Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
- 3.1 What are Contour Lines?
- 3.2 Deciphering the Language of Contour Lines
- 3.3 The Importance of Contour Lines
- 3.4 FAQs about Contour Lines:
- 3.5 Tips for Using Contour Lines:
- 3.6 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps
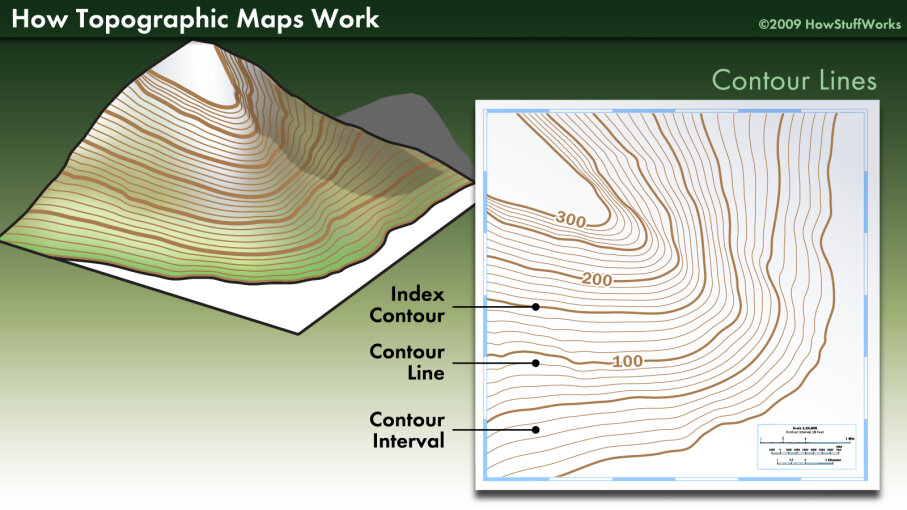
Topographic maps are essential tools for anyone navigating the