The Continental Divide: A Backbone of American Geography
Related Articles: The Continental Divide: A Backbone of American Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Continental Divide: A Backbone of American Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Continental Divide: A Backbone of American Geography

The Continental Divide, a prominent geographical feature traversing the North American continent, plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape and influencing the flow of water across vast regions. This article delves into the intricate details of the Continental Divide in the United States, exploring its formation, significance, and the various ways it impacts the environment and human life.
A Geological Tapestry: Understanding the Formation
The Continental Divide’s origins lie deep within the Earth’s geological history. The dramatic uplift of the Rocky Mountains, initiated millions of years ago, created a formidable barrier, effectively separating the watersheds of the continent. This geological event led to the formation of the Continental Divide, a line of high elevation that serves as the boundary between drainage basins.
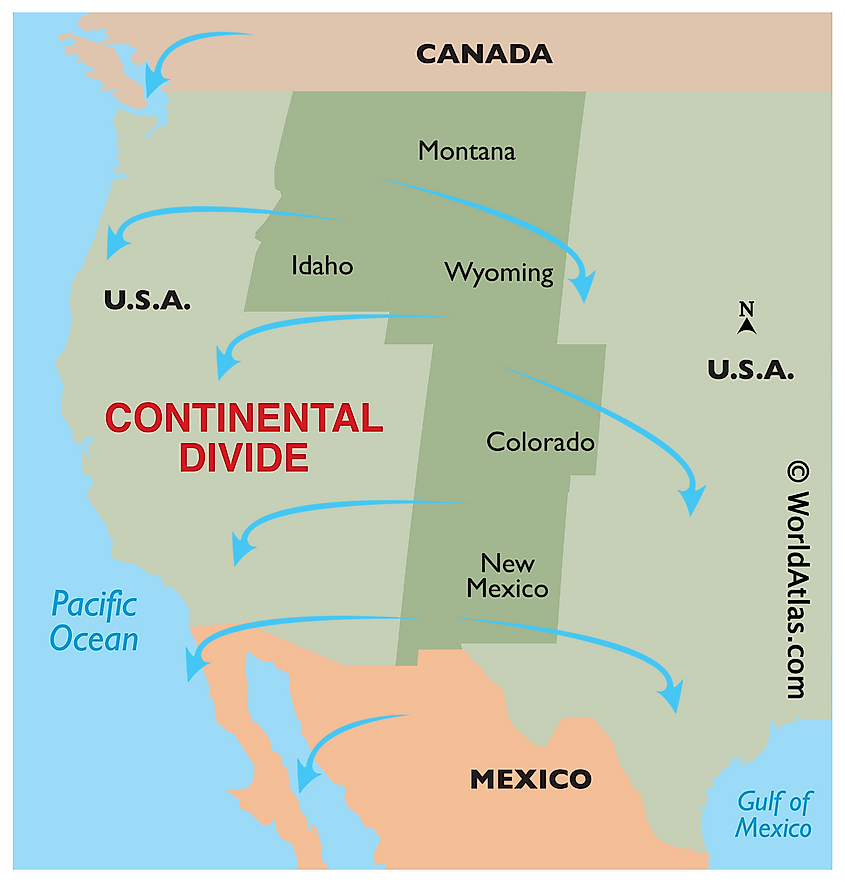
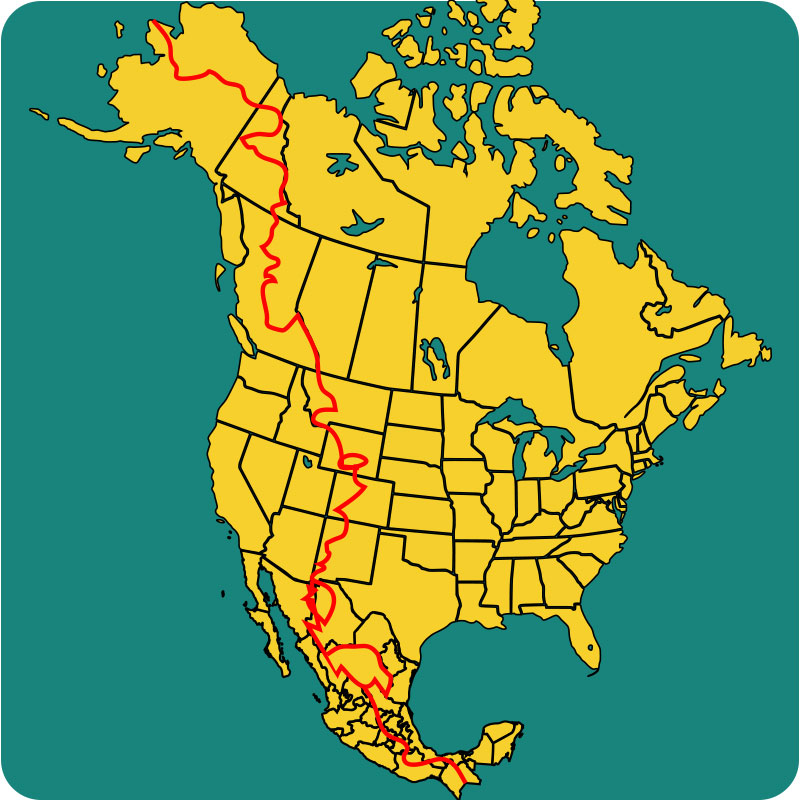
The Divide, often referred to as the "Great Divide," is not a single, continuous line but rather a series of mountain ranges and high points, each contributing to its overall structure. It stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north, meandering through the western United States and into Mexico, finally terminating in the Gulf of California.
