Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem
Related Articles: Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem
- 3.1 The Biblical Map: A Window to the Past
- 3.2 The Importance of the Biblical Map: A Deeper Understanding of Scripture
- 3.3 Engaging with the Biblical Map: Tools and Resources
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem

Jerusalem, a city steeped in history and faith, holds a profound significance for countless individuals across the globe. Its name evokes images of ancient temples, prophets, and the unfolding drama of biblical narratives. Understanding the geographical context of Jerusalem, as depicted in biblical maps, offers a crucial lens through which to interpret these narratives and appreciate the city’s enduring impact on human history.
The Biblical Map: A Window to the Past
Biblical maps, while not precise cartographic representations in the modern sense, provide invaluable insights into the physical landscape and the spatial relationships that shaped biblical events. These maps, often found in scholarly works, archaeological studies, and even religious texts, depict the city of Jerusalem and its surrounding areas within the context of the biblical narrative. They illuminate the geographical features that played a pivotal role in the lives of biblical figures and the development of religious traditions.
Key Features of the Biblical Map of Jerusalem:
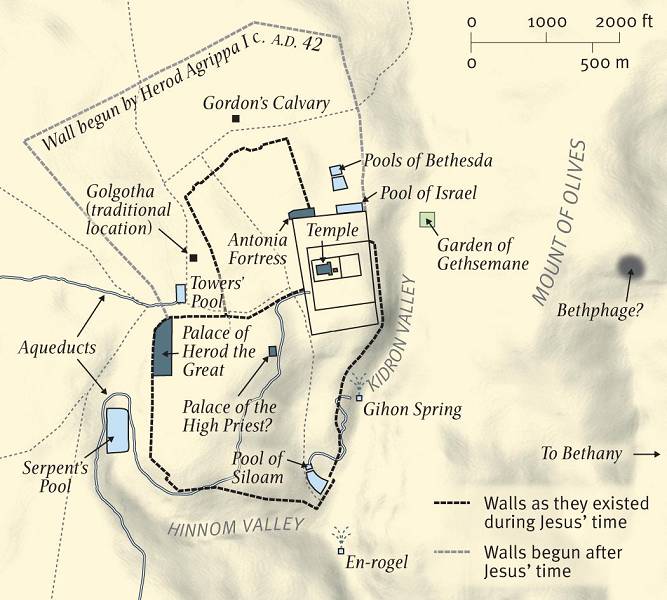
- The Temple Mount: This elevated plateau, known as the "Mount Moriah" in the Hebrew Bible, served as the location of the First and Second Temples, the focal point of Jewish religious life. The Temple Mount’s strategic location, overlooking the city, underscores its importance both as a place of worship and a symbol of religious authority.
- The City Walls: Jerusalem’s walls, mentioned frequently in the Bible, served as physical barriers and symbolic representations of the city’s boundaries and its protection. The walls’ presence shaped the city’s defensive strategies, its accessibility, and its social dynamics.
- The Kidron Valley: This valley, separating the Temple Mount from the Mount of Olives, played a significant role in the city’s topography. It served as a natural boundary, a burial ground, and a conduit for water supply. The Kidron Valley’s presence is reflected in various biblical narratives, highlighting its significance in the city’s physical and spiritual landscape.
- The Mount of Olives: This prominent hill, located east of the Temple Mount, held a special place in Jewish tradition. It served as a place of prayer, a burial ground for prophets, and a vantage point from which to view the city. The Mount of Olives is often mentioned in the Bible, highlighting its significance as a place of pilgrimage and contemplation.
- The Pool of Siloam: This natural spring, located near the southern wall of the city, provided water for the inhabitants of Jerusalem. Its importance in the city’s water supply system is reflected in biblical narratives and archaeological discoveries.
- The Western Wall: This remaining portion of the Second Temple’s retaining wall, known as the "Wailing Wall," holds immense religious significance for Jews worldwide. The Western Wall serves as a tangible reminder of the Temple’s former glory and a place for prayer and reflection.