outdoors, from hikers and campers to engineers and surveyors. These maps depict not only the location of features like roads and rivers but also the shape of the land itself, offering a three-dimensional representation on a two-dimensional surface. This crucial information is conveyed through the use of contour lines, a system of interconnected lines that reveals the elevation of the terrain.
What are Contour Lines?
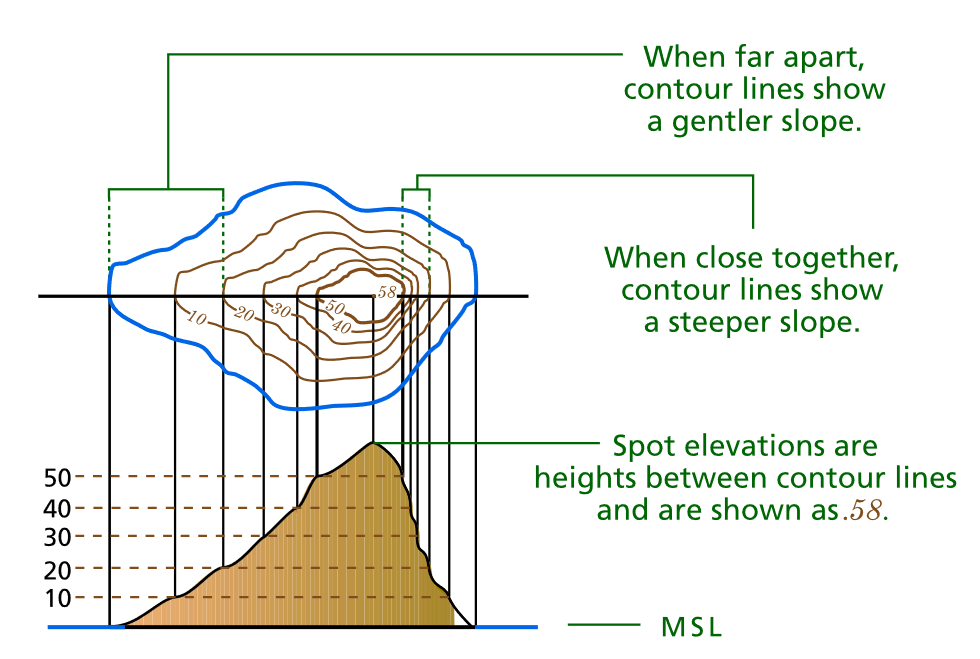
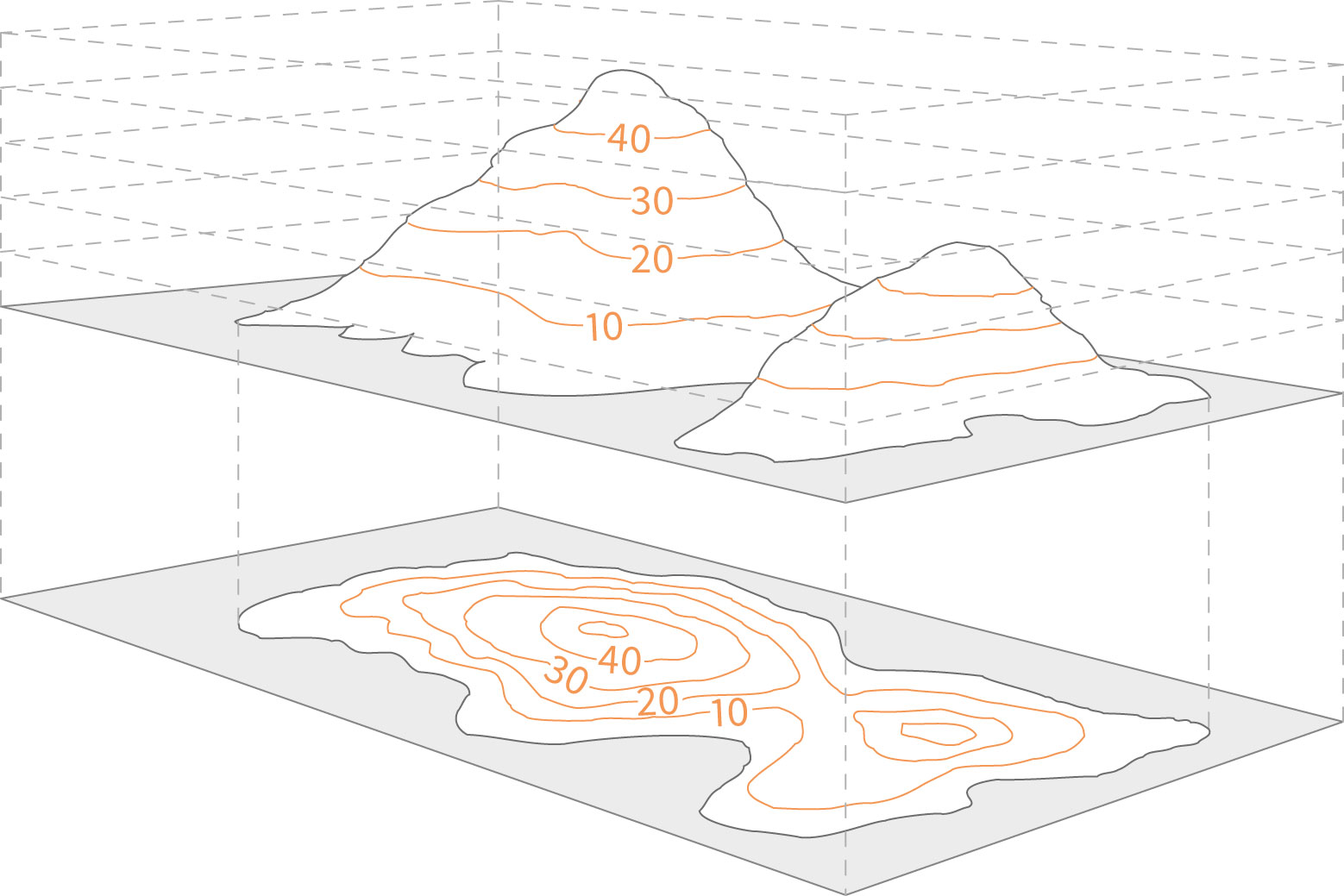
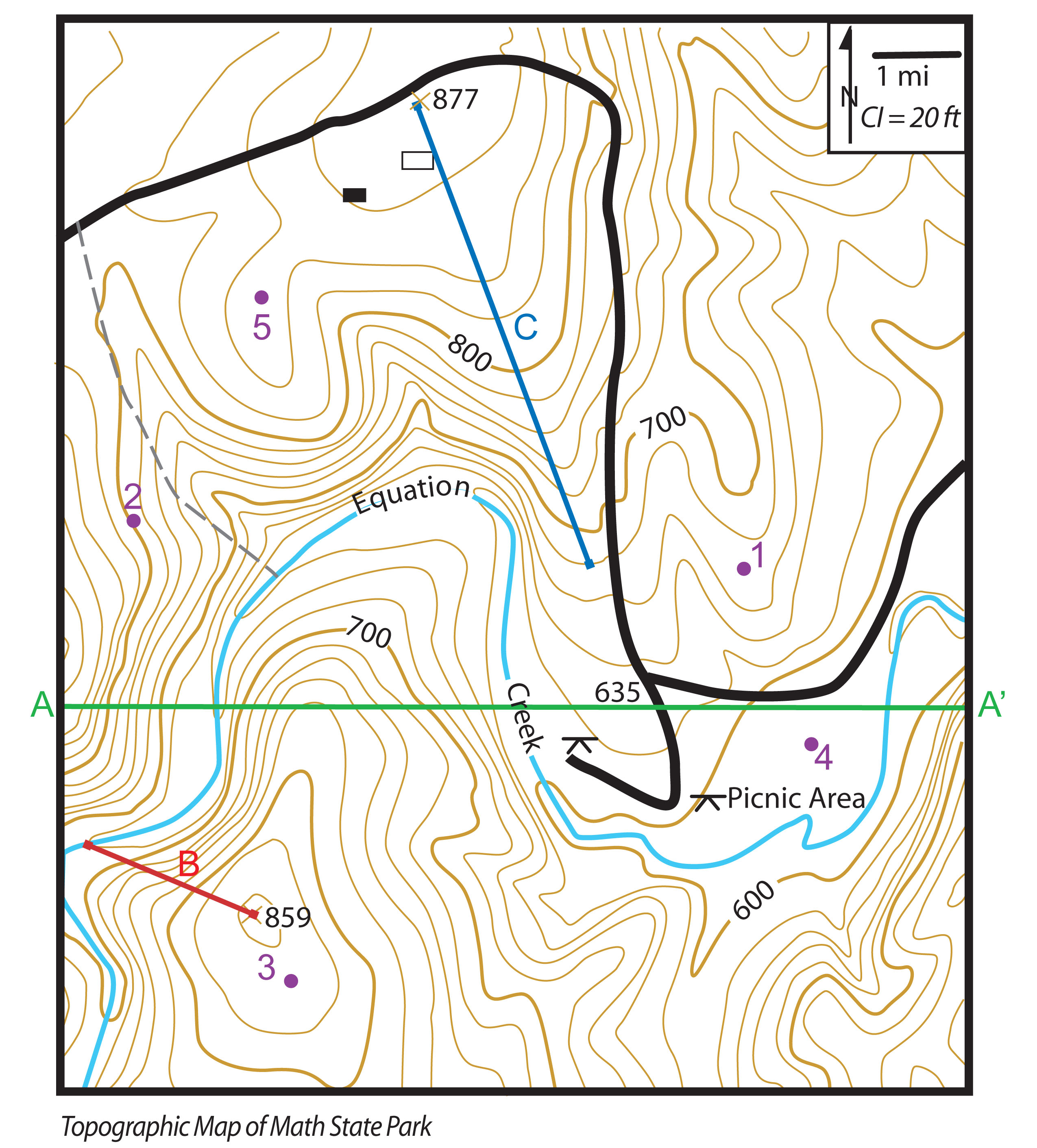
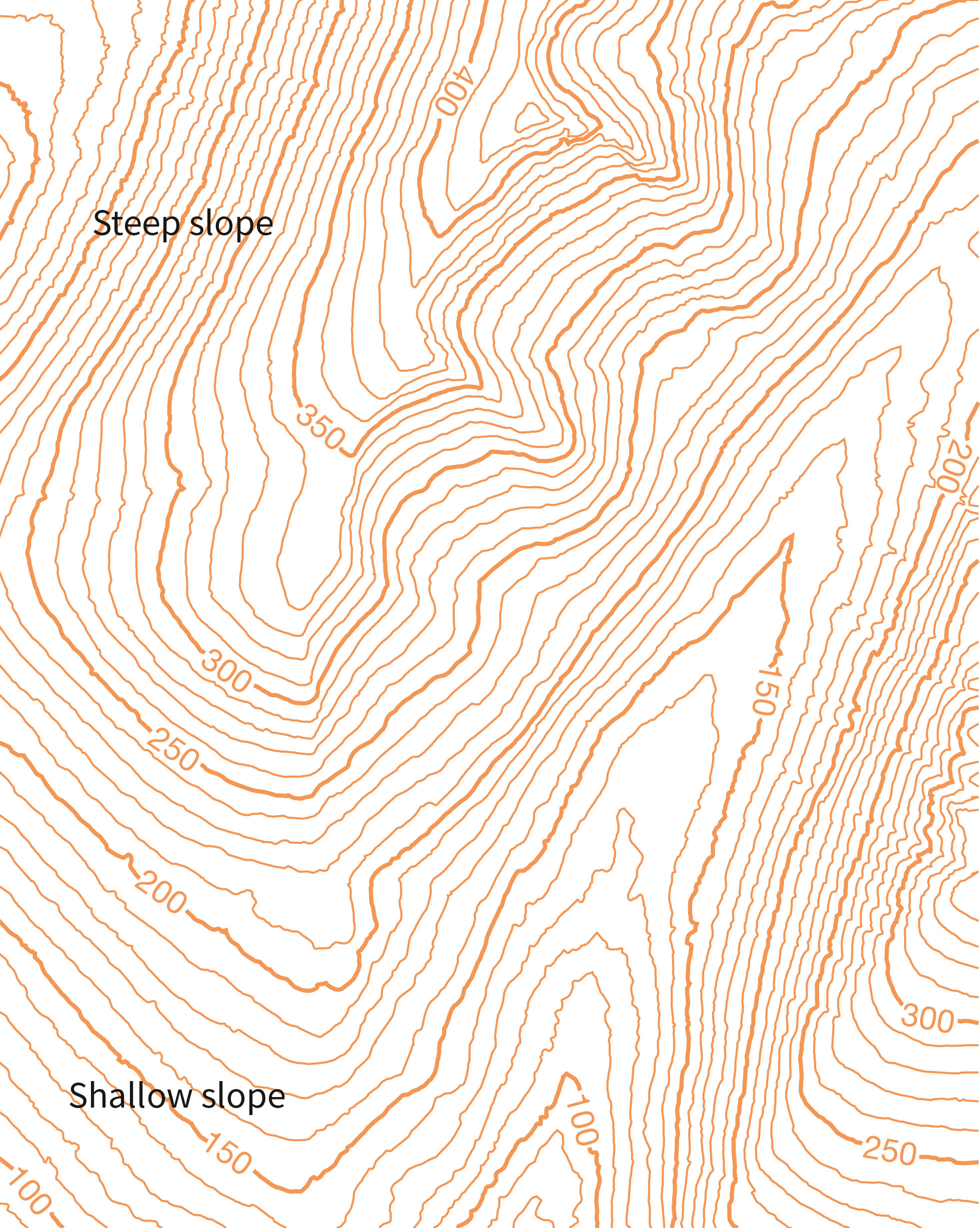
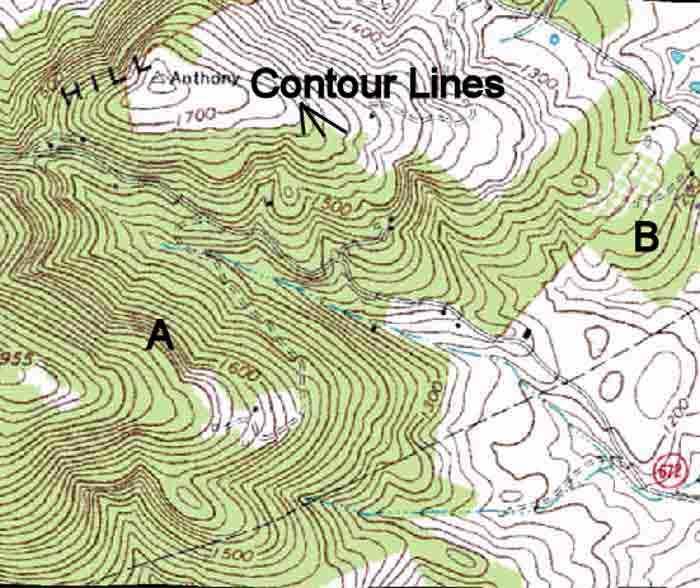
Contour lines are imaginary lines drawn on a map connecting points of equal elevation. They effectively trace the shape of the landscape, providing a visual representation of its ups and downs. Each contour line represents a specific elevation, and the difference in elevation between consecutive lines is known as the contour interval.
Imagine walking across a hilly terrain. As you ascend a slope, the elevation increases. A contour line would represent the path you take while maintaining a constant elevation. Every point on that line would be at the same height above sea level.
