Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States
Related Articles: Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States
- 3.1 Deciphering the Language of Weather Maps
- 3.2 The Importance of Weather Maps in Everyday Life
- 3.3 Navigating Weather Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States
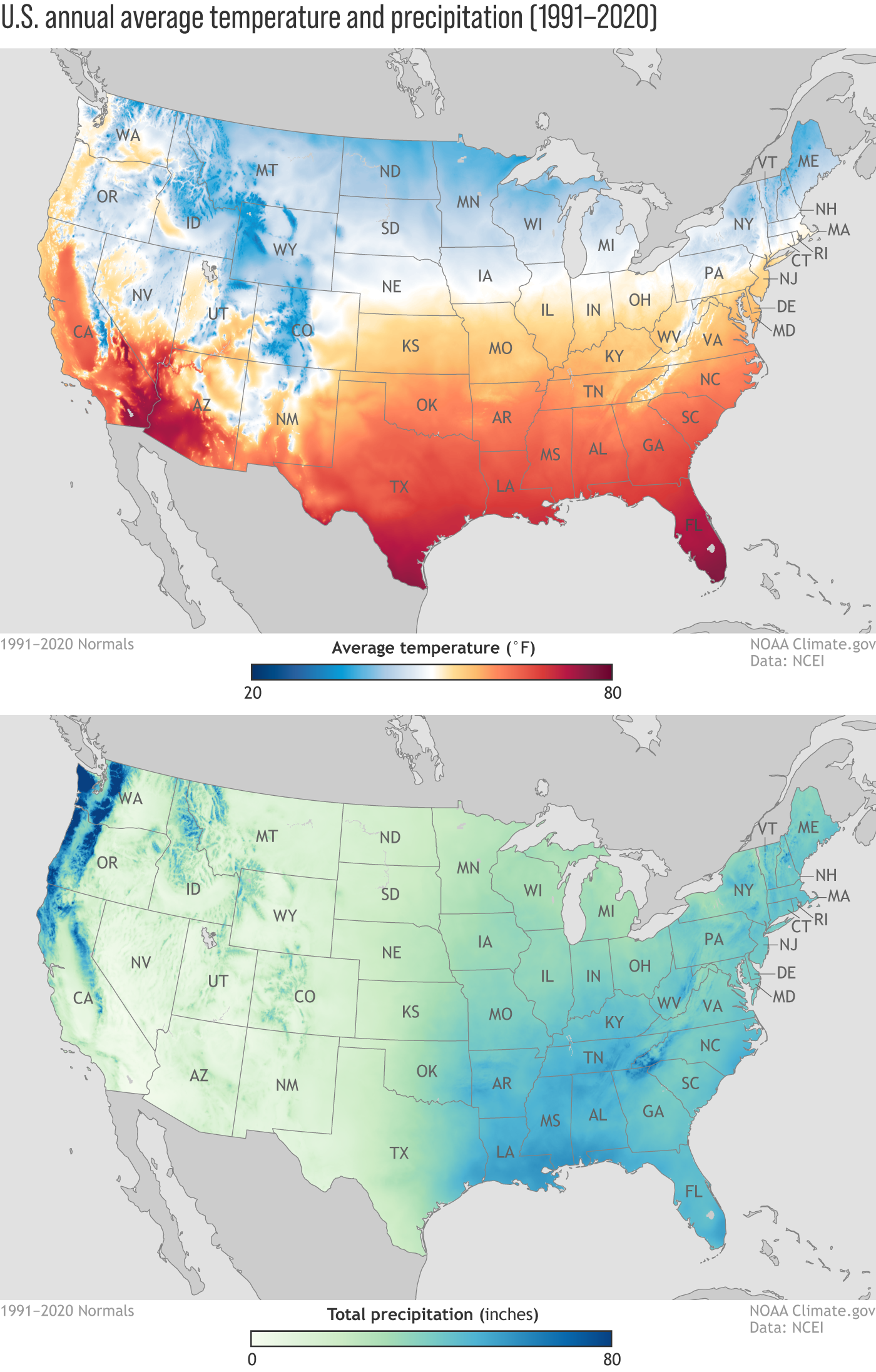
The United States, with its vast expanse and diverse climates, experiences a wide range of weather phenomena. From the arid deserts of the Southwest to the humid forests of the Southeast, understanding the weather patterns across the country is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, transportation, and public safety. Weather maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, serve as invaluable tools for visualizing and interpreting these patterns, providing insights into current conditions and forecasting future trends.
