Navigating the Eurozone: A Comprehensive Guide to the Economic Landscape of Europe
Related Articles: Navigating the Eurozone: A Comprehensive Guide to the Economic Landscape of Europe
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Eurozone: A Comprehensive Guide to the Economic Landscape of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Eurozone: A Comprehensive Guide to the Economic Landscape of Europe

The Eurozone, a dynamic economic entity, has profoundly shaped the European landscape since its inception in 1999. Comprising 20 member states, it represents a significant portion of the European Union (EU) and the global economy. Understanding the Eurozone’s geography, its evolution, and its impact is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the complex economic landscape of Europe.
A Visual Representation of Economic Integration
The Eurozone map serves as a powerful visual representation of the economic integration that has taken place in Europe. It highlights the member states that have adopted the euro as their official currency, signifying their commitment to a shared economic destiny. The map showcases a vibrant tapestry of nations, each with its unique history, culture, and economic strengths, united by a common currency and a commitment to economic stability.
The Eurozone: A Brief History
The genesis of the Eurozone can be traced back to the Maastricht Treaty of 1992, which laid the groundwork for the creation of the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). The treaty outlined the criteria for countries to adopt the euro, including stringent requirements for fiscal stability, inflation control, and convergence of interest rates.
The Eurozone officially launched on January 1, 1999, with 11 founding members. The introduction of the euro was a significant event, marking a paradigm shift in European economic cooperation. It aimed to eliminate exchange rate fluctuations, reduce transaction costs, and promote trade and investment within the Eurozone.
Expansion and Evolution
Since its inception, the Eurozone has witnessed several expansions, with new members joining the fold. The map has evolved over time, reflecting the changing dynamics of European integration. The most recent addition, Latvia, joined the Eurozone in 2014, bringing the total number of member states to 20.
The Benefits of the Eurozone
The Eurozone’s existence has brought numerous benefits to its member states, including:
- Economic Stability: The euro has contributed to price stability and reduced inflation across the Eurozone, creating a more predictable economic environment for businesses and consumers.
- Enhanced Trade: The elimination of exchange rate fluctuations has facilitated cross-border trade and investment within the Eurozone, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Increased Investment: The euro’s stability has attracted significant foreign investment into the Eurozone, boosting economic activity and job creation.
- Enhanced Financial Integration: The euro has fostered a deeper financial integration within the Eurozone, allowing for easier access to capital and promoting financial stability.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its achievements, the Eurozone faces significant challenges, including:
- Economic Divergence: The Eurozone’s member states have varying economic structures and growth rates, leading to economic imbalances and disparities.
- Fiscal Constraints: The Eurozone’s fiscal rules, designed to ensure fiscal stability, have been criticized for being too rigid, hindering the ability of member states to respond effectively to economic shocks.
- Political Tensions: The Eurozone has faced political tensions, particularly during the sovereign debt crisis, which threatened the integrity of the euro and the future of the Eurozone.
The Future of the Eurozone
Despite the challenges, the Eurozone remains a cornerstone of European integration. The future of the Eurozone will depend on its ability to address these challenges and continue to evolve and adapt to changing global economic conditions.
FAQs about the Eurozone Map
1. What is the purpose of the Eurozone map?
The Eurozone map visually represents the member states that have adopted the euro as their official currency. It provides a clear and concise overview of the geographic scope of the Eurozone.
2. How many countries are in the Eurozone?
As of 2023, there are 20 countries in the Eurozone.
3. What criteria must a country meet to join the Eurozone?
Countries must meet specific criteria related to fiscal stability, inflation, and convergence of interest rates to qualify for Eurozone membership.
4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of being in the Eurozone?
The advantages include price stability, enhanced trade, increased investment, and deeper financial integration. However, challenges include economic divergence, fiscal constraints, and political tensions.
5. Is the Eurozone a single currency area?
Yes, the Eurozone is a single currency area, meaning that all member states use the euro as their official currency.
Tips for Understanding the Eurozone Map
- Focus on the geographic location of member states: The map helps visualize the geographic distribution of Eurozone members, providing insights into the economic landscape of Europe.
- Consider the economic size and significance of member states: Analyze the relative economic size and importance of each member state within the Eurozone.
- Examine the historical context of Eurozone membership: Understand the reasons why specific countries have joined the Eurozone and the impact of their membership.
