Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California
Related Articles: Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California
- 3.1 The Calaveras Fault: A Closer Look
- 3.2 Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Deeper Dive
- 3.3 Calaveras Fault: Implications for California
- 4 FAQs about the Calaveras Fault
- 5 Tips for Living Near the Calaveras Fault
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Closure
Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California
The Calaveras Fault, a prominent geological feature traversing the heart of California, plays a crucial role in shaping the state’s landscape and influencing its seismic activity. This fault, a significant component of the San Andreas Fault system, has a long history of movement, leaving behind a visible imprint on the terrain and impacting the lives of millions of Californians. This article delves into the complexities of the Calaveras Fault, providing a comprehensive overview of its characteristics, significance, and implications.
The Calaveras Fault: A Closer Look
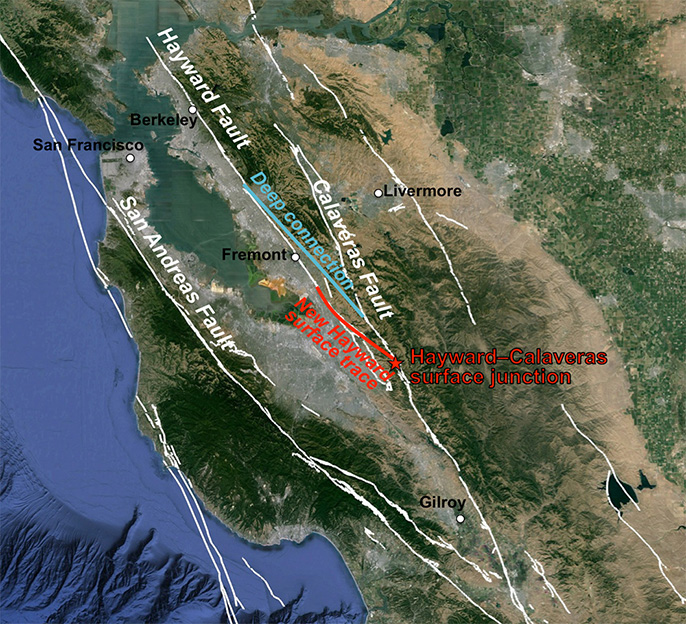
The Calaveras Fault, a major strike-slip fault, extends for approximately 190 miles (300 kilometers) through the central and northern parts of California. It stretches from the San Andreas Fault near Hollister in the south, traversing through the San Francisco Bay Area, and eventually reaching the Sierra Nevada foothills near the town of Sonora in the north. This fault is characterized by a predominantly horizontal movement, where the two sides of the fault slide past each other in opposite directions.
Geologic History and Formation:
The Calaveras Fault, like the San Andreas Fault, is a product of the relentless movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates. The Pacific Plate, on which California sits, is grinding northward against the North American Plate. This ongoing interaction, known as plate tectonics, has been shaping the landscape of California for millions of years. The Calaveras Fault is a testament to this dynamic process, representing a zone of active deformation within the broader San Andreas Fault system.
Seismic Activity:
The Calaveras Fault is known for its significant seismic activity. While it is not as active as the San Andreas Fault, it has produced several notable earthquakes throughout history. One of the most significant earthquakes on the Calaveras Fault occurred in 1989, the Loma Prieta earthquake, which registered a magnitude of 6.9 and caused widespread damage in the San Francisco Bay Area. This earthquake serves as a stark reminder of the potential seismic hazards posed by the Calaveras Fault.
Impact on the Landscape:
The Calaveras Fault has left its mark on the landscape of California, creating distinct geological features. The fault’s movement has caused the land on either side to shift, resulting in:
- Offsets: The Calaveras Fault has offset various geological features, including rivers, roads, and even entire mountain ranges. These offsets serve as a visual testament to the fault’s activity and can be observed in various locations along its path.
- Fault Scarps: The movement of the fault has created steep cliffs, known as fault scarps, which mark the boundary between the two sides of the fault. These scarps are often visible along the fault’s trace, providing a clear indication of the geological forces at play.
- Linear Valleys: The Calaveras Fault has also influenced the formation of linear valleys, which run parallel to the fault’s trace. These valleys are often characterized by their straight, elongated shape and are a result of the fault’s movement, which has created zones of weakness in the Earth’s crust.
Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Deeper Dive
The Relationship with the San Andreas Fault:
The Calaveras Fault is intricately connected to the San Andreas Fault. It is considered a "splay fault," branching off from the San Andreas Fault and extending eastward. This intricate relationship between the two faults has significant implications for seismic activity in California.
- Seismic Coupling: The Calaveras Fault acts as a "stress transfer zone," transferring stress from the San Andreas Fault to other areas. This means that the movement on the Calaveras Fault can influence the seismic activity on the San Andreas Fault and vice versa.
- Potential for Large Earthquakes: While the Calaveras Fault is not as active as the San Andreas Fault, it is still capable of producing large earthquakes. The potential for significant seismic events on the Calaveras Fault poses a serious threat to the densely populated areas it traverses.
