The Complexities of Palestine’s Representation on Maps
Related Articles: The Complexities of Palestine’s Representation on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Complexities of Palestine’s Representation on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complexities of Palestine’s Representation on Maps

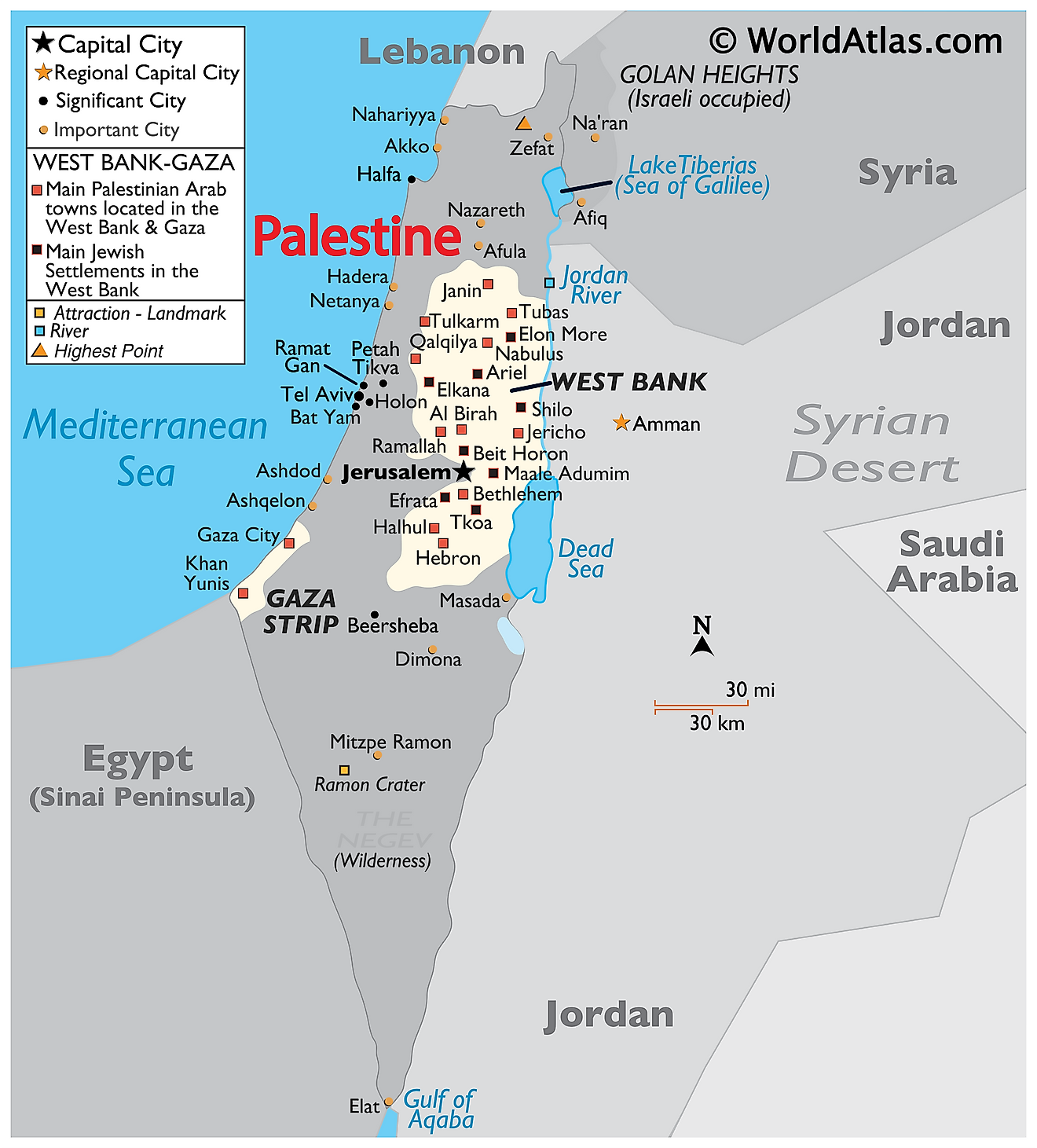
The question of why Palestine is not prominently featured on many maps is a complex one, interwoven with historical, political, and geographical factors. While the absence of Palestine from certain maps might appear straightforward, it is, in reality, a reflection of a deeply contested and multifaceted situation.
