The South Pole: A Geographic Extremes and a Scientific Hub
Related Articles: The South Pole: A Geographic Extremes and a Scientific Hub
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The South Pole: A Geographic Extremes and a Scientific Hub. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The South Pole: A Geographic Extremes and a Scientific Hub

The South Pole, the southernmost point on Earth, holds a unique position in our understanding of the planet. It is a location of extreme cold, perpetual darkness and light, and vast, icy landscapes. While its geographic location is relatively straightforward, its significance transcends mere coordinates, playing a vital role in scientific research and understanding Earth’s climate.
The South Pole’s Geographic Location
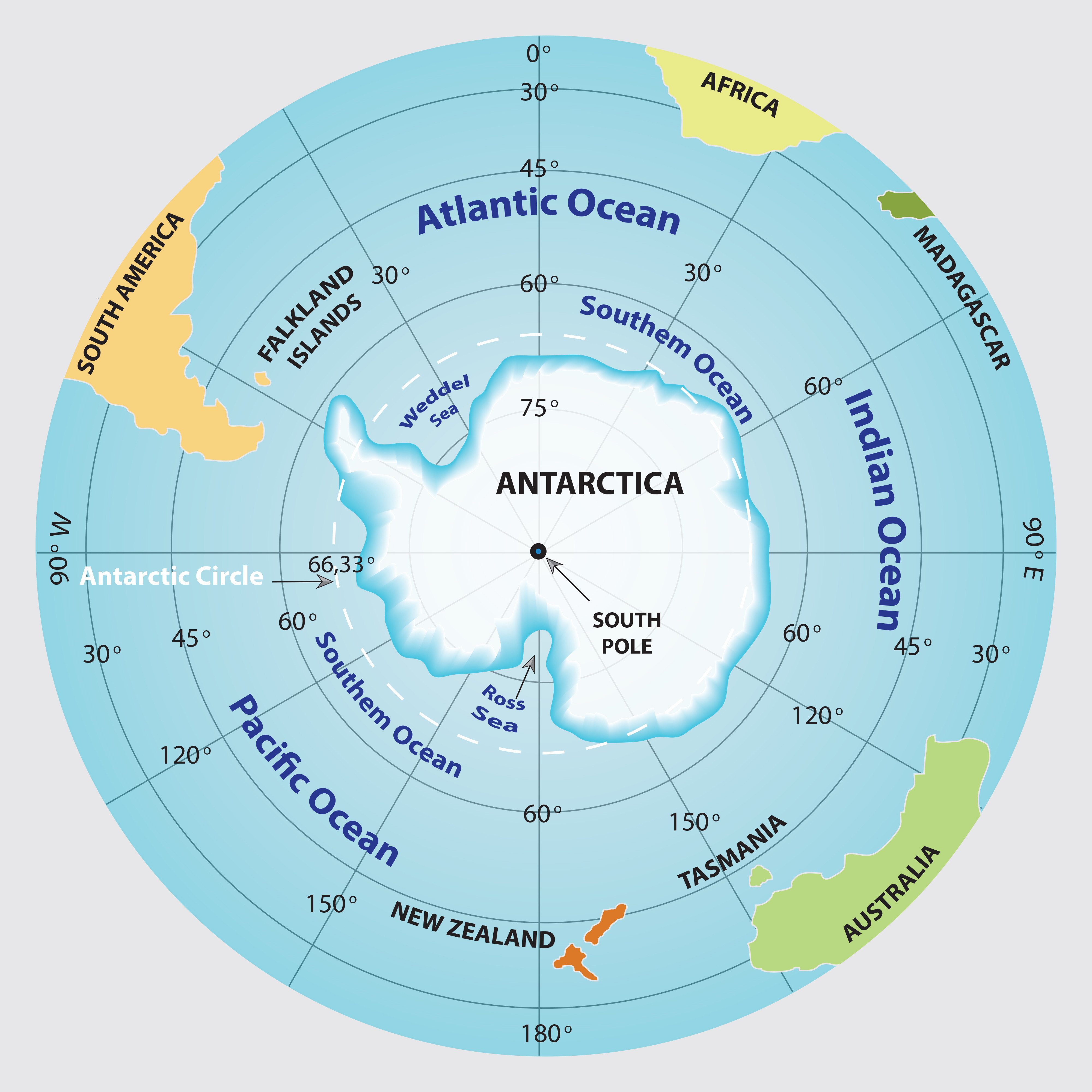
The South Pole is situated at the southern end of the Earth’s axis of rotation. This means it is the point furthest from the Equator, directly opposite the North Pole. On a map, it is typically represented as a point at the bottom of the globe, often marked with a red star or a specific symbol.