Deciphering the Language of Weather Maps
Weather maps, often referred to as synoptic charts, are visual representations of atmospheric conditions over a specific geographic area. They utilize a standardized system of symbols and lines to depict temperature, pressure, wind speed and direction, precipitation, and other meteorological variables.
Key Elements of a Weather Map:
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. Areas with closely spaced isobars indicate strong pressure gradients, which often correspond to areas of strong winds.
- Isotherms: Lines connecting points of equal temperature. These lines help visualize temperature variations across the map, highlighting thermal gradients and potential temperature inversions.
-
Fronts: Boundaries between different air masses, often marked by lines with symbols. Fronts represent areas of significant weather changes, including precipitation, wind shifts, and temperature fluctuations.
- Cold Front: A boundary where colder air is replacing warmer air. Cold fronts are typically associated with strong thunderstorms, gusty winds, and rapid temperature drops.
- Warm Front: A boundary where warmer air is replacing colder air. Warm fronts are generally associated with light to moderate precipitation, rising temperatures, and a decrease in wind speed.
- Stationary Front: A boundary where neither air mass is advancing. These fronts can produce persistent precipitation and cloudiness.
- Occluded Front: A complex front where a cold front overtakes a warm front. Occluded fronts are often associated with widespread precipitation and significant temperature changes.
- Symbols: Weather maps use various symbols to represent specific weather conditions, such as precipitation types (rain, snow, sleet, hail), cloud cover, visibility, and wind direction and speed.
The Importance of Weather Maps in Everyday Life
Weather maps are not just tools for meteorologists; they play a crucial role in shaping our daily lives.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather maps to monitor temperature, rainfall, and wind patterns, which directly impact crop yields. Accurate weather forecasts allow farmers to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting schedules.
- Transportation: Weather maps are essential for airlines, shipping companies, and road maintenance crews. They help predict potential disruptions caused by storms, fog, snow, or ice, enabling them to adjust routes, schedules, and safety measures accordingly.
- Public Safety: Weather maps are vital for emergency responders, helping them anticipate severe weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods. This information enables them to issue timely warnings, evacuate vulnerable areas, and prepare for potential disasters.
- Recreation: Outdoor enthusiasts, from hikers and campers to skiers and boaters, use weather maps to plan their activities and ensure their safety. Understanding weather patterns helps them choose appropriate clothing, equipment, and routes, minimizing the risk of exposure to hazardous conditions.
Navigating Weather Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding weather maps can seem daunting at first, but with a little practice, you can interpret the information they present. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the complexities of these visual tools:
- Identify the Date and Time: Weather maps are snapshots of atmospheric conditions at a specific point in time. Ensure you are looking at the most recent map to obtain accurate information.
- Locate Your Area of Interest: Find the specific location you are interested in on the map. This could be your city, state, or region.
- Examine the Isobars: Look for areas with closely spaced isobars, indicating strong pressure gradients and potential for strong winds.
- Observe the Fronts: Identify the locations of fronts and note their types (cold, warm, stationary, occluded). This will give you an idea of upcoming weather changes.
- Interpret the Symbols: Pay attention to the symbols used to represent precipitation, cloud cover, visibility, and wind direction and speed. These symbols provide valuable insights into current conditions.
- Read the Forecast: Most weather maps include a written forecast that summarizes the expected weather conditions for the next few hours or days. This information complements the visual representation and helps you understand the broader weather trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types of weather maps?
A: There are various types of weather maps, each focusing on different aspects of atmospheric conditions:
- Surface Maps: Depict weather conditions at the Earth’s surface, including temperature, pressure, wind, precipitation, and cloud cover.
- Upper-Air Maps: Show weather conditions at different altitudes, providing information about jet streams, temperature inversions, and other atmospheric features.
- Radar Maps: Utilize radar technology to visualize precipitation patterns and intensity, providing real-time updates on storms and rainfall.
- Satellite Maps: Capture images of the Earth’s surface from space, providing valuable insights into cloud cover, snow cover, and other weather-related features.
Q: How often are weather maps updated?
A: Weather maps are typically updated every few hours, depending on the source and the specific weather conditions. National weather agencies like the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States provide frequent updates to ensure the information is current and accurate.
Q: How can I access weather maps online?
A: Numerous online resources offer access to weather maps, including:
- National Weather Service (NWS): The NWS website provides a comprehensive collection of weather maps for the United States, including surface maps, radar maps, and satellite images.
- AccuWeather: A private weather forecasting company that offers interactive weather maps with detailed information on current conditions and forecasts.
