Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the AGMA Map: A Framework for Sustainable Groundwater Management
- 3.2 Benefits of the AGMA Map: A Legacy of Sustainable Groundwater Management
- 3.3 FAQs about the AGMA Map
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the AGMA Map
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Framework for Sustainable Water Management
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide

The Arizona Groundwater Management Act (AGMA), enacted in 1980, is a cornerstone of water resource management in the state. Its primary objective is to ensure the long-term sustainability of Arizona’s groundwater resources, particularly in the rapidly growing areas of the state. The act’s intricate structure and implementation are often referred to as the "AGMA Map," a metaphorical representation of the complex web of regulations, programs, and authorities that govern groundwater use in Arizona.
Understanding the AGMA Map: A Framework for Sustainable Groundwater Management
The AGMA Map, though not a literal map, provides a framework for understanding the intricate workings of the act. It outlines the various components of the act and their interconnectedness, highlighting the key elements that contribute to its success. Here’s a breakdown of the AGMA Map’s key components:
1. Active Management Areas (AMAs): The AGMA designates specific areas of the state as AMAs, encompassing regions with high groundwater demand and potential for depletion. These areas are subject to stricter regulations and management strategies to ensure sustainable groundwater use.
2. Groundwater Budgets: Each AMA has a designated groundwater budget, representing the maximum amount of groundwater that can be withdrawn annually to maintain a sustainable balance. This budget is determined through a rigorous assessment process that considers factors such as recharge, discharge, and existing water rights.
3. Water Rights and Permits: The AGMA regulates the allocation and use of groundwater through a system of water rights and permits. Existing water rights are protected, while new permits are granted based on availability and the need to ensure sustainable groundwater use.
4. Groundwater Conservation Programs: The AGMA encourages the development and implementation of groundwater conservation programs within AMAs. These programs aim to reduce groundwater use through measures such as water efficiency improvements, rainwater harvesting, and the use of alternative water sources.
5. Groundwater Replenishment: The AGMA promotes groundwater replenishment through various methods, including the injection of treated wastewater and the capture of surface water runoff. Replenishment efforts help maintain the long-term sustainability of groundwater resources.
6. Monitoring and Enforcement: The AGMA establishes a robust monitoring and enforcement system to ensure compliance with its provisions. This includes monitoring groundwater levels, enforcing water rights, and investigating potential violations.
7. Intergovernmental Cooperation: The AGMA promotes collaboration between various levels of government, including state, county, and municipal authorities, to ensure effective groundwater management. This intergovernmental cooperation is essential for coordinating efforts and addressing shared challenges.
8. Public Participation: The AGMA emphasizes public participation in groundwater management decisions. This includes providing opportunities for stakeholders, including water users, environmental groups, and the general public, to engage in the process and contribute to the development of sustainable groundwater policies.
Benefits of the AGMA Map: A Legacy of Sustainable Groundwater Management
The AGMA Map, through its comprehensive framework, has significantly contributed to the sustainable management of Arizona’s groundwater resources. Its benefits are multi-faceted and have a profound impact on the state’s water security and economic development.
1. Ensuring Groundwater Sustainability: The AGMA Map’s focus on groundwater budgets, conservation programs, and replenishment efforts has effectively addressed the challenges of groundwater depletion in Arizona. This has ensured the long-term sustainability of this vital resource for future generations.
2. Protecting Existing Water Rights: The AGMA Map safeguards existing water rights while ensuring the availability of groundwater for future needs. This balance between protecting existing rights and promoting sustainable use has been crucial for maintaining stability and economic growth in Arizona.
3. Promoting Water Conservation: The AGMA Map encourages the implementation of water conservation measures, leading to a reduction in groundwater demand. This has not only helped preserve groundwater resources but also contributed to the state’s overall water efficiency.
