Navigating the Earth: Understanding True North and Magnetic North
Related Articles: Navigating the Earth: Understanding True North and Magnetic North
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Earth: Understanding True North and Magnetic North. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Earth: Understanding True North and Magnetic North

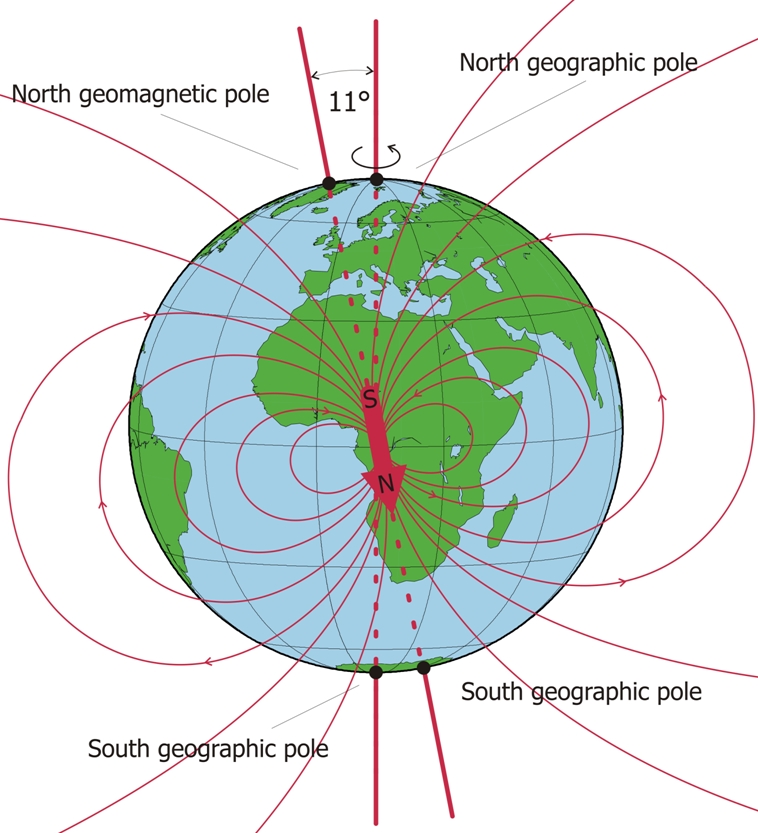
The Earth, a massive sphere spinning through space, is guided by a complex interplay of forces. One such force, magnetism, plays a crucial role in our understanding of direction and navigation. This magnetic field, generated by the Earth’s molten core, creates a magnetic north pole, a point that attracts the north end of a compass needle. However, this magnetic north pole is not the same as the true north pole, the geographic north pole, which is the point where the Earth’s axis of rotation intersects with the surface.
