Navigating the Sands of Time: A Journey Through Ancient Egypt’s Cities
Related Articles: Navigating the Sands of Time: A Journey Through Ancient Egypt’s Cities
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Sands of Time: A Journey Through Ancient Egypt’s Cities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Sands of Time: A Journey Through Ancient Egypt’s Cities
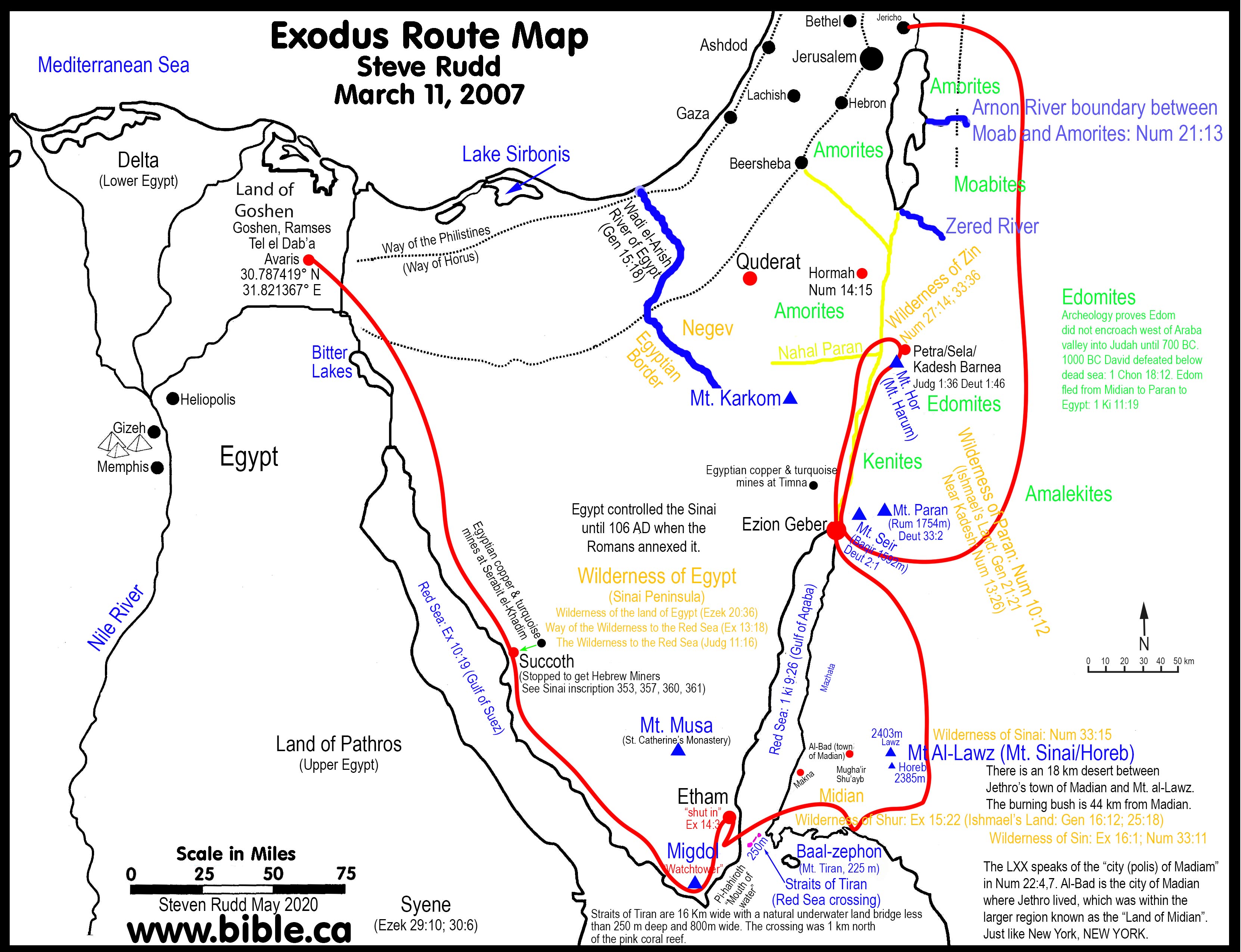
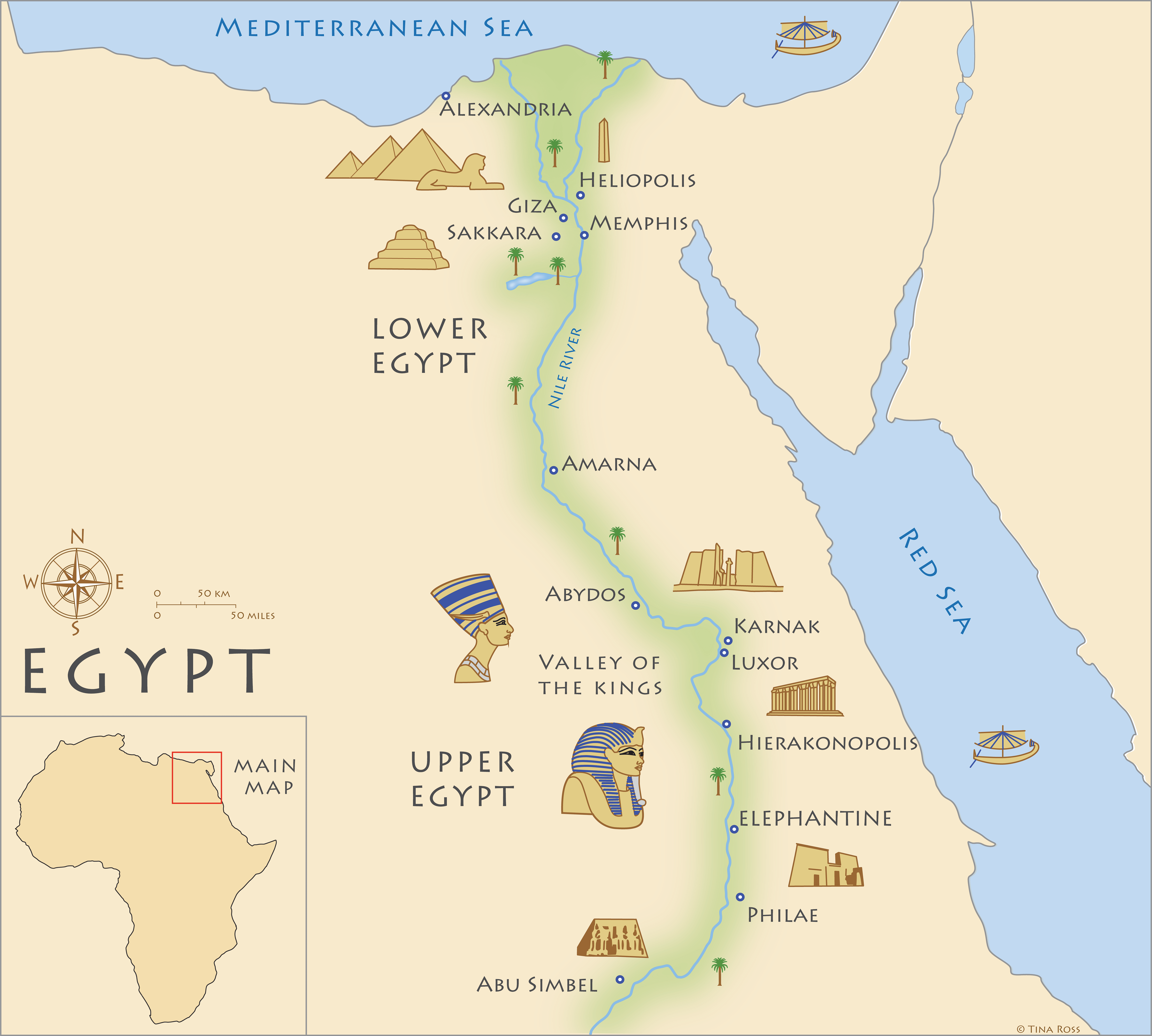
The ancient Egyptian civilization, renowned for its monumental architecture, intricate hieroglyphs, and enduring legacy, thrived across a vast expanse of the Nile Valley. This fertile strip of land, cradled by the world’s longest river, nurtured a complex network of cities that served as centers of political, economic, and religious power. Studying these cities, their layout, and their purpose provides invaluable insights into the daily lives, beliefs, and aspirations of the ancient Egyptians.
A Tapestry of Cities: Exploring the Urban Landscape
Ancient Egypt’s urban landscape was a dynamic and multifaceted entity. Cities emerged along the Nile’s banks, strategically positioned to maximize access to water, fertile land, and trade routes. The Nile’s annual inundation, while vital for agriculture, also posed challenges, necessitating sophisticated urban planning and flood control measures.
Key Cities and Their Significance:
-
Memphis (Men-nefer): Situated near the apex of the Nile Delta, Memphis served as the capital of ancient Egypt during the Old Kingdom (c. 2686-2181 BCE). Its strategic location facilitated trade and communication across the kingdom, solidifying its importance as a political and economic hub. The city was renowned for its magnificent temples, including the Temple of Ptah, the city’s patron deity, and the Temple of Apis, the sacred bull.