4. Supporting Economic Growth: The AGMA Map’s commitment to sustainable groundwater management has fostered a stable and reliable water supply, supporting economic growth and development in Arizona. This has attracted investment and created opportunities in various sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism.
5. Enhancing Environmental Protection: The AGMA Map’s focus on groundwater sustainability has positive environmental implications. By protecting groundwater resources, the act also helps maintain the health of associated ecosystems, including rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
6. Fostering Collaboration and Public Engagement: The AGMA Map promotes collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies, water users, and the public. This engagement ensures that groundwater management decisions reflect the diverse needs and perspectives of all stakeholders.
FAQs about the AGMA Map
1. What is the primary purpose of the AGMA Map?
The primary purpose of the AGMA Map is to ensure the long-term sustainability of Arizona’s groundwater resources by regulating groundwater use and promoting conservation measures.
2. What are the key components of the AGMA Map?
The key components of the AGMA Map include Active Management Areas (AMAs), groundwater budgets, water rights and permits, conservation programs, replenishment efforts, monitoring and enforcement, intergovernmental cooperation, and public participation.
3. How does the AGMA Map protect existing water rights?
The AGMA Map safeguards existing water rights while ensuring the availability of groundwater for future needs through a system of permits and regulations.
4. What are the benefits of the AGMA Map?
The AGMA Map has contributed to groundwater sustainability, protected existing water rights, promoted water conservation, supported economic growth, enhanced environmental protection, and fostered collaboration and public engagement.
5. How does the AGMA Map promote water conservation?
The AGMA Map encourages the implementation of water conservation programs within AMAs, leading to a reduction in groundwater demand.
6. What is the role of public participation in the AGMA Map?
The AGMA Map emphasizes public participation in groundwater management decisions, providing opportunities for stakeholders to engage in the process and contribute to sustainable groundwater policies.
7. How does the AGMA Map promote intergovernmental cooperation?
The AGMA Map promotes collaboration between various levels of government, including state, county, and municipal authorities, to ensure effective groundwater management.
8. How is the AGMA Map enforced?
The AGMA Map establishes a robust monitoring and enforcement system to ensure compliance with its provisions, including monitoring groundwater levels, enforcing water rights, and investigating potential violations.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the AGMA Map
1. Consult the Arizona Department of Water Resources (ADWR): The ADWR is the primary agency responsible for implementing the AGMA and can provide valuable information and resources on the act.
2. Explore the ADWR’s Online Resources: The ADWR website offers a wealth of information on the AGMA, including maps, reports, regulations, and data on groundwater resources.
3. Engage with Local Water Agencies: Local water agencies, such as cities, counties, and water districts, are responsible for managing groundwater within their jurisdictions and can provide insights into local water management practices.
4. Participate in Public Meetings and Workshops: The ADWR and local water agencies frequently hold public meetings and workshops to discuss groundwater issues and solicit feedback from stakeholders.
5. Stay Informed about Current Developments: The AGMA is a dynamic framework that is continually evolving to address new challenges and opportunities. Stay informed about current developments by subscribing to ADWR newsletters and following relevant news sources.
Conclusion: A Framework for Sustainable Water Management
The AGMA Map, a metaphorical representation of the complex web of regulations and programs governing groundwater use in Arizona, stands as a testament to the state’s commitment to sustainable water management. Its intricate framework, encompassing active management areas, groundwater budgets, water rights, conservation programs, and public participation, has effectively addressed the challenges of groundwater depletion and ensured the long-term sustainability of this vital resource. By understanding the AGMA Map and its various components, stakeholders can play an active role in safeguarding Arizona’s water future and ensuring the continued prosperity of the state.





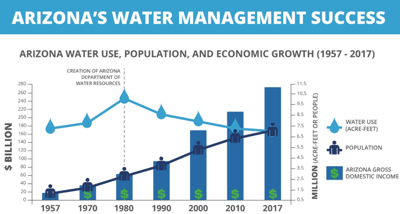


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of the Arizona Groundwater Management Act: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!