Mapping the Decline: A Visual Journey Through the Evolution of Coal Power Plants in the United States
Related Articles: Mapping the Decline: A Visual Journey Through the Evolution of Coal Power Plants in the United States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Decline: A Visual Journey Through the Evolution of Coal Power Plants in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Decline: A Visual Journey Through the Evolution of Coal Power Plants in the United States

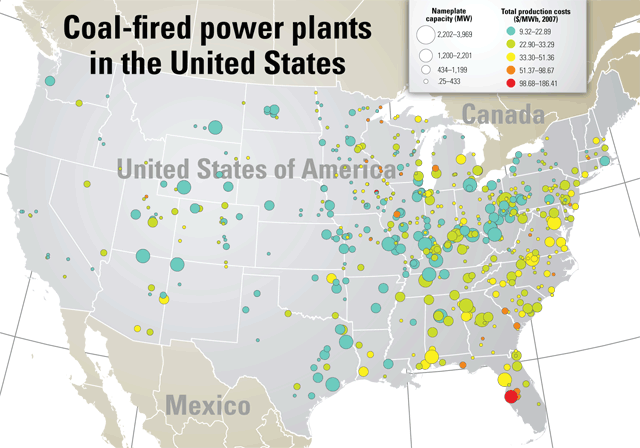
The United States has a long history of relying on coal for electricity generation. For decades, coal-fired power plants dominated the energy landscape, powering homes, businesses, and industries across the nation. However, the past two decades have witnessed a significant shift in the energy sector, with coal’s dominance gradually waning under the influence of environmental concerns, technological advancements, and policy changes. This transition is vividly illustrated through the evolution of the map of coal power plants in the United States.
A Visual Chronicle of Change:
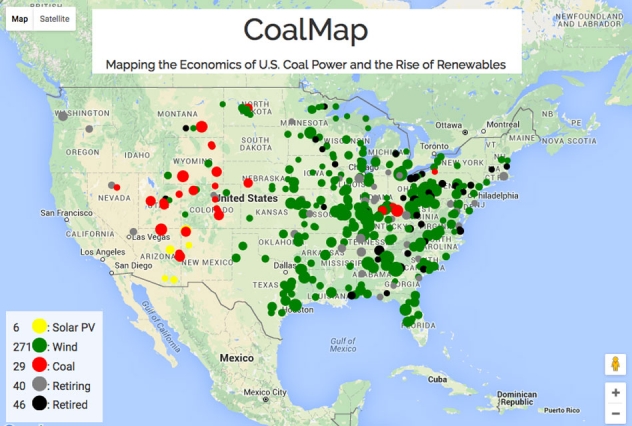
The map of coal power plants in the US offers a powerful visual narrative of this transformation. While the exact number and location of these plants have fluctuated over time, the overall trend is clear: a decrease in the number of operational plants and a shift in their geographical distribution.
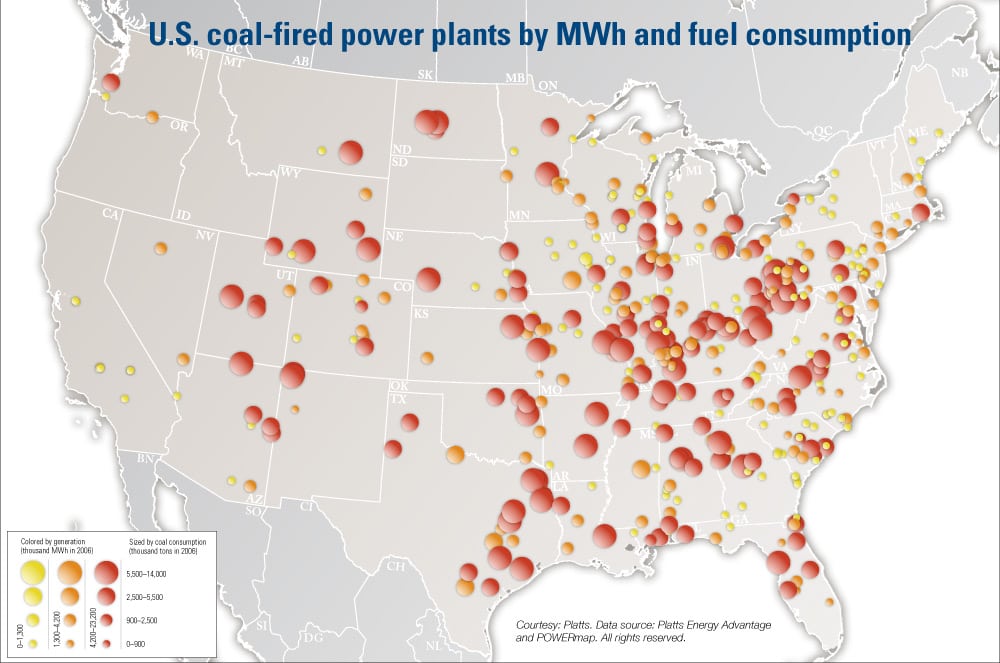
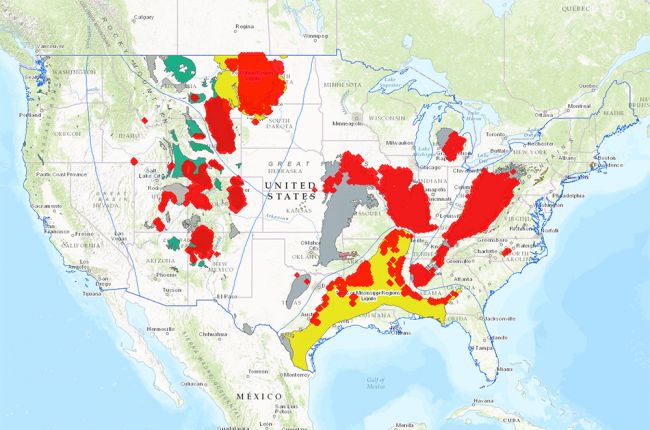
- The Peak of Coal: In the early 2000s, the map was densely populated with coal power plants, particularly in the eastern and midwestern regions. These areas, rich in coal deposits, became hubs for energy production, fueling industrial growth and economic prosperity.