Historical Context:
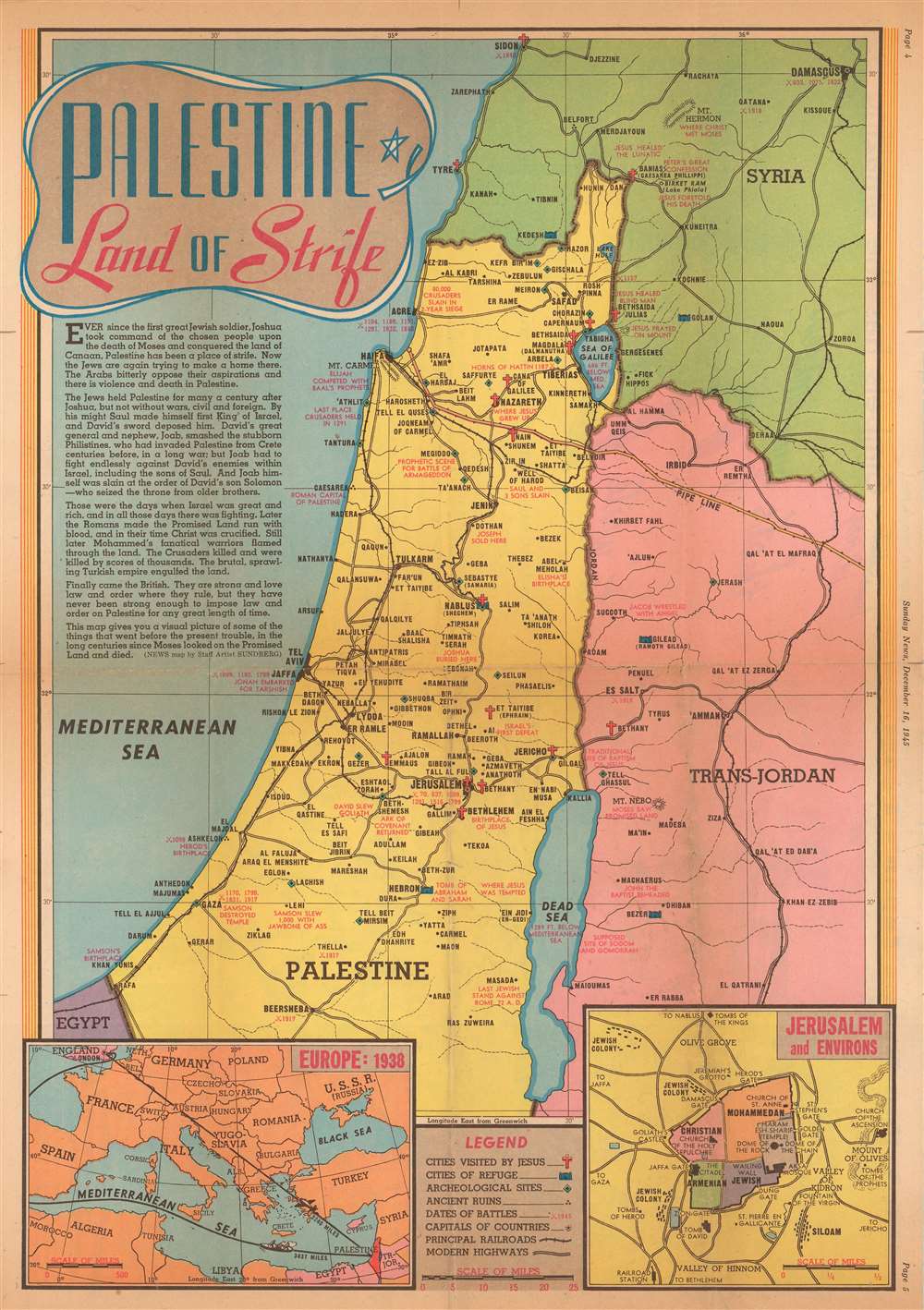
The historical narrative surrounding Palestine is crucial to understanding its current representation on maps. The region has been a focal point of various empires and civilizations throughout history, with its borders and identities fluctuating over time. Following World War I, the Ottoman Empire, which had ruled the region for centuries, was dissolved, and the British Mandate for Palestine was established. This period saw the emergence of competing claims to the land, primarily between Jewish and Arab populations.
