Delving into the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Five US Regions
Related Articles: Delving into the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Five US Regions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Five US Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Five US Regions
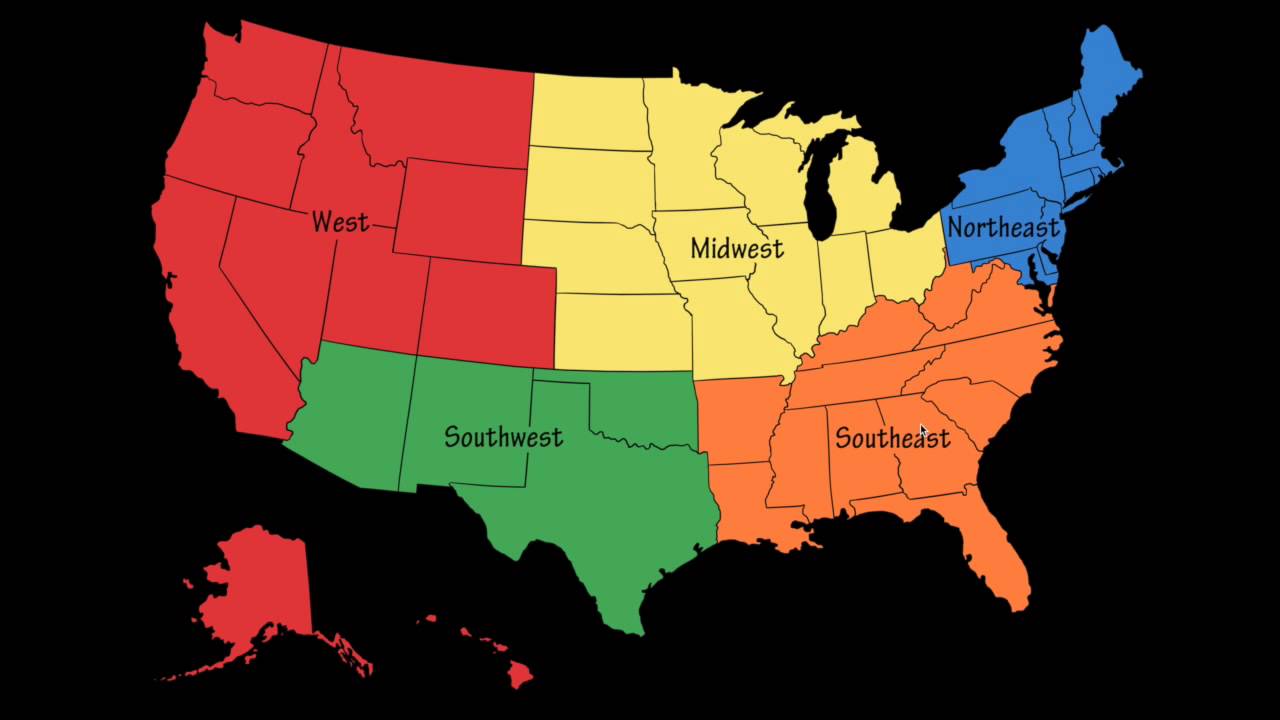
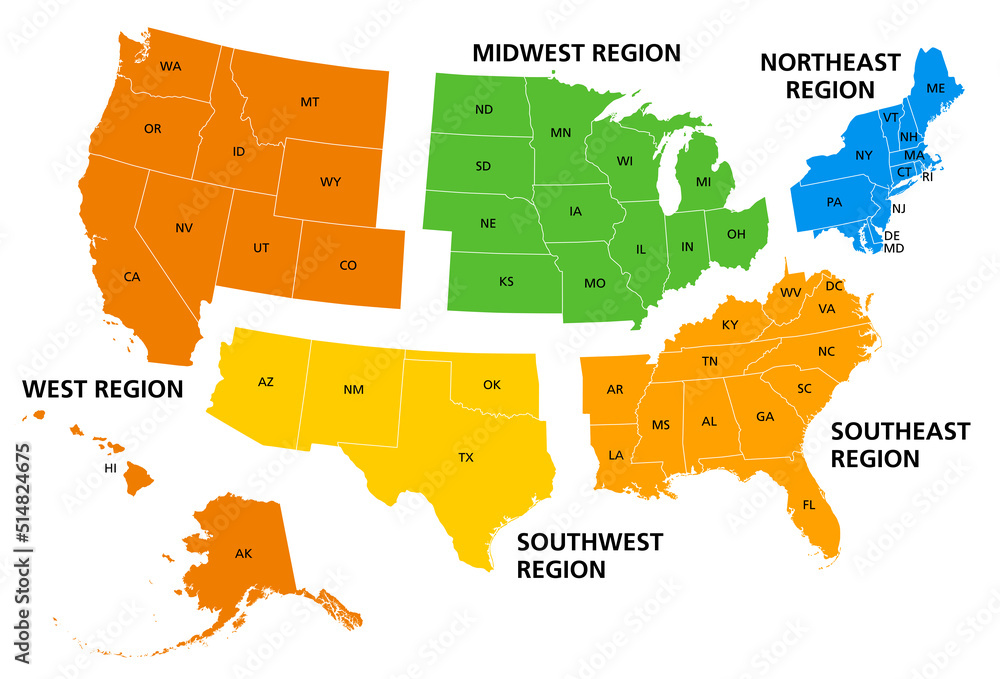
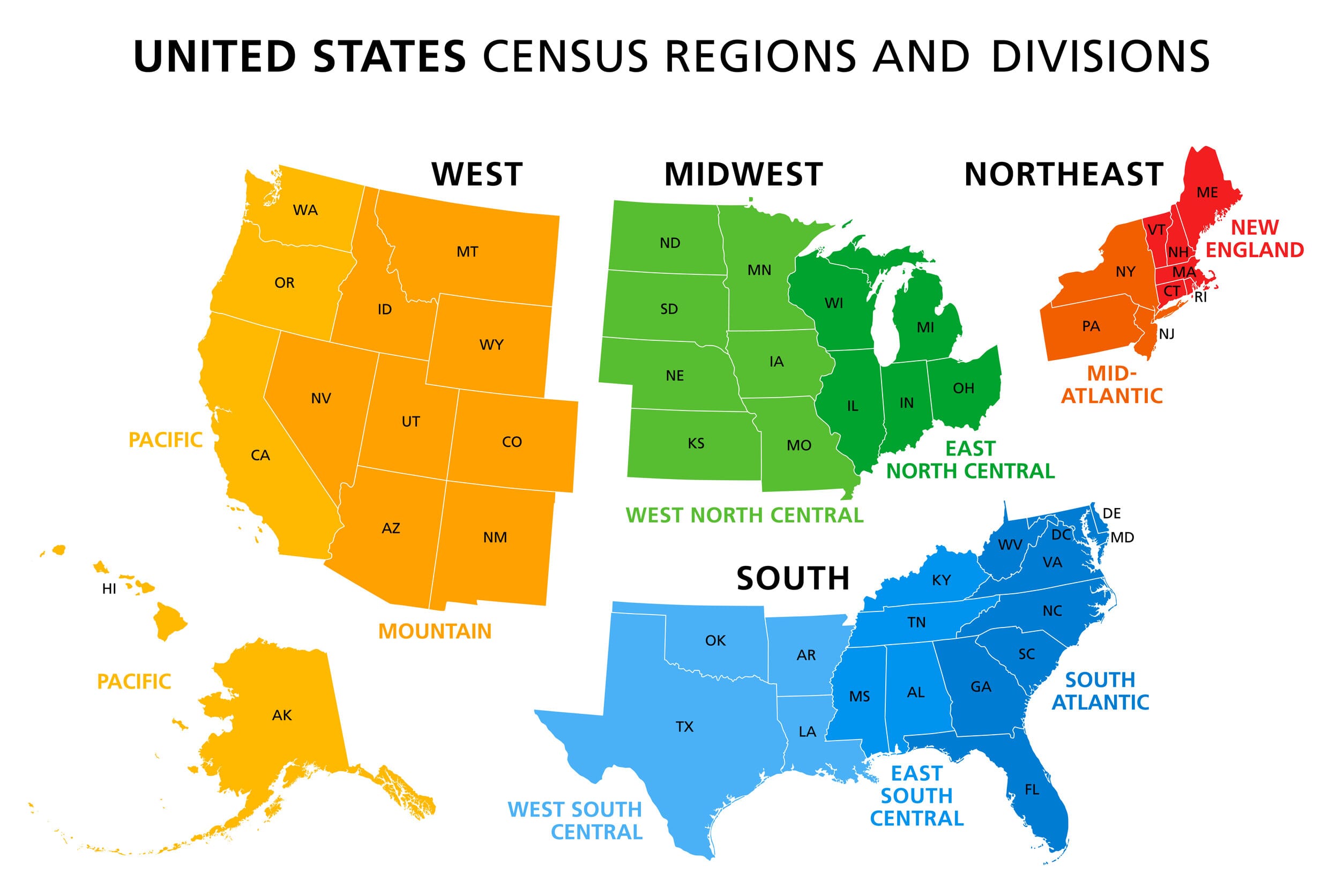
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, is often divided into five distinct regions for purposes of understanding its geography, culture, and history. This regional framework, while not universally accepted, provides a valuable tool for analyzing various aspects of the country. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these five regions, exploring their unique characteristics and the factors that contribute to their distinct identities.
1. The Northeast: A Region Steeped in History and Industry
The Northeast, often referred to as "New England" in its northernmost portion, is a region rich in history, culture, and industry. It encompasses the states of Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania.
Key Characteristics:
- Historical Significance: The Northeast played a pivotal role in the founding of the United States, with its early settlements, colonial history, and the Revolutionary War. This legacy is evident in the region’s numerous historical sites, museums, and architectural landmarks.
