Unveiling the Power of Physical Maps: A Visual Journey Through Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Physical Maps: A Visual Journey Through Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Physical Maps: A Visual Journey Through Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Physical Maps: A Visual Journey Through Geography

In an era dominated by digital maps, the tangible presence of a physical map often evokes a sense of nostalgia and a connection to a bygone era. However, dismissing their relevance would be a mistake. Physical maps, with their intricate details and tactile experience, continue to offer a unique perspective on our world, serving not only as tools for navigation but also as powerful instruments for learning, exploration, and understanding.
A Window into the World: Exploring the Essence of Physical Maps
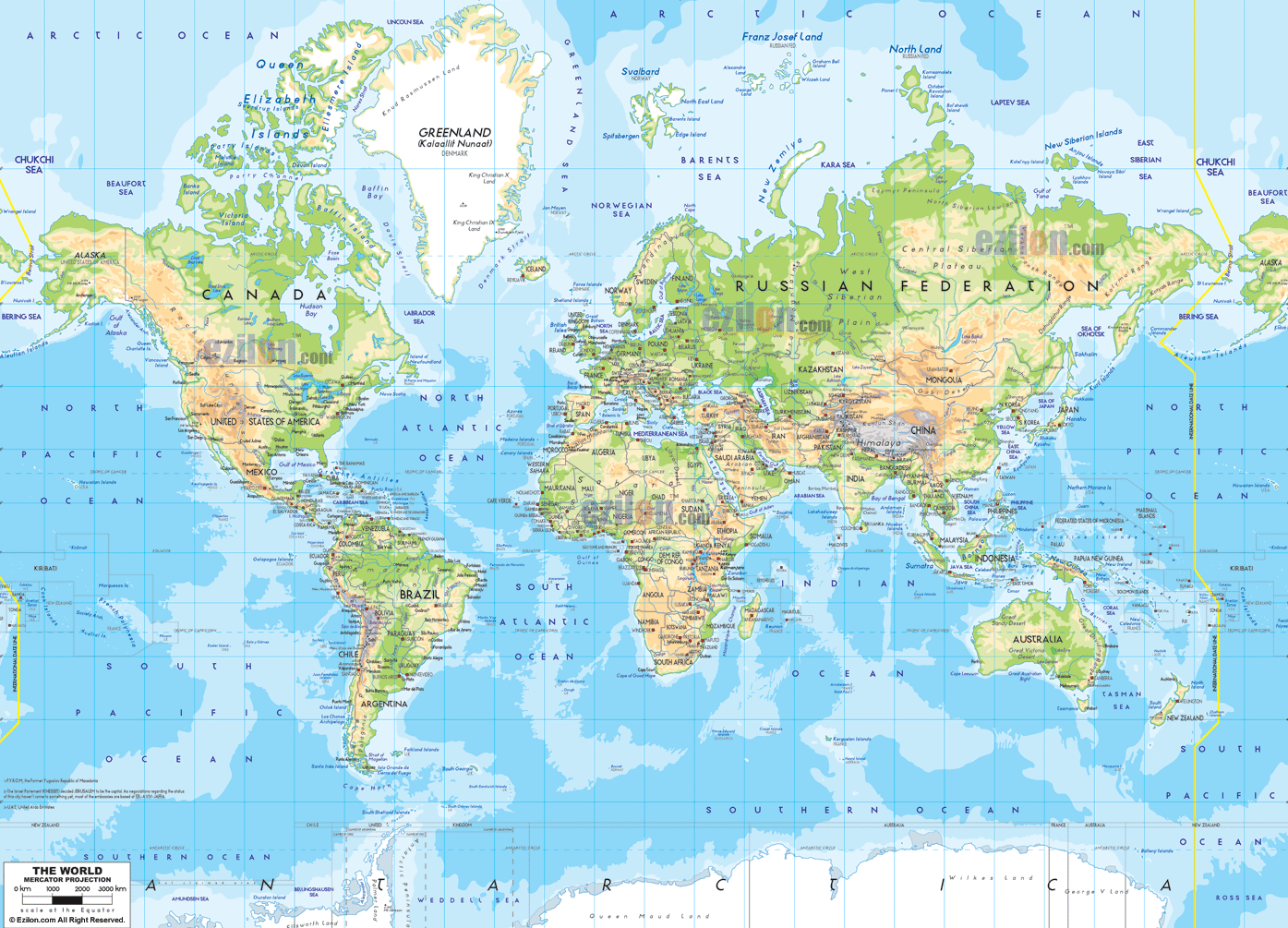
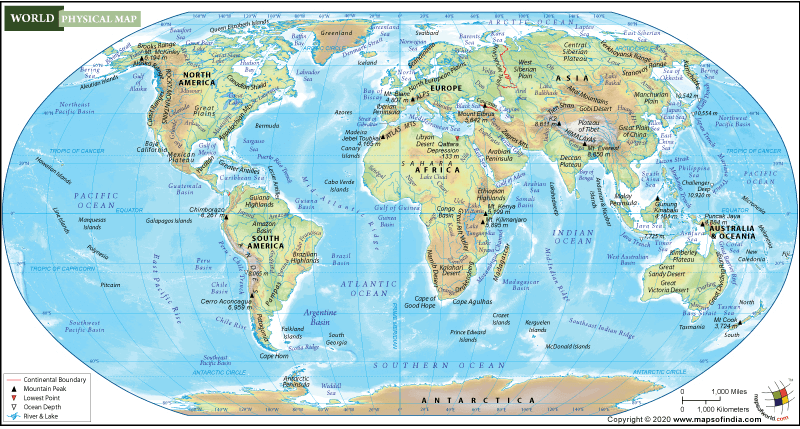
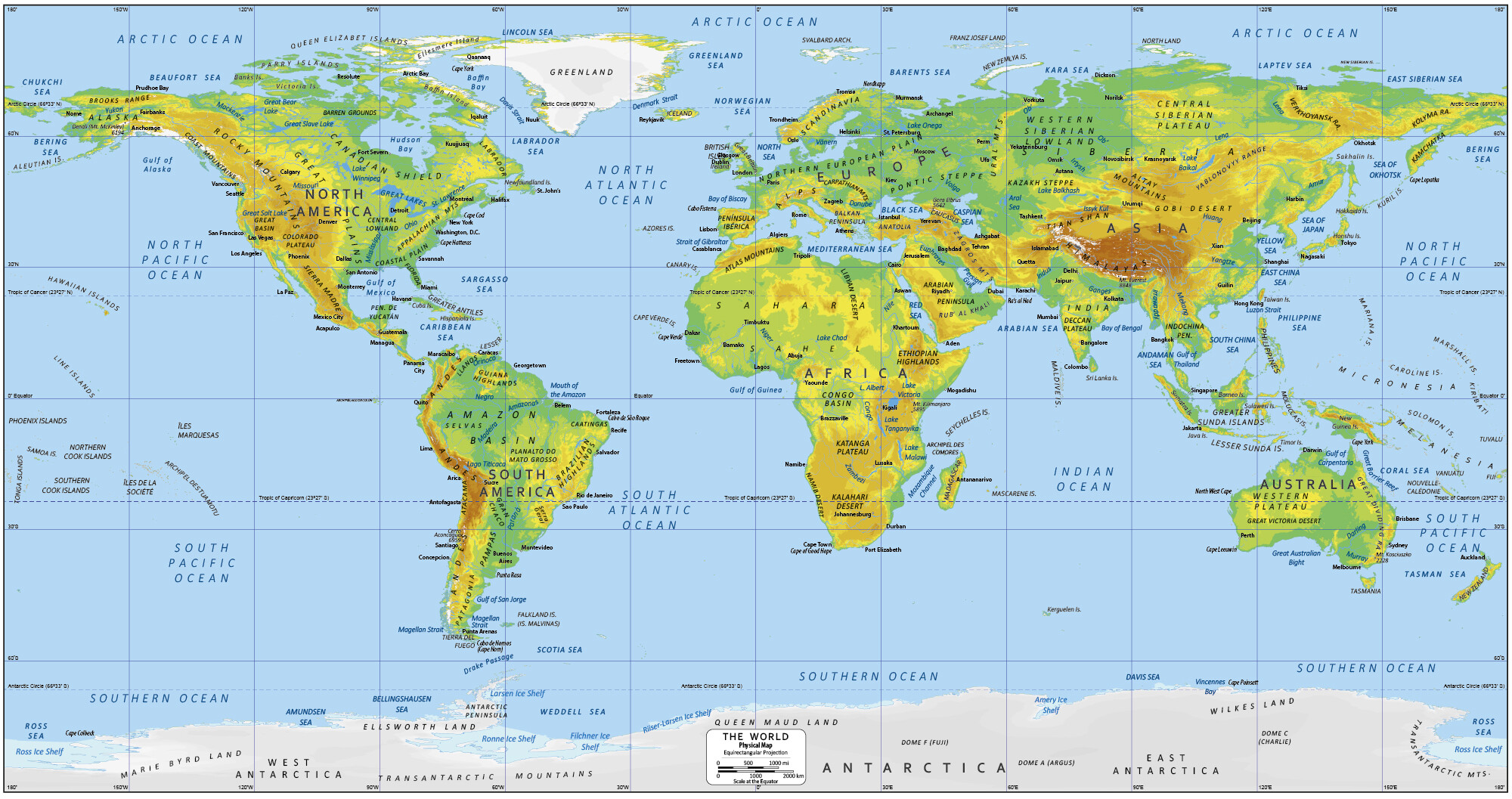
At their core, physical maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface. They depict geographical features, such as mountains, rivers, oceans, and cities, in a scaled-down form, allowing us to grasp the spatial relationships and distances