Deciphering the Language of Contour Lines
The key to understanding contour lines lies in recognizing their patterns and interpreting their significance. Here’s a breakdown of their key characteristics:
- Spacing: The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope. Conversely, widely spaced contour lines indicate a gentler slope.
- Shape: The shape of contour lines reveals the form of the terrain. Circular lines indicate a hill or a depression, while lines that bend and curve suggest a valley or a ridge.
- Direction: The direction of the contour lines can reveal the flow of water. Water always flows downhill, so the contour lines will bend towards the lower elevation.
The Importance of Contour Lines
Contour lines play a vital role in various fields, offering a wealth of information about the terrain. Their applications include:
1. Navigation and Outdoor Recreation:
- Planning routes: Hikers and campers can use contour lines to assess the difficulty of a trail, identify potential hazards like steep slopes or cliffs, and choose the best route for their abilities.
- Estimating travel time: Contour lines provide an indication of the elevation gain and loss along a route, allowing for more accurate time estimates for hiking or biking.
- Understanding terrain: Contour lines reveal the shape of the land, allowing outdoor enthusiasts to anticipate obstacles and plan their activities accordingly.
2. Engineering and Construction:
- Site analysis: Engineers and architects use contour lines to analyze the topography of a site before planning infrastructure projects like roads, buildings, and dams.
- Slope stability: Contour lines help assess slope stability, crucial for designing safe and sustainable construction projects.
- Drainage design: Understanding the flow of water is essential for designing drainage systems, and contour lines provide valuable information about the terrain’s natural drainage patterns.
3. Environmental Studies and Conservation:
- Landform analysis: Contour lines are essential for mapping and studying landforms, including valleys, hills, and plateaus, providing insights into geological processes and the impact of human activities.
- Habitat mapping: Contour lines aid in identifying and mapping different habitats, crucial for understanding biodiversity and planning conservation efforts.
- Flood risk assessment: Contour lines can be used to map floodplains and assess flood risk, enabling better preparedness and mitigation strategies.
4. Military and Defense:
- Tactical planning: Contour lines are used to plan military operations, assess terrain suitability for deployment, and identify potential ambush points or defensive positions.
- Target identification: Contour lines can be used to identify potential targets and estimate the range and trajectory of projectiles.
- Navigation and reconnaissance: Contour lines play a crucial role in navigating complex terrain and planning reconnaissance missions.
FAQs about Contour Lines:
1. What is the difference between a contour line and an elevation point?
An elevation point represents a specific point on the map with a known elevation. A contour line, on the other hand, connects all points of equal elevation, creating a continuous line representing a specific elevation level.
2. How do contour lines represent a hill or a depression?
Contour lines that form closed loops indicate a hill or a depression. The elevation of the hill increases as the lines get closer, while the elevation of the depression decreases as the lines get closer.
3. How do contour lines indicate a valley or a ridge?
Contour lines that bend and curve in a "V" shape indicate a valley, with the "V" pointing uphill. Conversely, contour lines that bend and curve in a "U" shape indicate a ridge, with the "U" pointing downhill.
4. How do contour lines show the flow of water?
Water flows downhill, so contour lines bend towards the lower elevation. The direction of the bend indicates the direction of the water flow.
5. What is the contour interval?
The contour interval is the difference in elevation between consecutive contour lines. It is typically indicated on the map legend.
6. How do I determine the elevation of a point on a topographic map?
To determine the elevation of a point on a topographic map, locate the contour line that passes through that point and add or subtract the contour interval based on the position of the point relative to the contour line.
Tips for Using Contour Lines:
- Study the map legend: Pay attention to the contour interval and other important information provided on the map legend.
- Look for patterns: Identify the shapes and spacing of contour lines to understand the terrain.
- Use a ruler or compass: Use a ruler or compass to measure distances and elevations on the map.
- Practice with real-world examples: Explore actual landscapes and compare them to their representation on topographic maps.
- Consult with experienced users: Seek guidance from experienced hikers, campers, or professionals in relevant fields.
Conclusion:
Contour lines are an invaluable tool for navigating and understanding the terrain. They provide a visual representation of elevation changes, revealing the shape and form of the landscape. By understanding the characteristics and patterns of contour lines, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the terrain and make informed decisions for various activities, from outdoor recreation to engineering and environmental studies. The ability to read and interpret contour lines is an essential skill for anyone working or exploring in the outdoors, empowering them to navigate safely and effectively.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Contour Lines on Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!