The Importance of the Biblical Map: A Deeper Understanding of Scripture
The biblical map of Jerusalem offers more than just geographical information; it provides a framework for understanding the context and significance of biblical narratives. By visualizing the city’s layout and the locations mentioned in the Bible, readers can gain a deeper appreciation for:
- The Physical Environment: The biblical map helps readers understand the physical challenges and opportunities faced by biblical figures. The city’s topography, its water sources, and its strategic location shaped the lives of its inhabitants and influenced the unfolding of biblical events.
- The Social and Political Dynamics: The map reveals the city’s spatial organization and the different neighborhoods and communities that coexisted within its walls. This understanding sheds light on the social and political dynamics that shaped Jerusalem’s history and its role in the biblical narrative.
- The Religious Significance: The biblical map highlights the locations of key religious sites, such as the Temple Mount, the Mount of Olives, and the Western Wall. It provides a visual representation of the importance of Jerusalem as a center of worship and pilgrimage for Jews and Christians.
- The Historical Context: The map provides a geographical framework for understanding the historical events that shaped Jerusalem’s development. It allows readers to trace the city’s growth, its periods of prosperity and destruction, and its significance in the wider context of the ancient Near East.
Engaging with the Biblical Map: Tools and Resources
Several tools and resources can enhance our understanding and appreciation of the biblical map of Jerusalem:
- Interactive Maps: Online platforms and software applications offer interactive maps of Jerusalem, allowing users to explore different historical periods, identify key locations, and access relevant biblical passages.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Archaeological excavations in Jerusalem continue to uncover new insights into the city’s history and its depiction in the Bible. These discoveries provide tangible evidence that supports and enriches our understanding of the biblical map.
- Scholarly Works: Numerous academic studies and books delve into the historical, archaeological, and religious aspects of Jerusalem. These works provide comprehensive analyses of the city’s development and its representation in the Bible.
- Religious Texts: The Bible itself, particularly the Old Testament, provides a rich source of information about Jerusalem. Reading biblical passages with an awareness of the city’s geography can enhance our understanding of the narratives and the characters involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the different historical periods depicted in the biblical map of Jerusalem?
The biblical map of Jerusalem encompasses a vast historical period, spanning from the early days of the Israelite monarchy to the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE. It reflects the city’s development under various rulers, including King David, King Solomon, the Babylonian Exile, and the Roman occupation.
2. How accurate are the biblical maps of Jerusalem?
While biblical maps are not precise cartographic representations in the modern sense, they offer valuable insights into the city’s layout and the locations mentioned in the Bible. Archaeologists and historians continue to refine our understanding of the city’s geography based on archaeological evidence and textual analysis.
3. What is the significance of the Temple Mount in the biblical map of Jerusalem?
The Temple Mount, as the location of the First and Second Temples, holds immense religious significance for Jews and Christians. It served as the center of Jewish religious life and the site of key events in the biblical narrative, including the sacrifices offered by Abraham and the destruction of the Temple by the Romans.
4. How does the biblical map of Jerusalem relate to contemporary Jerusalem?
The biblical map of Jerusalem provides a historical context for understanding the city’s present-day layout and its significance as a place of pilgrimage and cultural intersection. While the city has undergone significant changes over the centuries, the locations depicted in the biblical map continue to hold religious and historical significance.
5. What are some practical tips for using the biblical map of Jerusalem?
- Identify Key Locations: Mark the locations mentioned in the biblical narrative on the map to gain a visual understanding of the city’s layout and the spatial relationships between different sites.
- Relate the Map to the Bible: Read biblical passages with an awareness of the city’s geography to gain a deeper understanding of the events and characters involved.
- Explore Historical Periods: Use interactive maps or scholarly works to explore the city’s development over different historical periods and understand how the map has changed over time.
- Visit Jerusalem: If possible, visit Jerusalem and experience the city’s historical and religious sites firsthand. This will provide a tangible connection to the biblical map and enhance your understanding of its significance.
Conclusion
The biblical map of Jerusalem serves as a powerful tool for exploring the city’s rich history, its religious significance, and its enduring impact on human civilization. It provides a visual framework for understanding the biblical narrative, allowing readers to connect with the physical landscape that shaped the lives of biblical figures and the development of religious traditions. By engaging with the biblical map of Jerusalem, we gain a deeper appreciation for the city’s enduring legacy and its role in the tapestry of human history.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Sacred Landscape: A Journey Through the Biblical Map of Jerusalem. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!