Guinea: A West African Nation on the World Map
Related Articles: Guinea: A West African Nation on the World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Guinea: A West African Nation on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Guinea: A West African Nation on the World Map
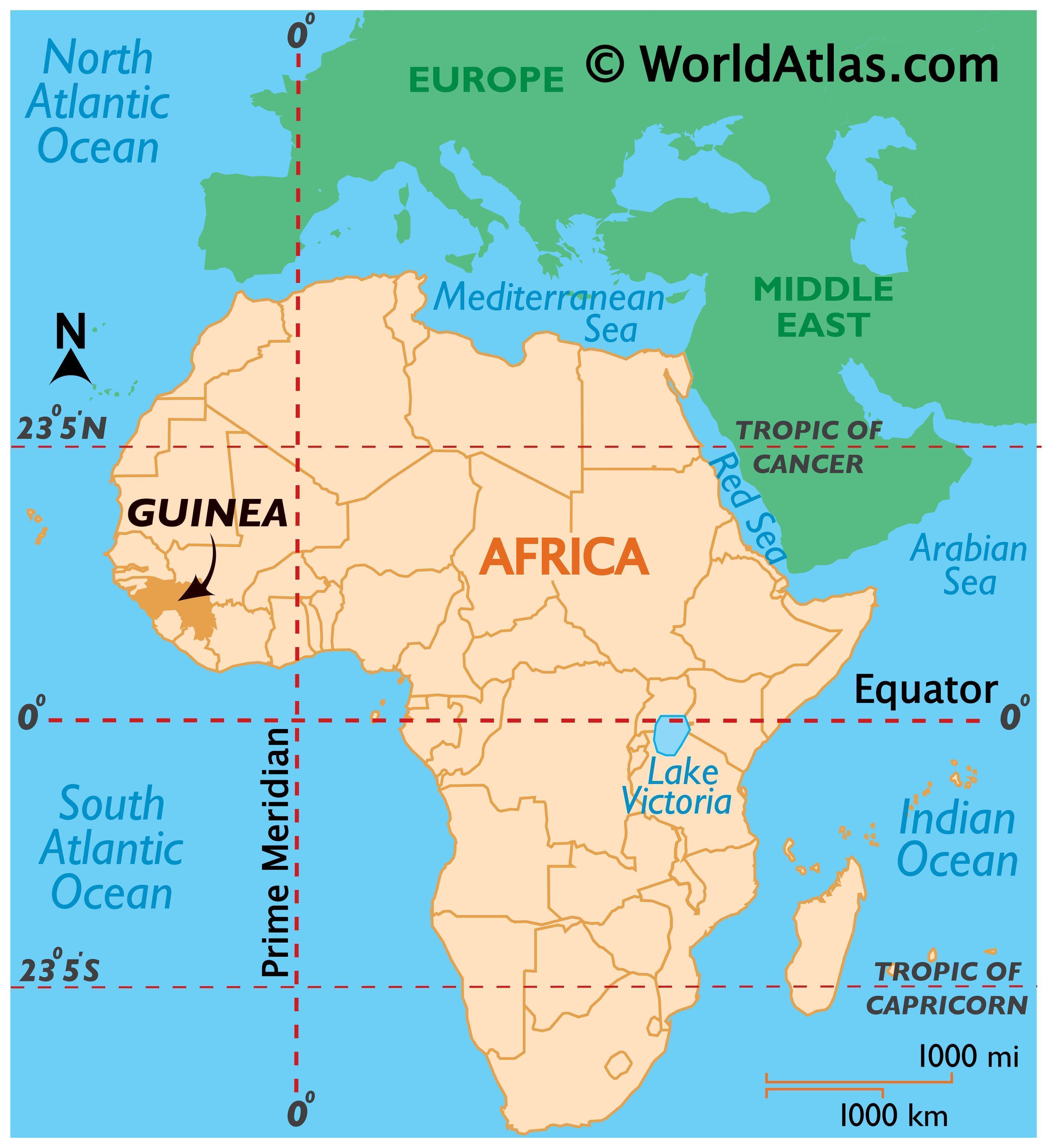
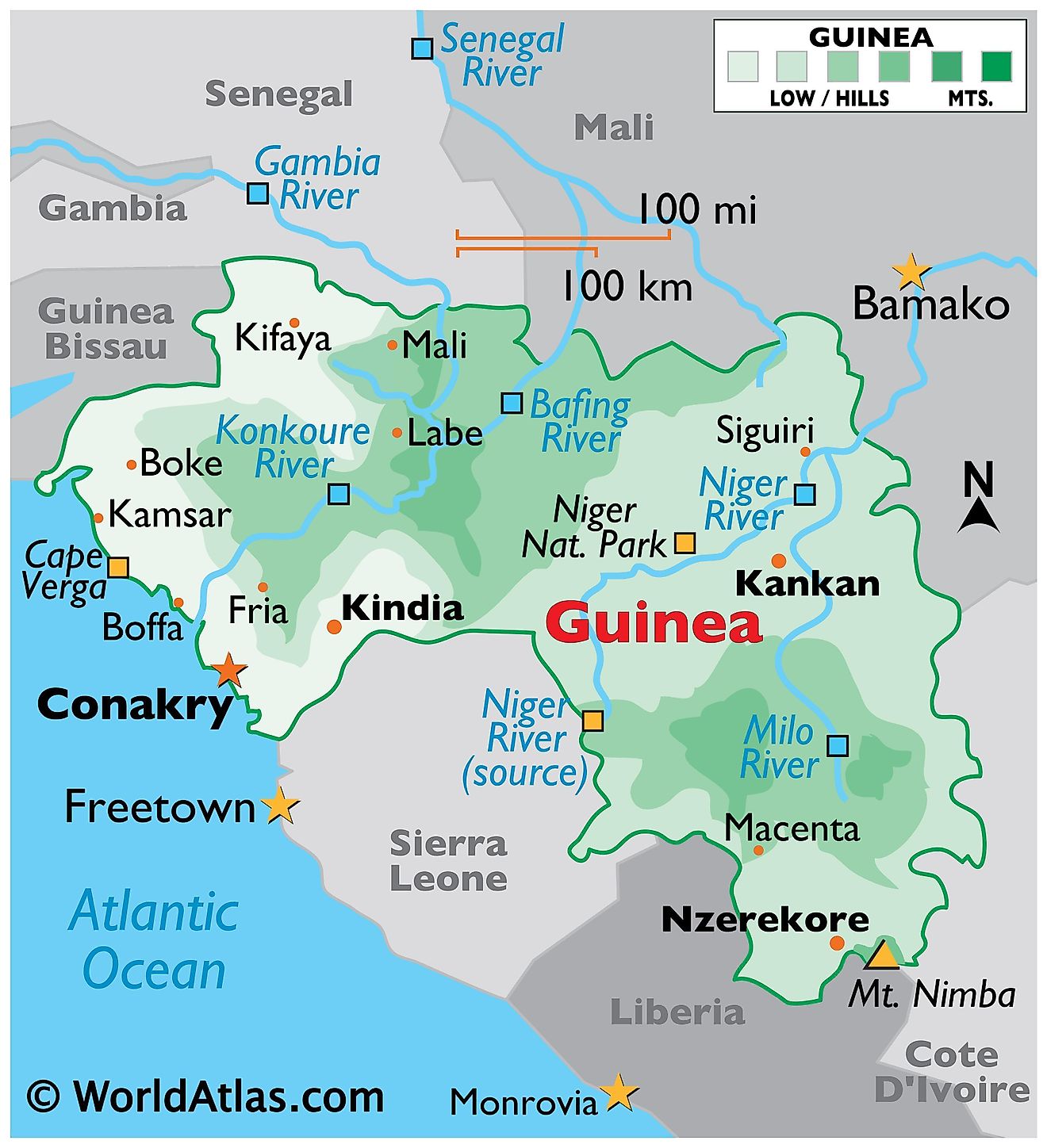
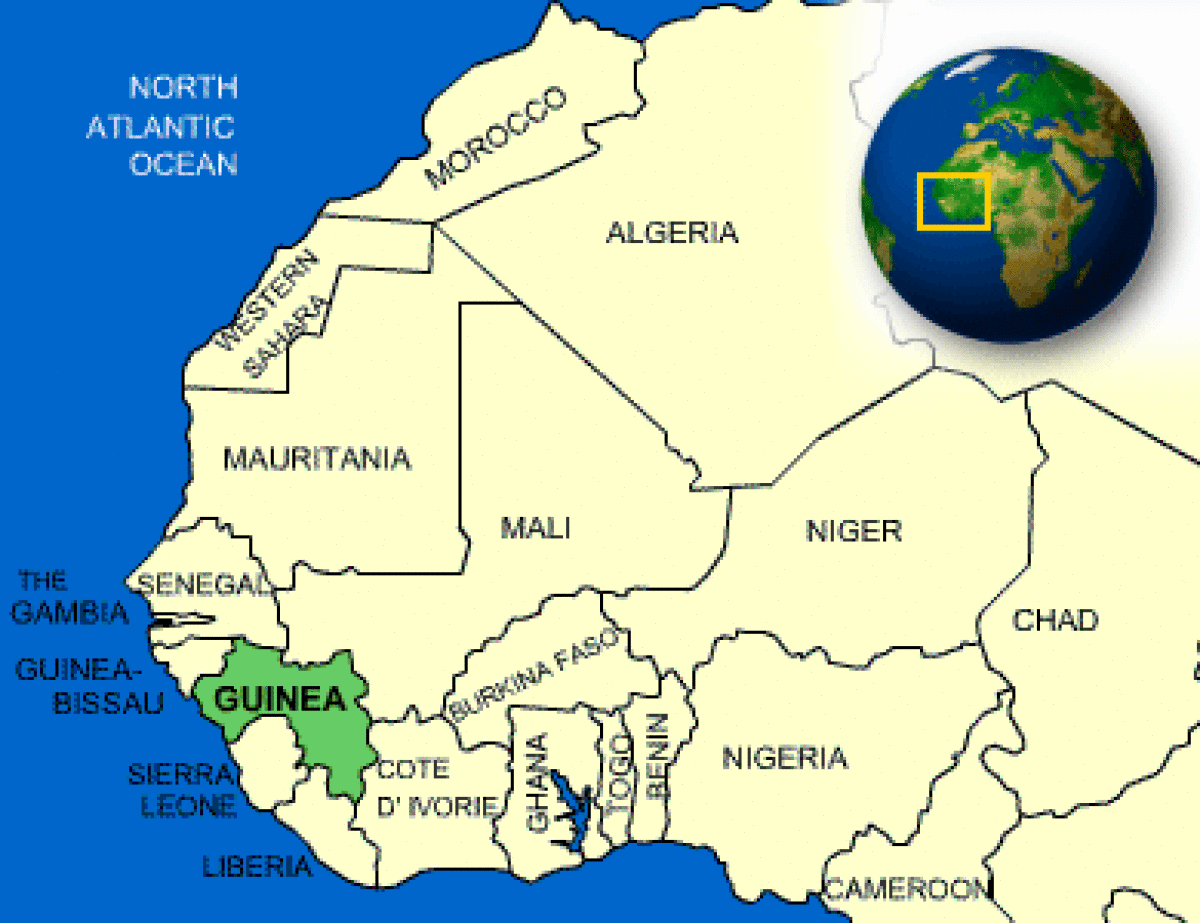
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a West African nation situated on the Atlantic coast. It shares borders with Senegal, Mali, Côte d’Ivoire, Liberia, Sierra Leone, and Guinea-Bissau. With a land area of approximately 245,857 square kilometers, Guinea is a geographically diverse country, characterized by its coastal plains, savannas, forests, and mountainous regions.
Geographic Location and Significance:
Guinea’s strategic location on the West African coast has played a pivotal role in its history and development. Its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean has facilitated trade and cultural exchange with other nations, while its inland regions have provided fertile land for agriculture. The country’s diverse topography has also contributed to its rich biodiversity and mineral wealth.
Historical Context:
Guinea’s history is deeply intertwined with the transatlantic slave trade. The region was a major source of enslaved people, and its coastline witnessed the tragic departure of countless Africans to the Americas. After centuries of colonial rule under the French, Guinea gained independence in 1958, becoming the first French colony in sub-Saharan Africa to declare independence.
Political Landscape:
Guinea has experienced periods of political instability since independence. The country has undergone several coups and military regimes, and its democratic institutions have faced challenges. However, in recent years, Guinea has made progress in promoting democracy and strengthening its governance structures.