between these elements. Unlike digital maps, which are often limited by screen size and resolution, physical maps can provide a comprehensive overview of a region or the entire globe, revealing the interconnectedness of our planet.
Beyond Navigation: The Multifaceted Value of Physical Maps
While physical maps have long been essential for navigation, their applications extend far beyond simply finding your way from point A to point B. Their value lies in their ability to:
- Foster Spatial Reasoning and Visualization: The act of tracing routes, identifying locations, and understanding geographical relationships on a physical map stimulates spatial reasoning and visualization skills. This is particularly beneficial for children, as it helps them develop a mental model of the world and navigate their surroundings more effectively.
- Promote Understanding of Geographic Concepts: Physical maps are excellent tools for teaching and learning about various geographic concepts. They can illustrate the distribution of natural resources, climate patterns, population density, and historical events, providing a visual context for complex geographical phenomena.
- Encourage Exploration and Curiosity: The tactile experience of handling a physical map and tracing its contours can ignite curiosity and a desire to learn more about the world. It encourages exploration, both literal and figurative, as individuals delve deeper into the details and intricacies of a particular region.
- Provide a Historical Perspective: Old maps are valuable historical artifacts that offer insights into past cartographic practices, societal values, and the evolution of our understanding of the world. They serve as tangible reminders of how our perception of geography has changed over time.
- Enhance Artistic Appreciation: Beyond their practical uses, physical maps can be appreciated for their aesthetic appeal. The artistry of cartography, with its use of colors, symbols, and intricate designs, can transform a map into a work of art.
Types of Physical Maps: A Diverse Landscape of Representations
Physical maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific purposes and audiences. Some common types include:
- Relief Maps: These maps emphasize the Earth’s topography, showcasing mountains, valleys, and other landforms through variations in elevation. Often depicted with three-dimensional features, they provide a realistic representation of the terrain.