-
Thebes (Waset): As the capital of the New Kingdom (c. 1550-1070 BCE), Thebes (modern Luxor) rose to prominence as a religious and cultural center. The city boasted an impressive complex of temples, including the Temple of Karnak, one of the largest religious complexes ever built, and the Temple of Luxor, dedicated to the god Amun. The Valley of the Kings, located on the west bank of the Nile, served as the final resting place for pharaohs of the New Kingdom.
-
Alexandria: Founded by Alexander the Great in 332 BCE, Alexandria became a vibrant cosmopolitan center during the Ptolemaic Kingdom. It was a hub of trade, scholarship, and culture, renowned for its magnificent Library of Alexandria, considered one of the largest and most comprehensive libraries of the ancient world.
-
Abydos (Abedju): Situated in Upper Egypt, Abydos held immense religious significance as the burial place of the god Osiris, the god of the underworld. The city was also home to the Temple of Seti I, a stunning example of Egyptian temple architecture, and the Osireion, a subterranean complex dedicated to Osiris.
-
Saqqara (Sqr): Located near Memphis, Saqqara was a major necropolis where pharaohs and high officials were buried. The iconic Step Pyramid of Djoser, the first monumental stone pyramid, stands as a testament to the architectural ingenuity of the ancient Egyptians.
Urban Planning and Architectural Marvels
Ancient Egyptian cities were meticulously planned, reflecting a deep understanding of urban design and functionality. Cities were divided into distinct zones, each with specific functions. The central area typically housed the royal palace, administrative buildings, and temples. Residential areas were organized around the city center, often with access to canals and public spaces.
The architectural achievements of ancient Egypt are renowned worldwide. Monumental temples, towering pyramids, and intricate tombs showcase the mastery of stonework, engineering, and artistic expression. These structures served not only as places of worship and burial but also as symbols of power, wealth, and cultural identity.
Understanding the Importance of Ancient Egyptian Cities
The study of ancient Egyptian cities offers a unique window into the past, providing insights into:
-
Social Structure: The layout of cities, the location of public spaces, and the distribution of housing reveal the social hierarchy and the roles of different groups within society.
-
Economic Activities: The presence of markets, workshops, and trade routes sheds light on the economic activities that sustained the city and its inhabitants.
-
Religious Beliefs: The prominence of temples and the dedication of structures to specific deities highlight the importance of religion in ancient Egyptian life.
-
Political Power: The location and design of royal palaces and administrative buildings demonstrate the concentration of power and the mechanisms of governance.
FAQs
-
What were the primary sources of information about ancient Egyptian cities?
Archaeological evidence, including excavated ruins, inscriptions, and artifacts, provides invaluable insights into the layout, architecture, and daily life of ancient Egyptian cities. Historical texts, such as the writings of Herodotus and Strabo, offer valuable accounts of ancient cities, though they should be interpreted with caution as they often reflect the biases of the authors.
-
What challenges did ancient Egyptians face in urban planning?
The annual flooding of the Nile posed a significant challenge, requiring the development of sophisticated flood control measures to protect cities from inundation. Urban planning also had to account for the need for access to water, fertile land, and trade routes.
-
How did ancient Egyptian cities compare to other ancient urban centers?
Ancient Egyptian cities were characterized by their monumental architecture, their intricate planning, and their strong connection to religious beliefs. They differed from other ancient urban centers, such as those in Mesopotamia or Greece, in their emphasis on religious symbolism and their close relationship to the natural world.
Tips for Studying Ancient Egyptian Cities
-
Utilize Archaeological Resources: Explore online databases and publications from archaeological institutions to access information on excavated sites and artifacts.
-
Engage with Historical Texts: Read accounts of ancient historians and travelers to gain insights into the cities’ appearance, function, and cultural significance.
-
Visit Ancient Sites: If possible, visit ancient Egyptian cities to experience their grandeur firsthand and gain a deeper understanding of their history and significance.
Conclusion
The ancient Egyptian cities stand as enduring testaments to the ingenuity, artistry, and cultural achievements of a civilization that left an indelible mark on history. Through the study of these cities, we can glimpse the daily lives, beliefs, and aspirations of the ancient Egyptians, enriching our understanding of their complex and fascinating world. By exploring the urban landscape of ancient Egypt, we embark on a journey through time, connecting with the past and appreciating the enduring legacy of this extraordinary civilization.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Sands of Time: A Journey Through Ancient Egypt’s Cities. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!