Monitoring and Research:
Scientists and researchers closely monitor the Calaveras Fault for signs of seismic activity. This monitoring involves:
- Seismological Networks: Networks of seismometers are deployed across California, including along the Calaveras Fault, to detect and record earthquakes. These instruments provide valuable data on the frequency, magnitude, and location of seismic events.
- GPS Measurements: GPS stations are strategically placed along the fault to measure ground deformation. These measurements can detect subtle shifts in the Earth’s crust, indicating potential movement along the fault.
- Paleoseismic Studies: Researchers analyze geological deposits and landforms to reconstruct the history of earthquakes on the Calaveras Fault. This historical data helps scientists understand the fault’s long-term behavior and predict potential future events.
Calaveras Fault: Implications for California
Seismic Hazard:
The Calaveras Fault is a significant seismic hazard for California. The potential for large earthquakes on this fault poses a threat to infrastructure, public safety, and the economy. Understanding the fault’s behavior and predicting its future activity is crucial for mitigating seismic risks.
Infrastructure and Development:
The Calaveras Fault’s presence influences infrastructure development in California. Building codes and regulations are designed to minimize seismic risks in areas near the fault. This includes stricter building standards, earthquake-resistant designs, and the implementation of early warning systems.
Public Awareness:
Raising public awareness about the Calaveras Fault and its potential hazards is essential. Educating communities about earthquake preparedness, safety measures, and emergency response plans is crucial for ensuring the safety of residents.
Conclusion:
The Calaveras Fault is a vital component of the San Andreas Fault system, shaping the landscape and seismic activity of California. Understanding its characteristics, history, and potential for seismic events is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of communities. Through ongoing research, monitoring, and public awareness, California can better prepare for the challenges posed by this active fault and protect its residents from the hazards of earthquakes.
FAQs about the Calaveras Fault
Q: What is the Calaveras Fault, and where is it located?
A: The Calaveras Fault is a major strike-slip fault in California, extending approximately 190 miles (300 kilometers) from the San Andreas Fault near Hollister to the Sierra Nevada foothills near Sonora.
Q: How is the Calaveras Fault related to the San Andreas Fault?
A: The Calaveras Fault is a "splay fault" branching off from the San Andreas Fault. It is a significant component of the San Andreas Fault system and plays a role in transferring stress from the San Andreas Fault to other areas.
Q: How active is the Calaveras Fault?
A: While not as active as the San Andreas Fault, the Calaveras Fault is still capable of producing significant earthquakes. It has generated several notable earthquakes in the past, including the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
Q: What are the potential hazards associated with the Calaveras Fault?
A: The Calaveras Fault poses a significant seismic hazard to California. Potential hazards include:
- Large earthquakes that could cause widespread damage and disruption.
- Ground shaking that could damage buildings and infrastructure.
- Landslides and ground failures triggered by seismic activity.
- Tsunamis in coastal areas.
Q: What measures are being taken to mitigate the risks posed by the Calaveras Fault?
A: Various measures are being implemented to mitigate seismic risks, including:
- Building codes and regulations that promote earthquake-resistant construction.
- Early warning systems that provide advance notice of impending earthquakes.
- Public awareness campaigns that educate communities about earthquake preparedness and safety measures.
- Research and monitoring efforts to better understand the fault’s behavior and predict future seismic events.
Q: What can individuals do to prepare for an earthquake on the Calaveras Fault?
A: Individuals can take several steps to prepare for an earthquake:
- Secure heavy objects that could fall during shaking.
- Develop a family emergency plan and practice earthquake drills.
- Keep a disaster preparedness kit with essential supplies.
- Learn about earthquake safety measures, such as drop, cover, and hold on.
Q: What is the future outlook for the Calaveras Fault?
A: The Calaveras Fault will continue to be an active seismic zone in California. Scientists and researchers are working to better understand its behavior and predict future events. By monitoring the fault, conducting research, and implementing mitigation measures, California can better prepare for the challenges posed by this active fault.
Tips for Living Near the Calaveras Fault
- Understand Your Risk: Familiarize yourself with the location of the Calaveras Fault and the potential hazards it poses to your area.
- Secure Your Home: Take steps to secure your home against earthquake damage, such as anchoring heavy objects and installing earthquake-resistant bracing.
- Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a family emergency plan, including evacuation routes and communication methods.
- Prepare a Disaster Kit: Assemble a disaster preparedness kit with essential supplies, such as water, food, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about earthquake preparedness and safety measures by following local news and official sources.
- Participate in Earthquake Drills: Practice earthquake drills regularly with your family and community.
- Support Earthquake Research: Support organizations that conduct research and monitoring of the Calaveras Fault to improve our understanding of seismic hazards.
Conclusion
The Calaveras Fault is a dynamic geological feature that plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape and seismic activity of California. Understanding its characteristics, history, and potential for earthquakes is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of communities. By staying informed, taking precautions, and supporting research efforts, we can better prepare for the challenges posed by this active fault and protect ourselves from the hazards of earthquakes.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Calaveras Fault: A Guide to the Seismic Landscape of California. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!