- Political Maps: These maps focus on political boundaries, highlighting countries, states, provinces, and cities. They are valuable for understanding political divisions, population distribution, and geopolitical relationships.
- Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific themes or data sets, such as population density, climate patterns, or resource distribution. They use color, shading, and symbols to visualize these themes and reveal patterns and trends.
- Road Maps: These maps focus on road networks, providing detailed information about highways, local roads, and points of interest. They are essential for planning road trips and navigating unfamiliar areas.
The Evolution of Physical Maps: From Ancient Origins to Modern Innovations
The history of physical maps dates back to ancient civilizations, with early examples dating back to the 3rd millennium BC. Over centuries, cartographic techniques have evolved, driven by advancements in technology, exploration, and scientific understanding.
- Early Maps: Ancient civilizations used clay tablets, papyrus, and parchment to create maps, often focusing on local areas or specific routes. Early maps were primarily based on observation and practical needs, with limited accuracy and detail.
- Medieval Maps: During the Middle Ages, maps became more complex and sophisticated, incorporating religious and mythical elements alongside geographical information. The development of the compass and astrolabe facilitated more accurate measurements and navigation.
- Age of Exploration: The Age of Exploration (15th-18th centuries) witnessed a surge in cartographic activity, driven by the desire to chart new lands and trade routes. This era saw the development of more accurate and detailed maps, based on astronomical observations and measurements.
- Modern Maps: The 19th and 20th centuries saw the rise of scientific cartography, with the use of advanced surveying techniques, aerial photography, and computer technology. Modern maps are highly accurate and detailed, incorporating a wide range of data and information.
FAQs about Physical Maps: Addressing Common Questions
1. Are physical maps still relevant in the digital age?
Despite the prevalence of digital maps, physical maps remain relevant for various reasons. They offer a tactile experience, promote spatial reasoning, provide a comprehensive overview, and serve as valuable historical artifacts.
2. What are the benefits of using physical maps in education?
Physical maps are excellent educational tools as they foster spatial reasoning, promote understanding of geographic concepts, and encourage exploration and curiosity. They offer a tangible and interactive way to learn about the world.
3. How can I find and collect physical maps?
Physical maps can be found at antique stores, flea markets, libraries, and online retailers. Specialized map stores and auction houses also offer a wide selection of maps.
4. How can I preserve physical maps?
To preserve physical maps, store them in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Handle them with care, avoiding excessive folding or creasing. Consider using archival-quality materials for storage and framing.
5. What are some popular physical map resources?
There are numerous resources for finding and collecting physical maps, including:
- National Geographic: Offers a wide range of maps, atlases, and globes.
- The Map House: A renowned map dealer specializing in antique and vintage maps.
- The Library of Congress: Holds a vast collection of historical and contemporary maps.
- eBay and Etsy: Online marketplaces where you can find a variety of maps.
Tips for Utilizing Physical Maps Effectively:
- Choose the right map for your purpose: Consider the scale, type, and detail level needed for your specific task or project.
- Use a magnifying glass or ruler: To examine fine details and measure distances accurately.
- Combine physical and digital maps: Utilize the strengths of both mediums for a comprehensive approach to map analysis.
- Engage in active learning: Trace routes, identify locations, and explore the map’s features to enhance understanding and retention.
- Share your maps with others: Encourage discussion and learning by sharing your maps and insights with friends, family, or colleagues.
Conclusion: Embracing the Enduring Value of Physical Maps
In an increasingly digital world, physical maps continue to hold a unique place. They offer a tangible connection to our planet, stimulate spatial reasoning, and provide a rich historical and artistic perspective. By embracing the enduring value of physical maps, we can foster a deeper understanding of our world, appreciate the artistry of cartography, and engage in a more immersive and meaningful exploration of geography.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Physical Maps: A Visual Journey Through Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!