Economic Profile:
Guinea’s economy is heavily reliant on its natural resources. Bauxite, a key ingredient in aluminum production, is the country’s most important export commodity. Other significant mineral resources include iron ore, gold, and diamonds. However, Guinea’s economic development has been hampered by poverty, corruption, and inadequate infrastructure.
Cultural Heritage:
Guinea boasts a rich and vibrant cultural heritage. Its diverse ethnic groups, each with their unique traditions, languages, and art forms, contribute to the country’s cultural tapestry. Music, dance, and storytelling are integral parts of Guinean culture, reflecting the country’s history, beliefs, and social values.
Tourism Potential:
Guinea possesses significant tourism potential. Its pristine beaches, lush forests, and historical sites offer diverse attractions for visitors. The country’s natural beauty, coupled with its rich cultural heritage, provides ample opportunities for eco-tourism and cultural immersion.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its abundant natural resources and cultural wealth, Guinea faces several challenges. Poverty, illiteracy, and inadequate healthcare systems remain prevalent. The country also struggles with corruption, political instability, and a lack of infrastructure.
However, Guinea also presents opportunities for development. Its vast mineral resources, growing agricultural sector, and tourism potential offer avenues for economic growth and social progress. The country’s strategic location and young population provide further advantages for future development.
International Relations:
Guinea maintains active diplomatic relations with numerous countries worldwide. Its strategic location in West Africa makes it a key player in regional affairs. The country participates in various international organizations, including the United Nations, the African Union, and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
Environmental Concerns:
Guinea’s environment faces several challenges, including deforestation, soil degradation, and pollution. The country’s mining industry, while a significant source of revenue, has also contributed to environmental damage. Sustainable development practices and environmental protection are crucial for Guinea’s long-term well-being.
Conclusion:
Guinea is a nation rich in history, culture, and natural resources. Its strategic location, diverse topography, and vibrant cultural heritage offer opportunities for development and progress. While the country faces challenges, its potential for economic growth and social advancement remains significant. By addressing its challenges and leveraging its strengths, Guinea can chart a path towards a brighter future for its people.
FAQs about Guinea:
Q: What is the capital of Guinea?
A: The capital of Guinea is Conakry.
Q: What is the official language of Guinea?
A: The official language of Guinea is French. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken throughout the country.
Q: What is the currency of Guinea?
A: The currency of Guinea is the Guinean franc (GNF).
Q: What is the population of Guinea?
A: The population of Guinea is estimated to be around 13 million.
Q: What are the major religions in Guinea?
A: The majority of Guineans are Muslims, followed by Christians and animists.
Q: What are some of the main industries in Guinea?
A: Guinea’s main industries include mining, agriculture, and fishing.
Q: What are some of the tourist attractions in Guinea?
A: Guinea’s tourist attractions include its pristine beaches, lush forests, historical sites, and national parks.
Q: What is the climate like in Guinea?
A: Guinea has a tropical climate with a rainy season from May to October and a dry season from November to April.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Guinea?
A: Guinea faces challenges such as poverty, illiteracy, inadequate healthcare, corruption, political instability, and environmental degradation.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for development in Guinea?
A: Guinea has opportunities for development in its mining sector, agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure.
Tips for Visiting Guinea:
- Obtain a visa: Visitors to Guinea require a visa, which can be obtained at Guinean embassies or consulates.
- Learn some basic French: French is the official language of Guinea, and it is helpful to know some basic phrases.
- Respect local customs: Guinea has a rich cultural heritage, and it is important to respect local customs and traditions.
- Be aware of health risks: Guinea is a tropical country, and visitors should be aware of health risks such as malaria and yellow fever.
- Pack light: Guinea’s roads can be challenging, and it is advisable to pack light.
- Bargain for goods: Bargaining is common in Guinea, and it is often possible to get a better price on goods and services.
- Consider a guided tour: A guided tour can provide valuable insights into Guinea’s history, culture, and attractions.
- Stay safe: As with any travel destination, it is important to stay aware of your surroundings and take necessary precautions to ensure your safety.
Conclusion:
Guinea is a complex and fascinating country with a rich history, diverse culture, and abundant natural resources. Despite the challenges it faces, Guinea holds significant potential for development and progress. Understanding its unique characteristics and appreciating its cultural heritage can foster greater awareness and appreciation for this West African nation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Guinea: A West African Nation on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!