Understanding Latitude and Longitude
To accurately pinpoint the South Pole’s location, we use the geographic coordinate system of latitude and longitude.
- Latitude: Measured in degrees north or south of the Equator, the South Pole has a latitude of 90° South. This makes it the southernmost point on Earth, with all other locations having a latitude of less than 90° South.
- Longitude: Measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, the South Pole has no specific longitude. This is because all lines of longitude converge at the poles.
The South Pole’s Unique Characteristics
The South Pole’s geographic location gives rise to a number of unique characteristics:
- Extreme Cold: The South Pole experiences temperatures that can plummet to -80°C (-112°F) or lower during the winter. This extreme cold is due to the angle of the sun’s rays and the absence of direct sunlight for several months.
- Perpetual Darkness and Light: Due to the Earth’s tilt, the South Pole experiences six months of continuous daylight during the summer solstice and six months of continuous darkness during the winter solstice. This phenomenon is known as polar night and polar day.
- Vast Icy Landscape: The South Pole is located in the middle of Antarctica, a continent covered in a thick ice sheet that averages 2,133 meters (7,000 feet) thick. This ice sheet holds about 70% of the world’s freshwater.
The South Pole’s Scientific Importance
The South Pole is not just a point on a map; it is a critical location for scientific research. The unique environment provides valuable insights into:
- Climate Change: The South Pole’s ice sheet acts as a giant climate archive, preserving information about past climate conditions. Studying ice cores extracted from the ice sheet allows scientists to reconstruct past temperatures, greenhouse gas concentrations, and other climate variables, providing valuable data for understanding climate change.
- Atmospheric Research: The South Pole’s remote location and clean air make it an ideal place to study the atmosphere. Scientists use instruments at the South Pole to monitor atmospheric composition, ozone levels, and other atmospheric parameters, contributing to our understanding of global atmospheric processes.
- Astronomy: The South Pole offers an exceptional view of the southern sky, providing a unique vantage point for astronomical observations. Telescopes at the South Pole are used to study distant galaxies, the cosmic microwave background radiation, and other celestial objects.
The South Pole’s Role in Global Navigation
While the South Pole itself is not directly used for navigation, it plays an important role in defining the Earth’s coordinate system. The South Pole, along with the North Pole, serves as a reference point for latitude and longitude, making it fundamental to global navigation systems like GPS.
FAQs about the South Pole’s Location
Q: Is the South Pole a country?
A: No, the South Pole is not a country. It is a geographical location within the continent of Antarctica, which is governed by an international treaty.
Q: Can I visit the South Pole?
A: Yes, it is possible to visit the South Pole, but it requires extensive planning and preparation. Tourist trips to the South Pole are typically organized by specialized tour companies, and they involve flying in from nearby research stations or using specialized ice-breaking ships.
Q: What is the time zone at the South Pole?
A: The South Pole does not have a specific time zone. Researchers at the South Pole typically use the time zone of their home country or the time zone of the nearest research station.
Q: Are there any permanent residents at the South Pole?
A: No, there are no permanent residents at the South Pole. It is a research station, and the population fluctuates depending on the research activities being conducted.
Tips for Understanding the South Pole’s Location
- Use a Globe: A globe provides a more accurate representation of the Earth’s shape and the South Pole’s location compared to a flat map.
- Study Latitude and Longitude: Understanding how latitude and longitude are used to locate points on Earth is crucial for comprehending the South Pole’s geographic position.
- Visualize the Earth’s Rotation: Consider how the Earth rotates on its axis, with the South Pole at the southern end of the axis, to visualize the South Pole’s unique position.
- Explore Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including interactive maps and websites dedicated to Antarctica, can provide more detailed information about the South Pole’s location and its significance.
Conclusion
The South Pole, though a seemingly remote and desolate point on a map, holds immense scientific and geographic significance. Its extreme environment serves as a natural laboratory for studying climate change, atmospheric processes, and the cosmos. Its location at the southernmost point on Earth defines our understanding of latitude and longitude, impacting global navigation systems. Understanding the South Pole’s location and its role in scientific research is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet and the importance of preserving this unique and valuable location.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The South Pole: A Geographic Extremes and a Scientific Hub. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!