Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps
- 3.1 Defining the Framework: The Essence of Synoptic Weather Maps
- 3.2 Building the Picture: The Components of a Synoptic Weather Map
- 3.3 The Art of Interpretation: Reading the Weather Map
- 3.4 Beyond the Snapshot: The Evolution of Weather Systems
- 3.5 The Importance of Synoptic Weather Maps: A Crucial Tool for Forecasting and Understanding Weather
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions: Unraveling the Mysteries of Synoptic Weather Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps: A Guide for the Curious
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing the Atmosphere
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps

The world’s atmosphere is a dynamic system, constantly in motion, driven by a complex interplay of forces. To comprehend this intricate dance of weather patterns, meteorologists rely on a powerful tool: the synoptic weather map. This article delves into the essence of synoptic weather maps, exploring their construction, interpretation, and vital role in forecasting and understanding weather phenomena.
Defining the Framework: The Essence of Synoptic Weather Maps
A synoptic weather map is a visual representation of the atmospheric conditions across a specific region at a given point in time. It serves as a snapshot of the weather, capturing the distribution of key meteorological variables like temperature, pressure, wind, precipitation, and cloud cover. These maps are a cornerstone of weather forecasting, providing a foundation for understanding current conditions and predicting future weather events.
Building the Picture: The Components of a Synoptic Weather Map
Synoptic weather maps are meticulously crafted, incorporating a variety of symbols and lines to convey a wealth of information. Let’s examine the key elements:
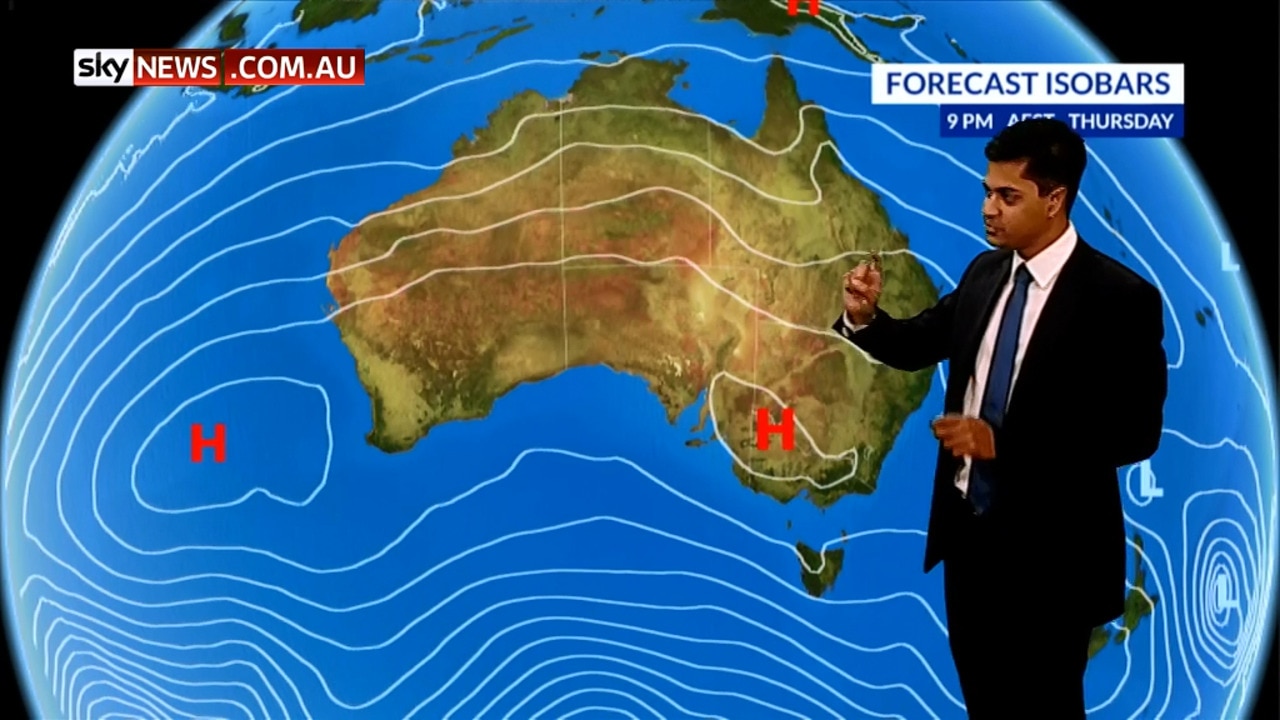
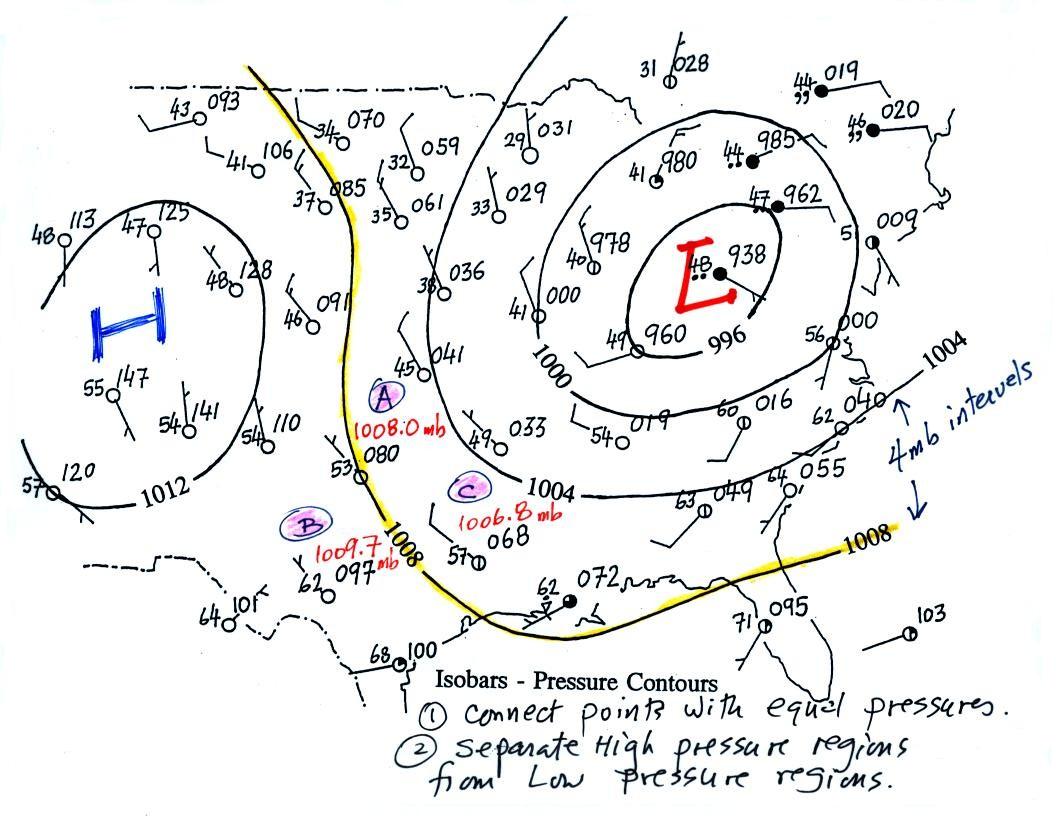
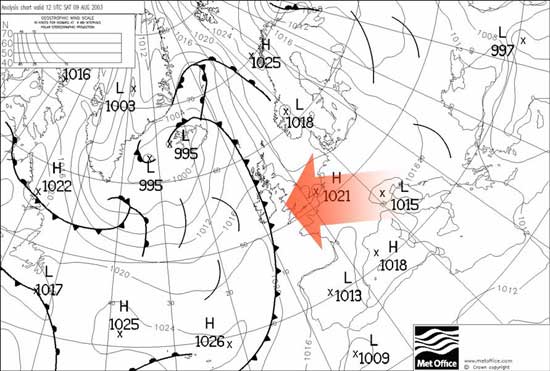
- Isobars: These lines connect points of equal atmospheric pressure, revealing areas of high and low pressure. High-pressure areas are typically associated with clear skies and calm conditions, while low-pressure areas often bring stormy weather.
- Isotherms: These lines connect points of equal temperature, highlighting areas of warm and cold air. Temperature gradients, or the rate of temperature change across a distance, are crucial for understanding the movement of air masses and the development of weather systems.
- Wind Barbs: These symbols depict wind direction and speed. The barb’s direction points towards the direction from which the wind is blowing, while the number of barbs and flags indicate the wind speed.
- Fronts: These lines represent boundaries between different air masses, often associated with significant weather changes. Cold fronts, where cold air pushes into warmer air, can bring thunderstorms and strong winds. Warm fronts, where warm air pushes into cooler air, often bring steady rain or snow.
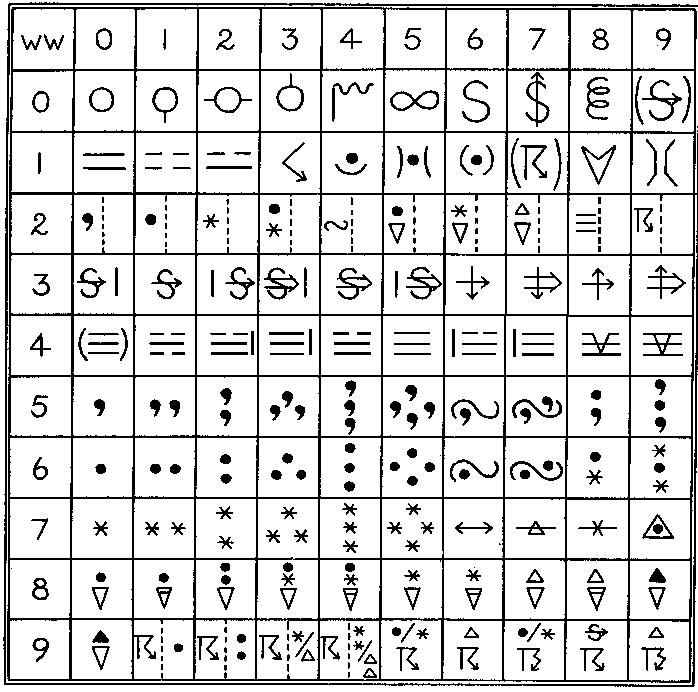
- Symbols for Precipitation and Cloud Cover: These symbols represent the type and intensity of precipitation, such as rain, snow, or hail, as well as the amount of cloud cover.
