Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe
Related Articles: Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe
- 3.1 The Importance of Tick Maps
- 3.2 Michigan Tick Map: Unveiling the Distribution of Tick Species
- 3.3 Understanding the Factors Influencing Tick Distribution
- 3.4 Preventing Tick Bites and Disease Transmission
- 3.5 FAQs about Michigan Tick Map
- 3.6 Tips for Staying Safe from Ticks in Michigan
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe

Ticks, small arachnids known for their blood-feeding habits, are prevalent throughout Michigan, posing a significant threat to human and animal health. These parasitic creatures can transmit various diseases, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis, making it crucial to understand their distribution and take necessary precautions.
The Importance of Tick Maps
Tick maps provide valuable information about the geographic distribution of different tick species in a specific region. These maps serve as a crucial tool for:
- Public Health Surveillance: By tracking tick populations and identifying areas with high tick densities, health officials can monitor the spread of tick-borne diseases and implement timely interventions.
- Disease Prevention: Understanding the presence of specific tick species in a region helps individuals and communities take proactive steps to reduce their risk of exposure to tick-borne illnesses.
- Research and Education: Tick maps are essential for researchers studying tick ecology, disease transmission, and the development of effective control measures. They also provide valuable educational resources for the public, increasing awareness about tick-borne diseases and prevention strategies.
Michigan Tick Map: Unveiling the Distribution of Tick Species
The Michigan Tick Map, developed by the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS), provides a comprehensive overview of the distribution of various tick species across the state. This map is a valuable resource for individuals, healthcare providers, and researchers seeking information about tick populations in specific areas.
Tick Species in Michigan:
Michigan is home to several tick species, each with its unique characteristics and disease transmission potential. The most common tick species in the state include:
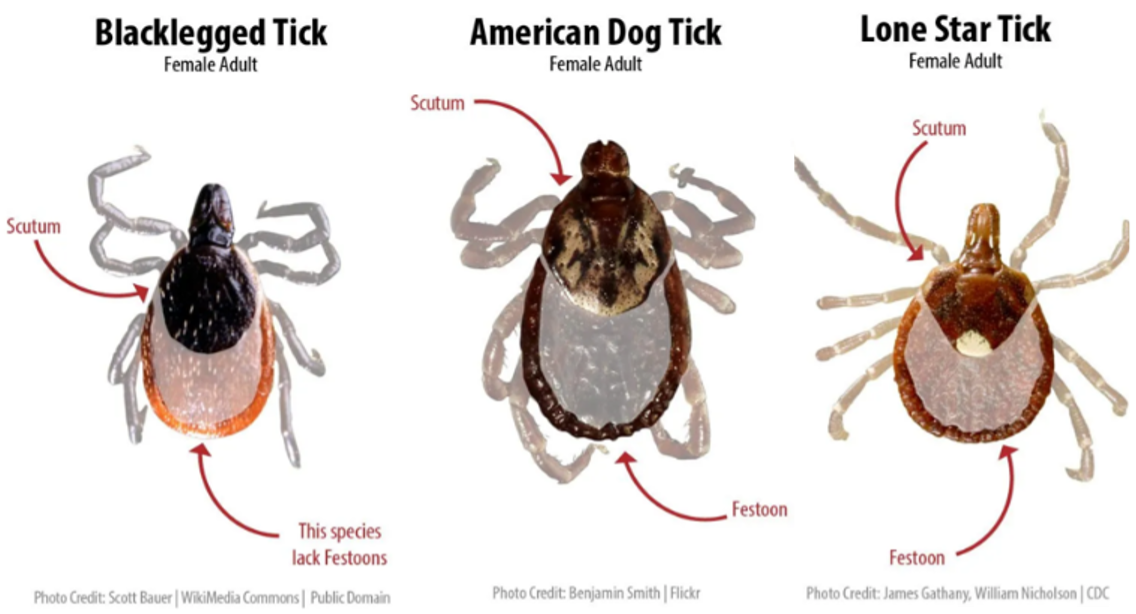
- Blacklegged Tick (Ixodes scapularis): Also known as the deer tick, this species is the primary vector for Lyme disease, babesiosis, and anaplasmosis. Blacklegged ticks are found throughout Michigan, with higher densities in the Lower Peninsula, particularly in the eastern and northern regions.
- American Dog Tick (Dermacentor variabilis): This tick is the primary vector for Rocky Mountain spotted fever, tularemia, and ehrlichiosis. American dog ticks are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas throughout Michigan.
- Lone Star Tick (Amblyomma americanum): This tick has recently expanded its range into Michigan, and its presence is increasing. It is known to transmit ehrlichiosis, STARI (Southern Tick-Associated Rash Illness), and potentially other diseases. Lone star ticks are typically found in areas with tall grasses, brush, and wooded areas.
