The Middle East: A Geopolitical Landscape Shaped by Oil
Related Articles: The Middle East: A Geopolitical Landscape Shaped by Oil
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Middle East: A Geopolitical Landscape Shaped by Oil. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Middle East: A Geopolitical Landscape Shaped by Oil
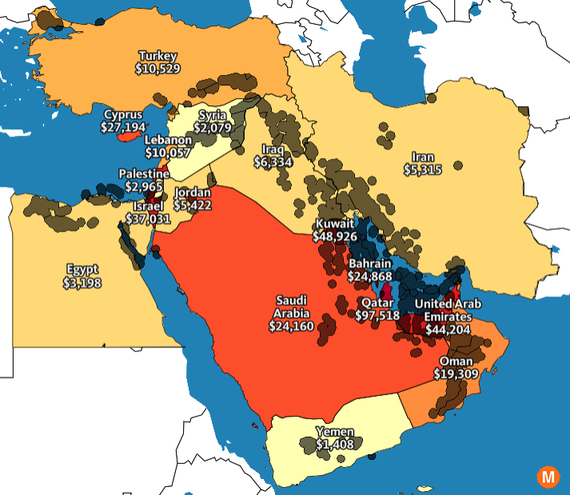
The Middle East, a region rich in history and culture, holds a unique position on the global stage due to its vast reserves of oil. This vital resource has profoundly shaped the region’s political landscape, economic development, and international relations. Understanding the Middle East’s oil map is crucial for comprehending the region’s dynamics and its impact on the world.
A Region Rich in Black Gold:
The Middle East boasts the world’s largest proven oil reserves, accounting for over half of global reserves. This concentration of oil wealth has made the region a focal point for global energy security, attracting international attention and investment. While oil reserves are distributed across various countries, certain nations stand out as significant producers:
- Saudi Arabia: The undisputed leader in oil production, Saudi Arabia holds the world’s largest proven oil reserves, estimated at over 290 billion barrels. The country plays a pivotal role in stabilizing global oil markets and influencing oil prices.
- Iran: With the world’s fourth-largest proven oil reserves, Iran holds significant potential for oil production. However, its oil industry has faced challenges due to international sanctions and internal political complexities.
- Iraq: Possessing the world’s fifth-largest proven oil reserves, Iraq has experienced a resurgence in oil production after years of conflict and instability.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): The UAE, a federation of seven emirates, holds the world’s seventh-largest proven oil reserves and is a major oil exporter.
- Kuwait: Kuwait holds the world’s eighth-largest proven oil reserves and is a significant oil producer, contributing significantly to global oil supply.
- Qatar: While not a major oil producer compared to its neighbors, Qatar holds significant natural gas reserves, making it a key player in the global energy market.
The Geopolitical Implications of Oil:
The vast oil reserves in the Middle East have had a profound impact on the region’s geopolitics. Here are some key implications:
- Economic Development: Oil revenues have fueled economic growth and development in many Middle Eastern countries. However, this dependence on oil has also created vulnerabilities, making economies susceptible to fluctuations in oil prices.
- Political Stability: Control over oil resources has been a source of political power and influence in the region. Conflicts over oil resources have been a recurring theme in the Middle East’s history, contributing to instability and tensions.
- International Relations: The Middle East’s oil reserves have drawn significant international interest, particularly from major energy consumers like the United States, China, and Europe. This has led to complex relationships and geopolitical maneuvering, often involving alliances and rivalries.
- Regional Dynamics: The concentration of oil wealth has created disparities between oil-rich and oil-poor countries in the region, leading to economic and political tensions.
The Future of Middle Eastern Oil:
The future of the Middle East’s oil industry is uncertain. While the region remains a dominant player in global oil production, several factors are shaping its future:
- Declining Oil Production: Many Middle Eastern countries are facing declining oil production due to aging oil fields and limited investment in new exploration.
- Renewable Energy Transition: The global shift towards renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, presents a challenge to the future of fossil fuels, including oil.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements, such as fracking and deep-sea drilling, have increased global oil supply, potentially reducing the dependence on Middle Eastern oil.
- Political Instability: Ongoing conflicts and political instability in the region pose a significant threat to oil production and infrastructure, creating supply disruptions and price volatility.
The Importance of the Middle East Oil Map:
Understanding the Middle East’s oil map is crucial for several reasons:
- Global Energy Security: The region’s oil reserves are vital for maintaining global energy security, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of oil to meet global demand.
- Economic Stability: Oil production and exports are major drivers of economic activity in the region, impacting global economic stability and financial markets.
- International Relations: The Middle East’s oil reserves are a significant factor in shaping international relations, influencing alliances, trade agreements, and geopolitical strategies.
- Climate Change: The future of oil production in the Middle East is intertwined with the global response to climate change, as the transition to renewable energy sources gains momentum.
FAQs:
- What are the largest oil reserves in the Middle East?
Saudi Arabia holds the world’s largest proven oil reserves, followed by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and the UAE.
- How does oil production in the Middle East impact global prices?
The Middle East’s oil production significantly influences global oil prices. Changes in production levels, political instability, and supply disruptions can lead to price fluctuations.
- What are the challenges facing the Middle East’s oil industry?
The Middle East’s oil industry faces challenges such as declining production, the global shift towards renewable energy, technological advancements, and political instability.
- How is the Middle East’s oil industry adapting to the global energy transition?
Some Middle Eastern countries are investing in renewable energy sources and diversifying their economies to reduce dependence on oil. However, the transition is complex and faces significant challenges.
Tips:
- Stay informed about global oil markets and trends.
- Follow developments in renewable energy technologies.
- Understand the geopolitical dynamics of the Middle East.
- Consider the potential impact of climate change on the region’s oil industry.
Conclusion:
The Middle East’s oil map is a dynamic and complex landscape with significant implications for global energy security, economic stability, and international relations. The region’s vast oil reserves have shaped its history, politics, and economy, but the future of its oil industry is uncertain. As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources and faces the challenges of climate change, the Middle East’s oil map will continue to evolve, requiring careful monitoring and analysis.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Middle East: A Geopolitical Landscape Shaped by Oil. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!