A Divide in the Landscape: Defining Watersheds
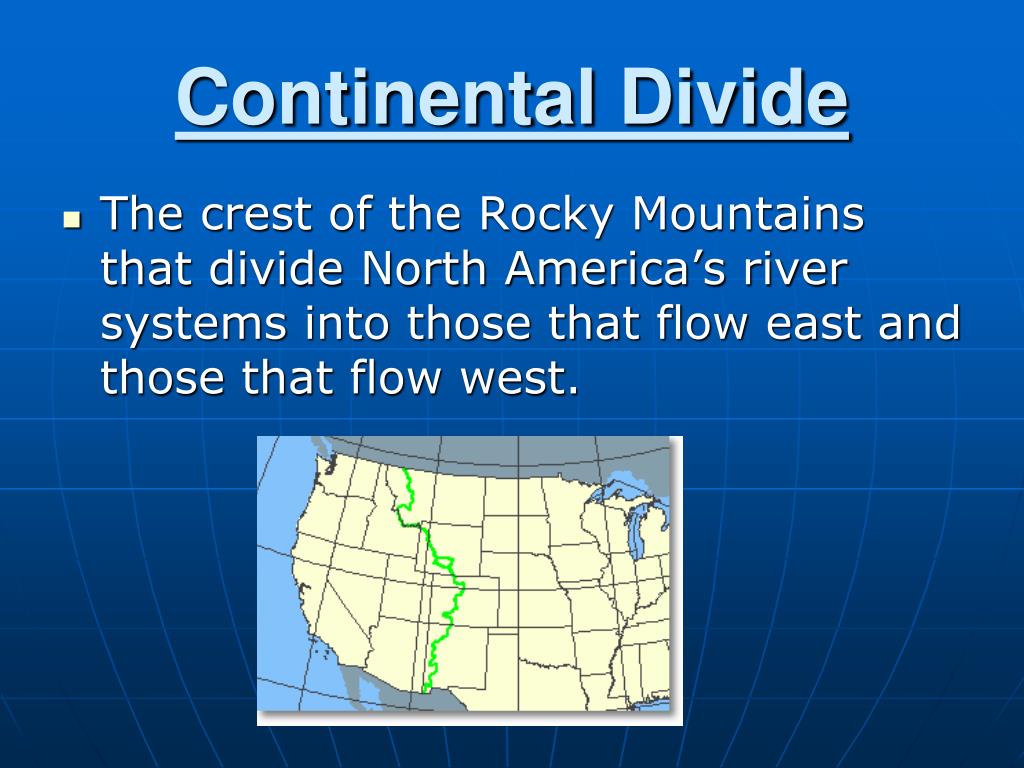
The Continental Divide’s primary function is to direct the flow of water. It acts as a geographical separator, guiding precipitation towards either the Atlantic Ocean or the Pacific Ocean. Water falling on the eastern side of the Divide flows eastward, eventually joining the Mississippi River and emptying into the Atlantic. Conversely, precipitation on the western side flows westward, feeding into rivers like the Colorado, Columbia, and Sacramento, ultimately reaching the Pacific Ocean.
This division of water flow has significant implications for the ecosystems and human settlements across the continent. It influences the distribution of plant and animal life, shapes the flow of rivers and streams, and impacts the availability of water resources for various human activities, including agriculture, industry, and domestic use.