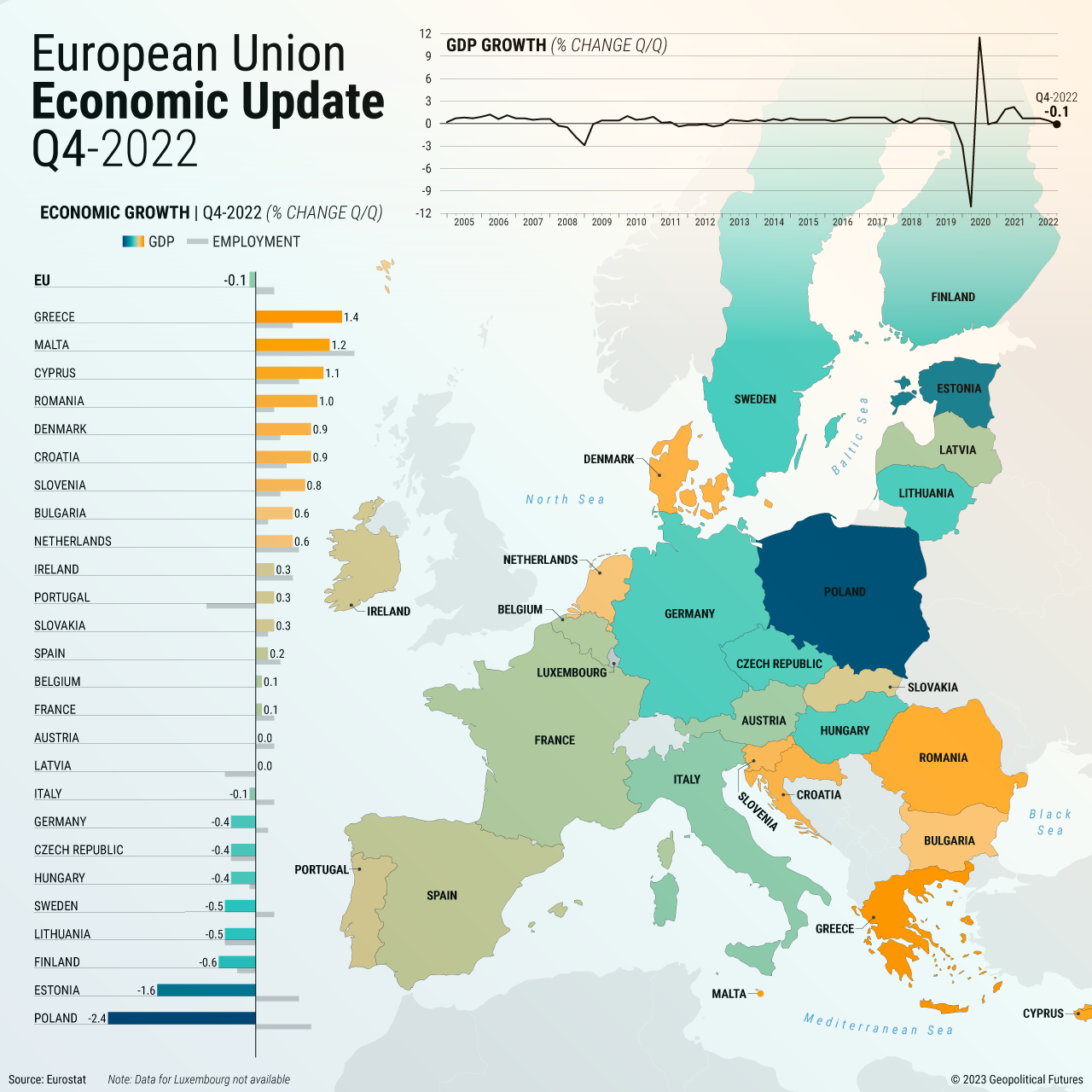
- Analyze the economic indicators of member states: Explore key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, to assess the economic performance of Eurozone members.
Conclusion
The Eurozone map serves as a vital tool for understanding the complex economic landscape of Europe. It provides a clear visual representation of the geographic scope of the Eurozone and its member states. By analyzing the map, one can gain insights into the economic integration of Europe, the benefits and challenges of the Eurozone, and the future prospects of this important economic entity. The Eurozone continues to evolve and adapt to changing global economic conditions, and its future will depend on its ability to address the challenges it faces and continue to foster economic stability and growth across its member states.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Eurozone: A Comprehensive Guide to the Economic Landscape of Europe. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!