This distinction between magnetic north and true north is critical for accurate navigation, particularly for long-distance travel or activities reliant on precise bearings. Understanding the difference and how to account for it is paramount for anyone using a compass or relying on magnetic navigation.
The Earth’s Magnetic Field: A Dynamic System
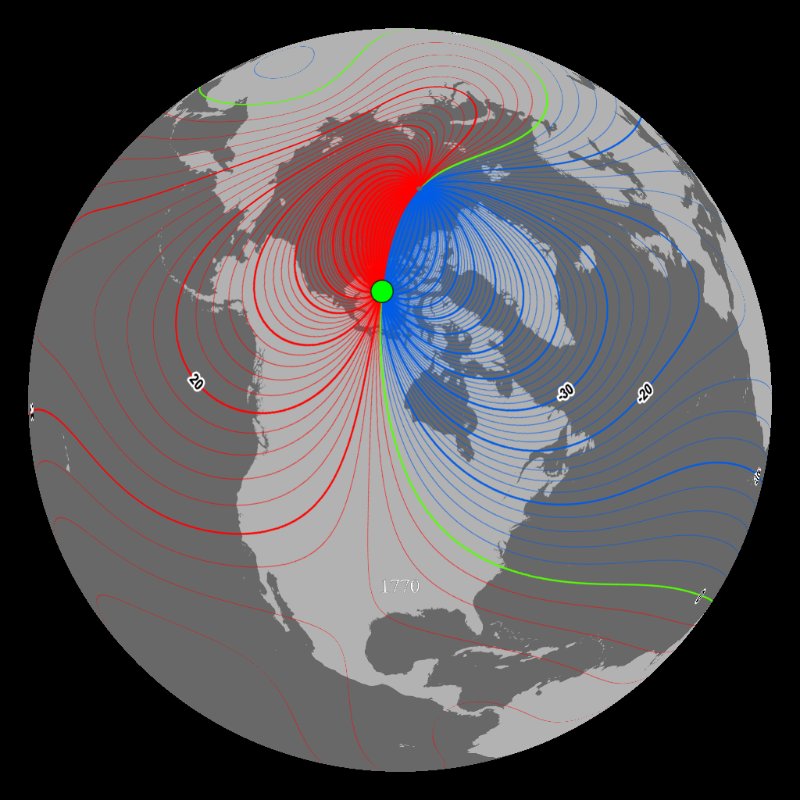
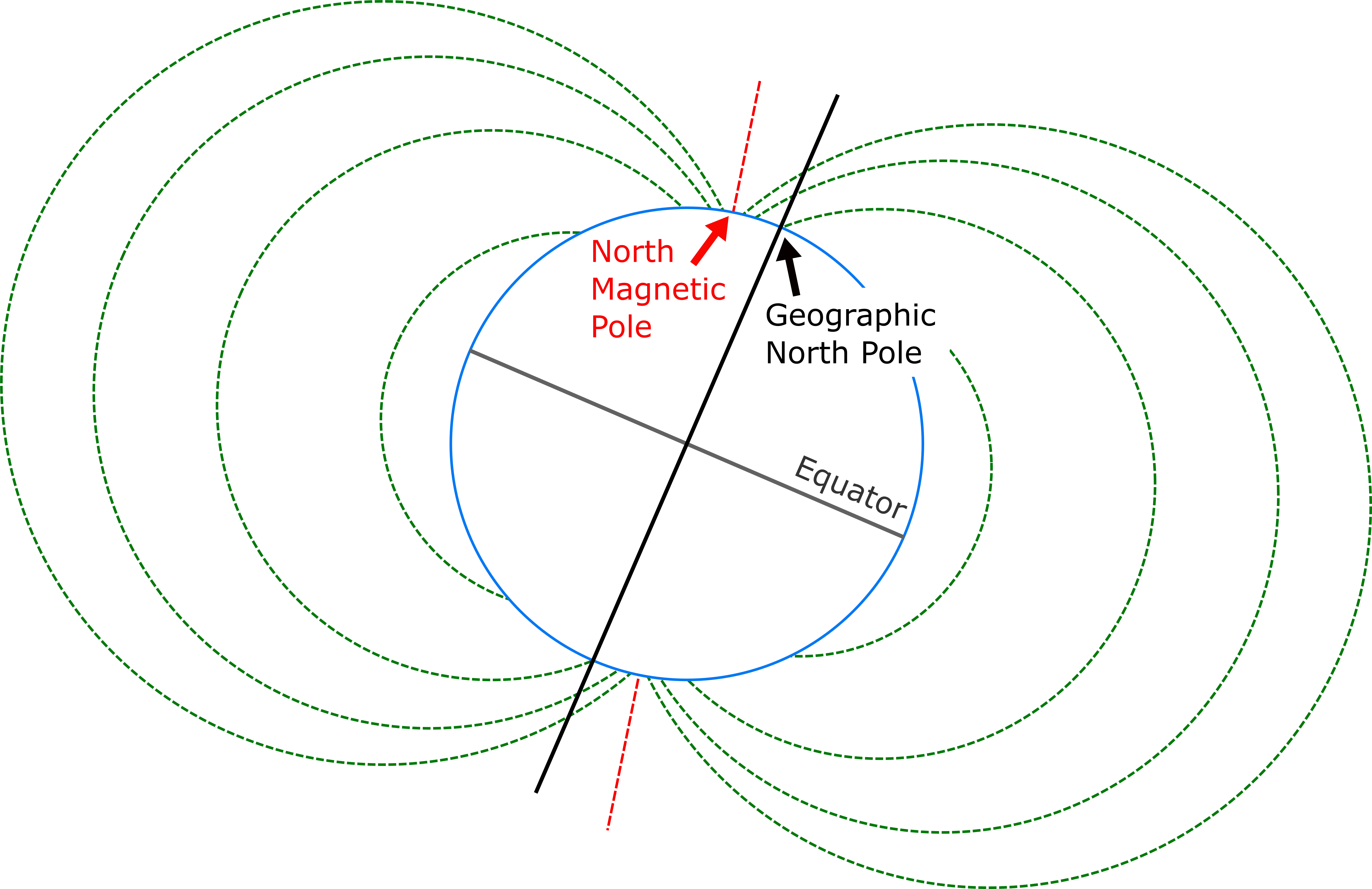
The Earth’s magnetic field, akin to a giant bar magnet, extends far beyond the planet’s surface. This field is not static; it fluctuates and shifts over time. The magnetic north pole, constantly in motion, wanders across the Arctic region, influenced by the dynamic processes within the Earth’s core. This movement, known as magnetic declination, is the angle between true north and magnetic north at any given location.