The Art of Interpretation: Reading the Weather Map
Decoding a synoptic weather map requires an understanding of how the various elements interact. By analyzing the patterns formed by isobars, isotherms, and fronts, meteorologists can identify areas of potential instability, track the movement of weather systems, and predict the likelihood of various weather events.
For example, a low-pressure system surrounded by isobars that converge towards its center indicates a potential for stormy weather. The location and movement of fronts can reveal the path of rain or snow, and the wind barbs can help determine the direction and strength of storms.
Beyond the Snapshot: The Evolution of Weather Systems
While a single synoptic weather map provides a snapshot of the atmosphere, its real power lies in its ability to reveal the evolution of weather systems over time. By comparing maps taken at different intervals, meteorologists can track the movement and development of weather patterns, allowing for more accurate predictions.
The Importance of Synoptic Weather Maps: A Crucial Tool for Forecasting and Understanding Weather
Synoptic weather maps are indispensable for weather forecasting, serving as a vital tool for meteorologists to:
- Predict Future Weather: By analyzing the current state of the atmosphere and its predicted evolution, meteorologists can forecast weather events with varying degrees of accuracy.
- Issue Severe Weather Warnings: Synoptic weather maps help identify areas at risk of severe weather, such as tornadoes, hurricanes, and heavy snowstorms, allowing for timely warnings to the public.
- Understand Climate Patterns: Long-term analysis of synoptic weather maps can reveal trends in climate patterns, providing valuable insights into the changing nature of the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Support Aviation Safety: Synoptic weather maps are critical for aviation safety, providing pilots with information about wind conditions, turbulence, and potential storms.
- Aid in Agriculture and Other Industries: Synoptic weather maps are essential for various industries, including agriculture, transportation, and energy production, allowing for informed decision-making based on predicted weather conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions: Unraveling the Mysteries of Synoptic Weather Maps
Q: What is the difference between a synoptic weather map and a surface weather map?
A: While both maps depict weather conditions at a specific time, a synoptic weather map typically covers a broader geographical area, often encompassing entire continents or even the globe. Surface weather maps, on the other hand, focus on a smaller region, often a country or state.
Q: How often are synoptic weather maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific agency or organization responsible for creating the maps. However, they are typically updated every 3-6 hours to reflect the dynamic nature of weather conditions.
Q: What are some limitations of synoptic weather maps?
A: While synoptic weather maps provide a valuable overview of weather conditions, they do have limitations:
- Limited Resolution: Synoptic maps are often generalized, representing large areas with a single data point. This can mask localized weather variations.
- Dependence on Data: The accuracy of synoptic weather maps relies on the quality and availability of meteorological data. Gaps in data coverage can affect the reliability of the maps.
- Simplification of Complex Processes: Synoptic maps represent complex atmospheric processes in a simplified manner, which may not capture the full range of factors influencing weather.
Q: How can I access synoptic weather maps?
A: Synoptic weather maps are readily available online from various sources, including:
- National Weather Service (NWS): The NWS provides a variety of weather maps and forecasts for the United States.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): NOAA offers a comprehensive suite of weather data and maps, including synoptic maps.
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): ECMWF provides global weather forecasts and synoptic maps.
Tips for Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps: A Guide for the Curious
- Start with the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the key elements of a synoptic weather map, such as isobars, isotherms, wind barbs, and fronts.
- Focus on the Patterns: Pay attention to the patterns formed by the lines and symbols on the map, as these reveal the movement and interaction of weather systems.
- Look for Trends: Compare maps from different time points to observe how weather patterns evolve over time.
- Consider the Context: Take into account the geographic location and season when interpreting synoptic weather maps.
- Seek Additional Information: Refer to other weather resources, such as weather forecasts and satellite imagery, to supplement your understanding of synoptic weather maps.
Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing the Atmosphere
Synoptic weather maps are a powerful tool for understanding and predicting weather patterns. By visualizing the distribution of key meteorological variables across a region, these maps provide a framework for interpreting current conditions and forecasting future events. From predicting severe weather events to supporting aviation safety and informing agricultural decisions, synoptic weather maps play a crucial role in our daily lives. As we continue to refine our understanding of the atmosphere, synoptic weather maps will remain an invaluable resource for navigating the dynamic world of weather.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Synoptic Weather Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!