- Dense Population: The Northeast is the most densely populated region in the US, with major cities like New York City, Boston, and Philadelphia serving as centers of commerce, finance, and culture.
- Industrial Heritage: The Northeast was once the heart of American industry, particularly in manufacturing, textiles, and shipbuilding. While some industries have declined, the region remains a significant economic powerhouse with a diverse range of businesses.
- Diverse Landscape: The Northeast features a varied landscape, ranging from the rugged mountains of New England to the rolling hills of Pennsylvania and the Atlantic coastline.
- Cultural Hub: The Northeast is home to world-renowned universities, museums, theaters, and art institutions, making it a center of intellectual and artistic activity.
2. The Midwest: The Heartland of America
The Midwest, often referred to as the "American Heartland," is a vast region encompassing the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, and Kansas.
Key Characteristics:
- Agricultural Dominance: The Midwest is known for its vast agricultural lands, producing a significant portion of the nation’s food supply. The region is renowned for its corn, soybeans, wheat, and livestock production.
- Industrial Legacy: The Midwest was also a major center of industrial activity in the 20th century, particularly in manufacturing, steel production, and automotive industries.
- Great Lakes Influence: The Great Lakes, which border the northern part of the Midwest, play a crucial role in the region’s economy and transportation.
- Diverse Population: The Midwest has a diverse population, with a mix of European, African American, and Native American heritage.
- Cultural Identity: The Midwest is often associated with values of hard work, community, and family, reflecting its agrarian roots.
3. The South: A Region of Transformation
The South, encompassing the states of Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Tennessee, Kentucky, Arkansas, and Louisiana, is a region undergoing significant transformation.
Key Characteristics:
- Historical Legacy: The South is deeply intertwined with the history of slavery and the Civil War, leaving a lasting impact on its culture and society.
- Rapid Growth: The South has experienced significant population growth in recent decades, fueled by economic opportunities and a warmer climate.
- Changing Economy: The South’s economy is diversifying, moving beyond its traditional agricultural and manufacturing base into areas like technology, tourism, and healthcare.
- Cultural Diversity: The South is a region of diverse cultural influences, reflecting its history of immigration and its proximity to Latin America and the Caribbean.