Navigating with True North and Magnetic North
Navigational tools like compasses rely on the Earth’s magnetic field. A compass needle aligns itself with the magnetic field lines, pointing towards magnetic north. However, this magnetic north is not always aligned with true north, the actual geographic north pole. This discrepancy, known as magnetic declination, varies depending on the location.
Maps and Magnetic Declination: A Necessary Adjustment
To ensure accurate navigation, maps incorporate magnetic declination information. This information is usually presented on a compass rose or a separate declination diagram. The declination value indicates the angle by which magnetic north deviates from true north at a specific location. This angle, measured in degrees, is essential for adjusting compass readings to obtain true bearings.
Understanding Magnetic Declination: A Key to Accurate Navigation
Navigators use magnetic declination to correct compass readings and obtain true bearings. To compensate for the difference between magnetic north and true north, they adjust their compass readings by adding or subtracting the declination value. This adjustment ensures that the compass readings accurately reflect the direction of true north.
The Importance of Magnetic Declination in Modern Navigation
The concept of magnetic declination remains relevant in modern navigation, even with the advent of GPS technology. While GPS devices provide accurate location information, they do not necessarily account for magnetic declination. For activities like orienteering, hiking, or sailing, where compass readings are crucial, understanding magnetic declination and its impact on compass readings is essential.
Factors Affecting Magnetic Declination
Magnetic declination is influenced by several factors:
- Location: Declination varies significantly across the globe, with the largest deviations occurring closer to the magnetic poles.
- Time: The Earth’s magnetic field is constantly changing, causing magnetic declination to shift over time.
- Solar Activity: Solar storms and other solar events can temporarily disrupt the Earth’s magnetic field, impacting declination.
Navigational Tools for Accounting for Magnetic Declination
Various tools are available to assist navigators in accounting for magnetic declination:
- Maps: Most maps incorporate magnetic declination information, typically indicated on a compass rose or a separate declination diagram.
- Compass Rose: A compass rose on a map depicts magnetic north and true north, along with the angle of declination.
- Declination Calculators: Online calculators and mobile apps can provide the current declination value for a specific location.
- Declination Adjustment Tools: Some compasses feature adjustable declination settings, allowing users to manually input the declination value for their location.
Tips for Using Magnetic Declination in Navigation
- Check the Map: Always consult the map for the current declination value for your location.
- Use a Compass Rose: Familiarize yourself with the compass rose on the map and identify true north and magnetic north.
- Adjust Compass Readings: Add or subtract the declination value to your compass readings to obtain true bearings.
- Be Aware of Time and Location: Keep in mind that declination can change over time and varies by location.
- Utilize Tools: Utilize declination calculators, apps, or compass adjustment tools to ensure accurate declination values.
FAQs: True North vs. Magnetic North
1. What is the difference between true north and magnetic north?
True north is the geographical north pole, the point where the Earth’s axis of rotation intersects with the surface. Magnetic north is the point towards which a compass needle points, influenced by the Earth’s magnetic field.
2. Why is magnetic declination important for navigation?
Magnetic declination is the difference between true north and magnetic north. Accounting for this difference is crucial for obtaining accurate bearings and navigating effectively.
3. How do I find the declination value for my location?
You can find declination values on maps, compass roses, or using declination calculators and apps.
4. How do I adjust my compass readings for declination?
Add or subtract the declination value to your compass readings depending on whether magnetic north is east or west of true north.
5. Does magnetic declination change over time?
Yes, the Earth’s magnetic field constantly changes, causing magnetic declination to shift over time.
6. Can I use a GPS device to account for magnetic declination?
GPS devices provide accurate location information but do not necessarily account for magnetic declination. For activities reliant on compass readings, understanding declination is still essential.
7. What are the consequences of not accounting for magnetic declination?
Navigating without accounting for declination can lead to inaccurate bearings, resulting in misdirection and potentially dangerous situations.
Conclusion: Navigating with Accuracy
Understanding the difference between true north and magnetic north and the concept of magnetic declination is crucial for accurate navigation. By correctly accounting for declination, navigators ensure precise bearings and maintain the correct course. Whether you are using a compass for hiking, sailing, or orienteering, mastering the principles of true north and magnetic north will enhance your navigation skills and ensure safe and efficient journeys.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Earth: Understanding True North and Magnetic North. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!