The Continental Divide: More Than Just Water
Beyond its role in water management, the Continental Divide also plays a vital role in shaping the landscape and influencing the climate of the western United States. Its towering peaks and rugged terrain create a diverse range of ecosystems, supporting a rich tapestry of flora and fauna.
The elevation of the Divide creates a "rain shadow" effect, where the western slopes receive more rainfall than the eastern slopes. This difference in precipitation contributes to the unique characteristics of the various ecosystems found on either side of the Divide.
Exploring the Continental Divide: A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes
Traveling along the Continental Divide offers a unique and unforgettable experience. From the snow-capped peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the arid deserts of the Southwest, the Divide traverses a variety of landscapes, each with its distinct beauty and ecological significance.
The Rocky Mountains: The Continental Divide runs through the heart of the Rocky Mountains, where towering peaks, alpine meadows, and pristine forests create a breathtaking vista. This region is home to a wide array of wildlife, including elk, deer, bears, and mountain lions.
The Great Basin: As the Divide moves westward, it traverses the Great Basin, a region characterized by arid landscapes, salt flats, and isolated mountain ranges. The Great Basin is known for its unique flora and fauna, adapted to survive in harsh conditions.
The Sierra Nevada: The Continental Divide intersects with the Sierra Nevada mountain range, home to towering granite peaks, deep canyons, and giant sequoia trees. This region is a popular destination for outdoor recreation, offering opportunities for hiking, camping, and skiing.
The Continental Divide Trail: A Path of Discovery
For outdoor enthusiasts seeking a challenging and rewarding journey, the Continental Divide Trail (CDT) offers a unique opportunity to traverse the entire length of the Divide. Spanning over 3,100 miles, the CDT winds through rugged terrain, offering breathtaking views, diverse wildlife encounters, and a profound connection to the natural world.
The Importance of the Continental Divide: A Lifeline for Life
The Continental Divide’s significance extends far beyond its geographical boundaries. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and stability of ecosystems, providing essential resources for human communities, and shaping the character of the American West.
Protecting the Continental Divide: A Shared Responsibility
The Continental Divide faces various threats, including climate change, habitat fragmentation, and overuse. Conservation efforts are essential to protect this vital ecological resource and ensure its continued role in supporting life and shaping the landscape.
FAQs about the Continental Divide
Q: What is the Continental Divide, and where is it located?
A: The Continental Divide is a line of high elevation that separates the watersheds of North America, directing water flow towards either the Atlantic or Pacific Oceans. It traverses the western United States, stretching from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Gulf of California in the south.
Q: What is the significance of the Continental Divide?
A: The Continental Divide is a crucial geographical feature that shapes the landscape, influences water flow, and supports diverse ecosystems. It also plays a vital role in the availability of water resources for human communities.
Q: How does the Continental Divide impact the environment?
A: The Continental Divide influences precipitation patterns, creates distinct ecosystems, and supports a wide variety of plant and animal life. It also shapes the flow of rivers and streams, impacting water availability and the distribution of aquatic species.
Q: What are some threats to the Continental Divide?
A: Threats to the Continental Divide include climate change, habitat fragmentation, overuse, and pollution. These factors can disrupt ecosystems, reduce water availability, and impact the overall health of the Divide.
Q: What can be done to protect the Continental Divide?
A: Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the Continental Divide, including reducing human impact, promoting sustainable practices, and addressing climate change. Public awareness and engagement are vital to ensure the long-term health and stability of this vital resource.
Tips for Exploring the Continental Divide
- Plan your trip carefully: Research the area you plan to visit, consider the time of year, and be prepared for varying weather conditions.
- Respect the environment: Pack out all trash, stay on designated trails, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Be aware of potential hazards: Altitude sickness, wildlife encounters, and extreme weather conditions are all potential risks.
- Learn about the local ecosystem: Educate yourself about the plants, animals, and ecological processes that contribute to the unique character of the Divide.
- Support conservation efforts: Consider donating to organizations dedicated to protecting the Continental Divide and its surrounding ecosystems.
Conclusion
The Continental Divide stands as a testament to the dynamic forces that shape our planet. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of nature, highlighting the importance of protecting our natural resources for future generations. Understanding the Continental Divide’s significance and the threats it faces is crucial for ensuring its continued role in supporting life and shaping the landscape of the American West.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Continental Divide: A Backbone of American Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!