- The Rise of Clean Energy: The early 2010s marked a turning point. The map began to show a decline in the number of operational coal plants, as renewable energy sources, particularly wind and solar, gained traction. This shift was driven by factors such as environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions, rising costs associated with coal mining and transportation, and the increasing availability of cleaner alternatives.
- The Continuing Transition: The map continues to evolve, reflecting the ongoing transition away from coal. Many plants have been retired or converted to other energy sources, while new renewable energy projects are being developed, particularly in regions with abundant wind and solar resources.
Beyond the Numbers: Understanding the Impact
The map of coal power plants in the US is more than just a visual representation of energy production. It offers valuable insights into the social, economic, and environmental impacts of this energy source.
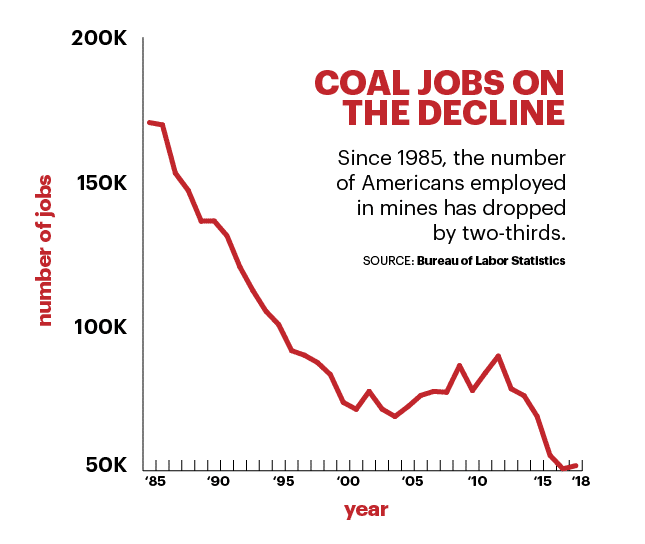
- Economic Implications: The decline of coal power has had significant economic repercussions, particularly in coal-producing regions. Job losses in mining and power plant operations have led to economic hardship and social unrest in some communities. However, the transition to cleaner energy sources has also created new job opportunities in renewable energy sectors, fostering economic diversification and growth.
- Environmental Considerations: The shift away from coal has been driven by environmental concerns, particularly those related to air pollution and climate change. Coal-fired power plants are major emitters of greenhouse gases, contributing significantly to global warming. The closure of these plants has resulted in a reduction in air pollution and a positive impact on public health.
- Energy Security: The US is increasingly relying on diverse energy sources, including renewable energy, natural gas, and nuclear power. This diversification enhances energy security by reducing dependence on a single fuel source and mitigating the risks associated with price fluctuations or supply disruptions.
FAQs About the Map of Coal Power Plants in the US:
1. How many coal power plants are there in the US?
The number of operational coal power plants in the US has been steadily declining. As of 2023, there are approximately 200 coal-fired power plants in operation, down from over 500 in the early 2000s.
2. Where are most coal power plants located?
The majority of remaining coal power plants are concentrated in the eastern and midwestern regions of the US, where coal deposits are abundant. However, the geographical distribution is shifting, with fewer plants operating in areas where environmental regulations are stricter and renewable energy options are more viable.
3. Why are coal power plants being retired?
Coal power plants are being retired for a variety of reasons, including:
- Environmental regulations: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented regulations aimed at reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from power plants, making it increasingly expensive to operate coal-fired facilities.
- Economic factors: The cost of coal mining and transportation has risen, while the cost of renewable energy technologies has declined, making coal less competitive.
- Technological advancements: Renewable energy technologies have advanced significantly, offering cost-effective and cleaner alternatives to coal.
- Public opinion: Public awareness of the environmental impacts of coal has grown, leading to increased pressure on policymakers to transition to cleaner energy sources.
4. What are the alternatives to coal power?
The main alternatives to coal power include:
- Renewable energy sources: Wind, solar, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy are becoming increasingly competitive and are playing a significant role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Natural gas: Natural gas is a cleaner-burning fossil fuel than coal and has become a major source of electricity generation in recent years.
- Nuclear power: Nuclear power plants are a low-carbon source of electricity, but they face challenges related to safety, waste disposal, and public perception.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Coal Power Plants in the US:
- Focus on the trends: Look for patterns in the distribution and number of coal power plants over time. Pay attention to the areas where plants are being retired or converted to other energy sources.
- Consider the context: Understand the factors driving the decline of coal power, such as environmental regulations, economic factors, and technological advancements.
- Look beyond the map: The map of coal power plants is just one piece of the puzzle. Explore data on energy production, emissions, and policy changes to gain a comprehensive understanding of the energy transition.
Conclusion:
The map of coal power plants in the US is a powerful visual representation of the ongoing energy transition. It reveals the decline of a once-dominant energy source and the emergence of cleaner alternatives. While the transition has brought challenges, it also presents opportunities for economic diversification, environmental protection, and energy security. As the map continues to evolve, it will provide valuable insights into the future of energy in the United States.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Decline: A Visual Journey Through the Evolution of Coal Power Plants in the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!