Nangarhar Province: A Geographical and Historical Overview
Related Articles: Nangarhar Province: A Geographical and Historical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Nangarhar Province: A Geographical and Historical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Nangarhar Province: A Geographical and Historical Overview

Nangarhar Province, nestled in eastern Afghanistan, holds a significant place in the country’s history and geography. Its strategic location, diverse landscape, and rich cultural heritage have shaped its past and continue to influence its present. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Nangarhar, exploring its physical features, historical significance, and contemporary challenges.
Geographical Landscape:
Nangarhar Province is characterized by its varied terrain, ranging from the fertile plains of the Kunar River Valley to the rugged mountains of the Hindu Kush. The Kunar River, a major tributary of the Kabul River, flows through the province, providing essential irrigation and transportation routes. The province’s eastern border is marked by the Durand Line, a disputed frontier with Pakistan.
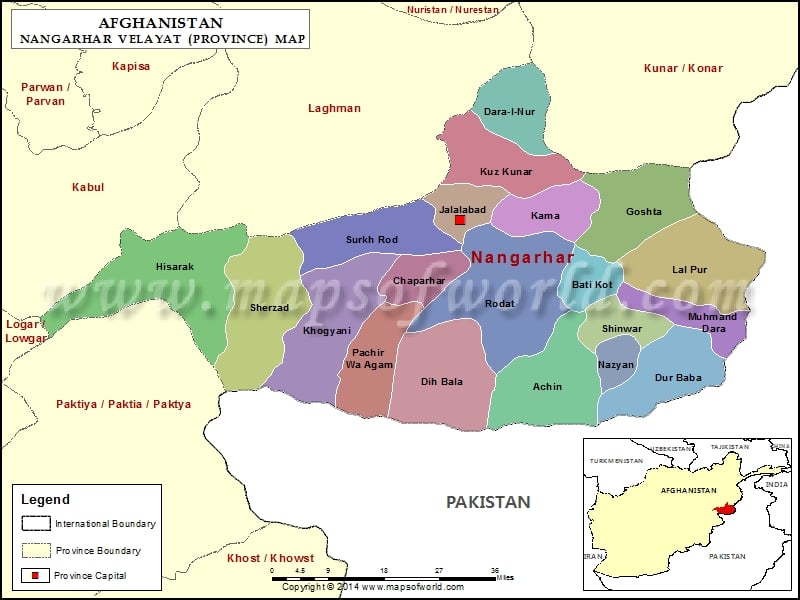
Major Cities and Districts:
Nangarhar is divided into 23 districts, each with its unique characteristics and contributions to the province’s overall development. The provincial capital, Jalalabad, is a bustling city known for its vibrant markets, historical sites, and strategic importance. Other significant cities include:
- Jalalabad: The largest city in Nangarhar, serving as the provincial capital and a major commercial hub.
- Behsud: Located in the eastern part of the province, Behsud is known for its agricultural production and traditional handicrafts.
- Rodat: Situated in the south-central region, Rodat is a key agricultural center and a popular destination for its natural beauty.
- Hesarak: Located in the west of the province, Hesarak is known for its production of fruits and vegetables.
Historical Significance:
Nangarhar boasts a rich history dating back to ancient times. The region has been a crossroads of civilizations, witnessing the rise and fall of empires. The province was once part of the ancient Gandhara civilization, known for its exquisite Buddhist art and architecture. Remains of this era can still be found in the form of ancient stupas, monasteries, and sculptures, attracting tourists and scholars alike.
During the Mughal period, Nangarhar flourished under the patronage of the Mughal emperors. The province was a key trading center on the Silk Road, connecting the East and West. The city of Jalalabad was a major hub for commerce and culture, attracting travelers and merchants from across the region.
Modern Challenges:
Despite its rich history and strategic location, Nangarhar faces several challenges in the modern era. The province has been affected by the ongoing conflict in Afghanistan, leading to instability, displacement, and economic hardship.
Furthermore, the province is vulnerable to natural disasters, including droughts and floods. The changing climate patterns pose a significant threat to agricultural production and water resources, impacting the livelihoods of many residents.
Economic Activity:
Agriculture remains a major source of income for the people of Nangarhar. The province is known for its production of fruits, vegetables, and grains. The Kunar River Valley is particularly fertile, producing a variety of crops.
Nangarhar also has a growing industrial sector, with factories producing textiles, carpets, and other goods. The province is also home to several small businesses and shops, contributing to the local economy.
Cultural Heritage:
Nangarhar is a melting pot of cultures, with a diverse population of Pashtuns, Tajiks, and other ethnic groups. The province is known for its rich cultural heritage, with traditional music, dance, and handicrafts. The province is also home to several historical sites, including the ancient city of Ghazni and the ruins of the Buddhist monastery at Surkh Kotal.
Tourism Potential:
Nangarhar has significant tourism potential, with its rich history, diverse landscape, and cultural heritage. The province is home to several historical sites, natural attractions, and cultural events that could attract visitors from around the world.
FAQs:
Q: What is the population of Nangarhar Province?
A: The population of Nangarhar Province is estimated to be around 1.8 million people.
Q: What is the main language spoken in Nangarhar?
A: The main language spoken in Nangarhar is Pashto, with Dari also widely spoken.
Q: What are the major industries in Nangarhar?
A: The major industries in Nangarhar are agriculture, textiles, carpets, and handicrafts.
Q: What are the major tourist attractions in Nangarhar?
A: Major tourist attractions in Nangarhar include the ancient city of Ghazni, the ruins of the Buddhist monastery at Surkh Kotal, the Jalalabad Museum, and the Nangarhar National Park.
Tips for Visiting Nangarhar:
- It is advisable to consult with the local authorities and travel agencies before planning a trip to Nangarhar, as security conditions can change rapidly.
- Respect local customs and traditions, and dress modestly when visiting religious sites.
- Learn some basic Pashto or Dari phrases to facilitate communication with locals.
- Take precautions against food and waterborne illnesses.
- Be aware of your surroundings and take steps to protect yourself from theft.
Conclusion:
Nangarhar Province is a region of immense historical, cultural, and economic significance. Despite the challenges it faces, Nangarhar holds immense potential for development and prosperity. By harnessing its natural resources, promoting its rich cultural heritage, and fostering peace and stability, Nangarhar can contribute significantly to the progress of Afghanistan.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Nangarhar Province: A Geographical and Historical Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!