- The Weather Channel: A popular weather news channel that provides online access to weather maps, radar images, and forecasts.
Q: What are some tips for interpreting weather maps effectively?
A: Here are some tips to help you make the most of weather maps:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Symbols: Spend time studying the symbols used on weather maps to understand their meaning.
- Practice Reading the Maps: Regularly consult weather maps and try to interpret the information they present.
- Compare Maps from Different Sources: Cross-reference information from multiple sources to get a more comprehensive view of the weather patterns.
- Look for Trends: Observe how weather patterns evolve over time by comparing maps from different days or hours.
- Consult with a Meteorologist: If you have specific questions or need expert interpretation, reach out to a professional meteorologist.
Conclusion
Weather maps are indispensable tools for understanding and predicting the weather patterns that influence our lives. By comprehending the language of these maps, we can gain valuable insights into current conditions, anticipate future changes, and make informed decisions about our activities. From farmers planning their crops to pilots navigating flights, weather maps play a crucial role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and informed decision-making across diverse sectors. As technology continues to advance, weather maps will become even more sophisticated, providing increasingly accurate and detailed information to help us navigate the unpredictable world of weather.





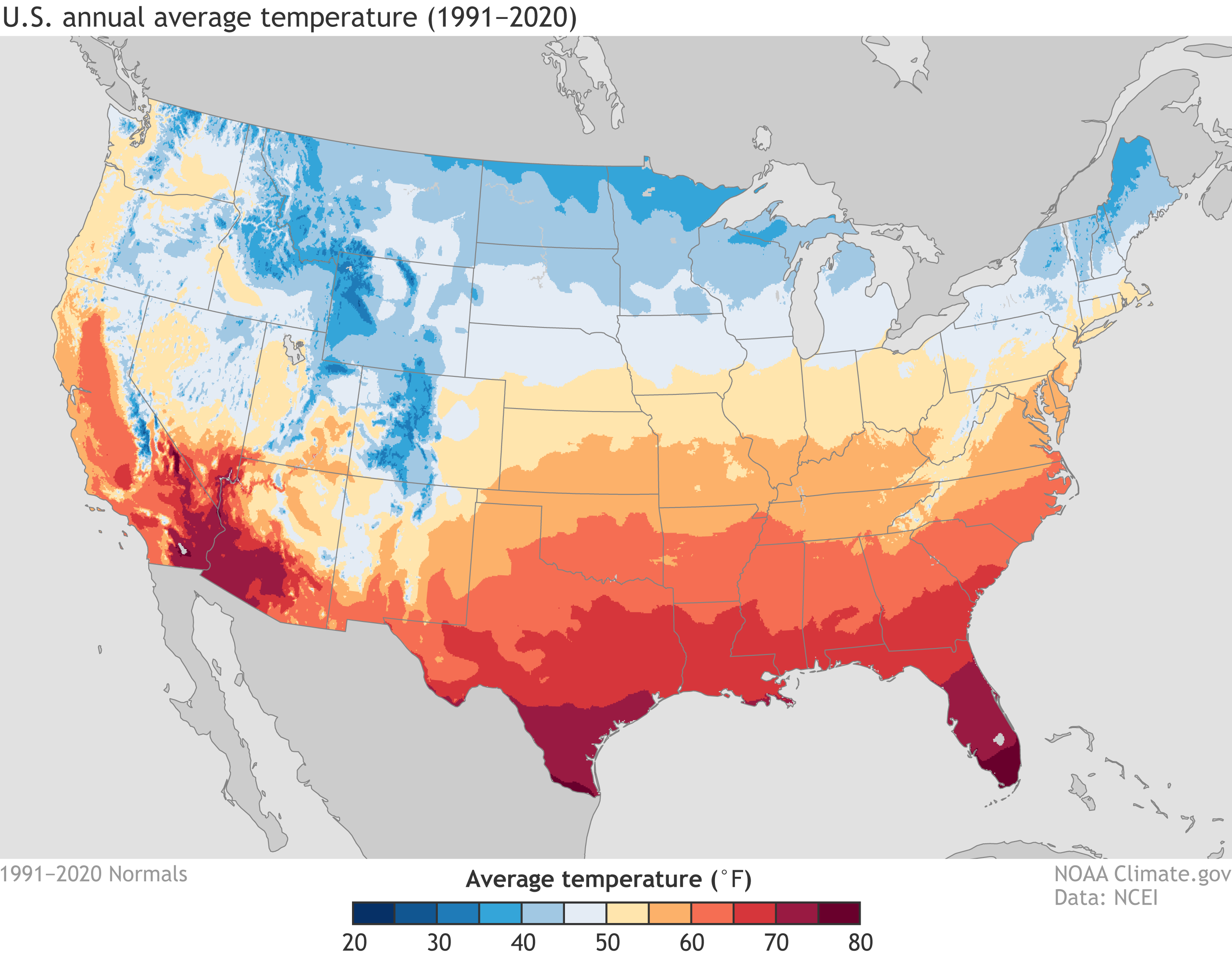

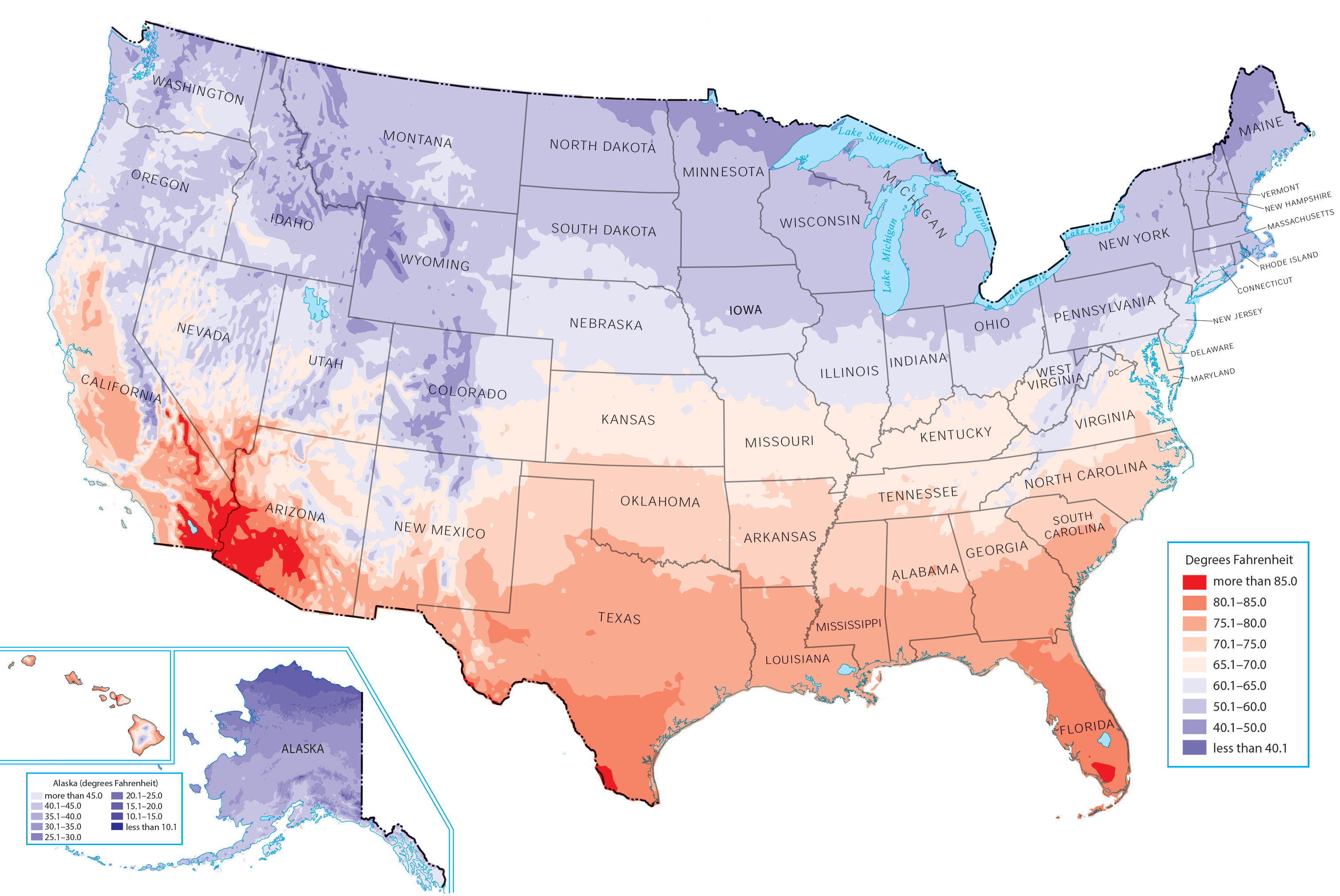
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Weather Maps Across the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!