- Woodchuck Tick (Ixodes cookei): This tick is primarily found in the northern Lower Peninsula and the Upper Peninsula. While it is not known to transmit Lyme disease, it can carry other pathogens, such as babesiosis.
Interpreting the Michigan Tick Map:
The Michigan Tick Map uses color-coding to indicate the presence and abundance of different tick species in specific areas. Areas with higher densities of a particular tick species are represented by darker shades of the corresponding color. This allows users to quickly identify areas with a higher risk of encountering specific tick species and potential disease transmission.
Accessing the Michigan Tick Map:
The Michigan Tick Map can be accessed online through the MDHHS website. It is a user-friendly tool that allows users to zoom in on specific areas, view tick distribution data, and access additional information about tick-borne diseases.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Tick Distribution
Several factors contribute to the distribution of tick populations in Michigan, including:
- Climate: Ticks thrive in warm, humid environments with moderate temperatures. The climate in Michigan is generally favorable for tick survival and reproduction, particularly in the southern and eastern parts of the state.
- Habitat: Ticks require specific habitats for survival and reproduction. They prefer areas with tall grasses, brush, and wooded areas that provide shelter and access to hosts.
- Host Availability: Ticks rely on hosts, such as deer, mice, and other mammals, for blood meals and to complete their life cycle. The availability of suitable hosts in a particular area significantly influences tick populations.
- Human Activity: Human activities, such as hiking, camping, and gardening, can increase the risk of encountering ticks. This is because humans can unknowingly transport ticks to new areas or create habitats that are favorable for tick survival.
Preventing Tick Bites and Disease Transmission
Understanding the distribution of ticks in Michigan is essential for taking proactive steps to prevent tick bites and the transmission of tick-borne diseases. Here are some key prevention strategies:
- Avoid Tick-Infested Areas: Be aware of areas with high tick densities, such as wooded areas, tall grasses, and brush. Avoid these areas or take extra precautions when venturing into them.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When in tick-infested areas, wear light-colored clothing that allows you to easily spot ticks. Tuck your pants into your socks and wear long sleeves to minimize skin exposure.
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or permethrin to exposed skin and clothing. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe and effective use.
- Check for Ticks Regularly: Conduct thorough tick checks on yourself, your children, and pets after spending time outdoors. Pay particular attention to areas with folds of skin, such as behind the knees, armpits, and groin.
- Remove Ticks Promptly: If you find a tick attached to your skin, remove it promptly using tweezers. Grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull upwards steadily. Avoid twisting or squeezing the tick, as this could increase the risk of disease transmission.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you experience any symptoms of a tick-borne illness, such as fever, headache, rash, or muscle aches, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
FAQs about Michigan Tick Map
1. How often is the Michigan Tick Map updated?
The Michigan Tick Map is updated periodically based on new data and research findings. It is important to consult the MDHHS website for the most up-to-date information.
2. What is the significance of the different colors on the Michigan Tick Map?
Different colors on the map represent the presence and abundance of specific tick species. Darker shades indicate higher densities of a particular species, while lighter shades indicate lower densities.
3. Does the Michigan Tick Map include data on the presence of tick-borne diseases?
The Michigan Tick Map primarily focuses on the distribution of tick species. However, it provides links to additional resources, including information about tick-borne diseases, prevention strategies, and reporting procedures.
4. Is the Michigan Tick Map available as a mobile app?
Currently, the Michigan Tick Map is not available as a mobile app. However, it can be accessed on mobile devices through the MDHHS website.
5. What should I do if I find a tick on my pet?
If you find a tick on your pet, remove it promptly using tweezers. Consult your veterinarian for advice on tick prevention and treatment options for your pet.
Tips for Staying Safe from Ticks in Michigan
- Avoid tick-infested areas during peak tick season: Tick activity is highest during the spring and summer months, so be extra cautious during these times.
- Create a tick-free zone around your home: Keep your lawn mowed, trim back bushes and trees, and remove leaf litter to reduce tick habitat.
- Talk to your doctor about tick-borne disease prevention: Discuss your risk factors and potential preventive measures, such as tick-borne disease vaccines.
- Report tick bites and potential cases of tick-borne diseases: Contact your local health department to report tick bites and suspected cases of tick-borne diseases. This information helps track disease outbreaks and implement public health interventions.
Conclusion
The Michigan Tick Map is a valuable tool for understanding the distribution of tick species in the state and taking proactive steps to prevent tick bites and the transmission of tick-borne diseases. By staying informed about tick populations and implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals and communities can significantly reduce their risk of exposure to these potentially serious illnesses. Remember, vigilance and awareness are crucial in protecting yourself and your loved ones from the dangers of ticks.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Guide to Staying Safe. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
