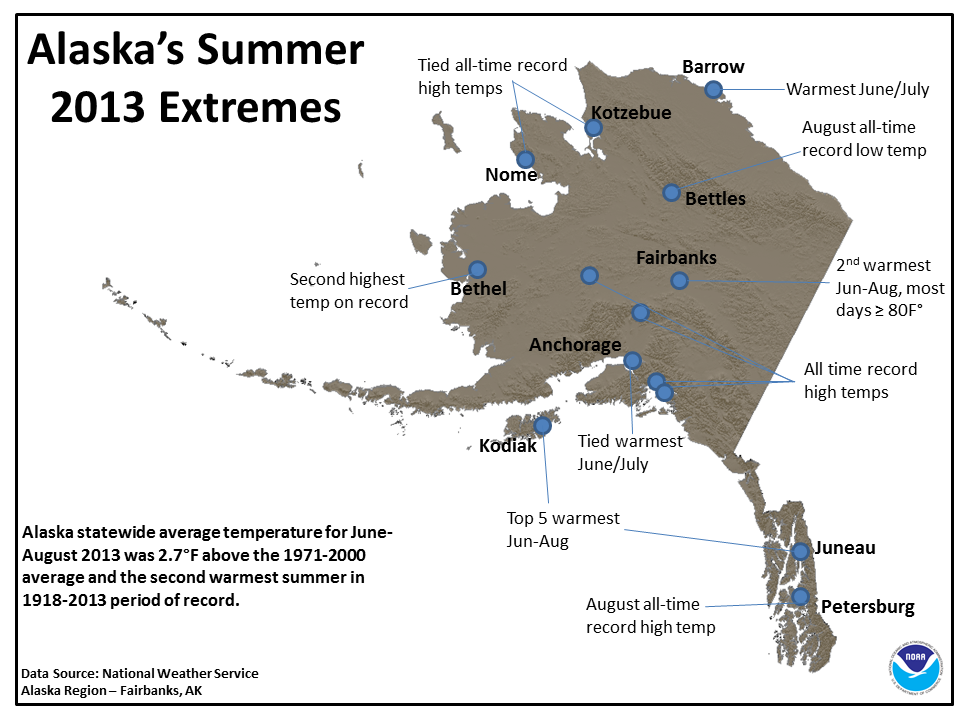
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Alaska: A Land of Extremes, Positioned at the Top of the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!