The 1947 Partition Plan and Its Aftermath:
In 1947, the United Nations proposed a partition plan dividing the British Mandate for Palestine into two states: one Jewish and one Arab. This plan was accepted by the Jewish leadership but rejected by the Arab leadership, leading to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. This war resulted in the establishment of the State of Israel and the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, a situation known as the "Nakba" ("catastrophe").
The Palestinian Territories:
Following the 1967 Six-Day War, Israel occupied the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem. These territories are currently under Israeli control, though they are recognized by the international community as Palestinian territories. The lack of a formal independent Palestinian state, coupled with the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, has led to a complex and often contested political landscape.
International Recognition and Statehood:
While Palestine has been recognized by over 130 countries as a state, it has not yet been granted full membership in the United Nations. This lack of formal recognition, coupled with the ongoing conflict, contributes to the absence of Palestine as a clearly defined state on many maps.
The Impact of Political and Geographical Factors:
The absence of Palestine on maps is often a reflection of political positions and biases. Some maps, particularly those produced in Israel or countries with close ties to Israel, may omit Palestine or depict it as a disputed territory. Conversely, maps produced by Palestinian organizations or those sympathetic to the Palestinian cause may depict Palestine as a fully independent state.
The Importance of Accurate and Inclusive Mapping:
The representation of Palestine on maps is not merely a technical issue but a matter of historical accuracy, political sensitivity, and ethical responsibility. Maps are powerful tools that shape our understanding of the world and influence our perceptions of political realities. An accurate and inclusive representation of Palestine on maps is crucial for promoting understanding, fostering dialogue, and acknowledging the Palestinian narrative.
Addressing the Question: Why is Palestine Not on the Map?
The question of why Palestine is not on the map is not a simple one. It is a reflection of a complex historical, political, and geographical reality. It is crucial to understand the historical context, the ongoing conflict, and the lack of a formally recognized Palestinian state. While the absence of Palestine from certain maps may appear straightforward, it is in fact a complex issue that requires nuanced understanding and critical analysis.
FAQs:
1. Why is Palestine not recognized as a state by all countries?
The international recognition of Palestine as a state is a contentious issue. While over 130 countries have recognized Palestine, others, particularly close allies of Israel, have not. This lack of universal recognition is largely due to the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the differing perspectives on the status of the Palestinian territories.
2. What are the main obstacles to the establishment of a Palestinian state?
The establishment of a Palestinian state is a complex and multifaceted issue. The main obstacles include the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the lack of a negotiated settlement on key issues such as borders, Jerusalem, and settlements, and the continued Israeli control over the Palestinian territories.
3. How can the representation of Palestine on maps be improved?
Improving the representation of Palestine on maps requires a multifaceted approach. It involves promoting awareness of the historical and political context, encouraging the use of accurate and inclusive maps, and advocating for the recognition of Palestine as a state. It also requires engaging in critical analysis of the maps we use and understanding the biases and perspectives they reflect.
4. What are the consequences of omitting Palestine from maps?
Omitting Palestine from maps can perpetuate a distorted understanding of the region, reinforcing the narrative that Palestine is not a legitimate entity. It can also contribute to the marginalization and erasure of the Palestinian narrative, hindering the pursuit of a peaceful and just resolution to the conflict.
Tips for Understanding the Representation of Palestine on Maps:
- Be critical of the maps you encounter. Consider the source, the purpose, and the biases that may be present.
- Research different perspectives on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Understand the historical context, the competing claims, and the complexities of the situation.
- Support organizations that promote accurate and inclusive mapping. Engage in discussions about the importance of representation and the need for fair and unbiased portrayals of the region.
- Advocate for the recognition of Palestine as a state. Encourage your representatives to support international efforts towards a peaceful and just resolution to the conflict.
Conclusion:
The question of why Palestine is not on the map is a complex one that reflects a multitude of historical, political, and geographical factors. The absence of Palestine from certain maps is not a simple oversight but a reflection of a contested and multifaceted reality. Understanding the historical context, the ongoing conflict, and the lack of a formally recognized Palestinian state is crucial for interpreting the representation of Palestine on maps. By engaging in critical analysis, promoting accurate and inclusive mapping, and advocating for the recognition of Palestine, we can contribute to a more just and equitable representation of the region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complexities of Palestine’s Representation on Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!