- Natural Beauty: The South boasts a variety of natural landscapes, from the Appalachian Mountains to the beaches of the Gulf of Mexico.
4. The West: A Region of Adventure and Innovation
The West, encompassing the states of Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, Nevada, Idaho, Oregon, Washington, California, Alaska, and Hawaii, is a region of vast landscapes, diverse cultures, and innovative spirit.
Key Characteristics:
- Mountainous Terrain: The West is dominated by the Rocky Mountains, which provide breathtaking scenery and opportunities for outdoor recreation.
- Diverse Landscapes: The West also features deserts, forests, grasslands, and coastlines, creating a diverse range of ecosystems.
- Frontier Spirit: The West has long been associated with a spirit of adventure and independence, reflecting its history of exploration and westward expansion.
- Economic Powerhouse: The West is home to major technology centers, such as Silicon Valley in California, as well as significant energy resources.
- Cultural Blend: The West has a diverse population, influenced by Native American cultures, Hispanic heritage, and Asian immigration.
5. The Southwest: A Region of Ancient Cultures and Modern Cities
The Southwest, often considered a sub-region of the West, encompasses the states of Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Oklahoma, and sometimes includes parts of California and Nevada.
Key Characteristics:
- Ancient Cultures: The Southwest is home to ancient Native American cultures, such as the Pueblo peoples, whose legacy is evident in their archaeological sites and traditional art forms.
- Hispanic Influence: The Southwest has a strong Hispanic heritage, reflected in its language, food, and cultural traditions.
- Diverse Landscape: The Southwest is characterized by its arid landscapes, including deserts, canyons, and mesas.
- Economic Growth: The Southwest has experienced significant economic growth in recent decades, driven by industries such as technology, tourism, and energy.
- Cultural Crossroads: The Southwest is a cultural crossroads, where Native American, Hispanic, and Anglo-American influences converge.
Benefits of Understanding US Regions
Understanding the five US regions provides numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Historical Perspective: Examining the unique histories of each region helps to understand the development of the United States as a whole.
- Cultural Appreciation: Recognizing the distinct cultural identities of each region promotes appreciation for the diversity of American society.
- Economic Insight: Understanding the economic strengths and challenges of each region provides a broader perspective on national economic trends.
- Geographic Awareness: Familiarity with the geography of each region fosters an appreciation for the vastness and diversity of the United States.
- Informed Policymaking: Recognizing regional differences can inform policy decisions that address the specific needs and concerns of each region.
FAQs
Q: Are these five regions universally accepted?
A: No, there is no single, universally accepted definition of US regions. Different organizations and institutions may use alternative classifications based on specific criteria.
Q: Can a state belong to multiple regions?
A: Yes, some states, particularly those located on regional borders, may share characteristics with multiple regions. For instance, Texas can be considered part of both the Southwest and the South.
Q: How do these regional divisions relate to political divisions?
A: The five US regions do not directly correspond to political divisions like states or congressional districts. However, regional identities can influence political attitudes and voting patterns.
Q: How do these regions change over time?
A: The boundaries and characteristics of these regions can evolve over time due to factors such as population shifts, economic changes, and cultural trends.
Tips for Understanding US Regions
- Explore Maps and Geographic Data: Utilize maps and geographic data to visualize the boundaries and characteristics of each region.
- Read Regional Literature: Engage with books, articles, and documentaries that focus on the history, culture, and geography of specific regions.
- Travel and Experience: Visiting different regions firsthand allows for a deeper understanding of their unique qualities.
- Engage in Conversations: Discuss regional differences with people from various parts of the country to gain diverse perspectives.
- Embrace Interconnectedness: Recognize that while each region has its distinct identity, they are also interconnected and influence each other.
Conclusion
Dividing the United States into five regions offers a valuable framework for understanding its diverse geography, history, culture, and economy. While these regional classifications are not absolute, they provide a useful tool for analyzing various aspects of the nation. Recognizing the unique characteristics and interconnectedness of these regions fosters a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of the American experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Five US Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!